A* Navigation
Overview and Key Concepts
A* (pronounced "A Star") is a search algorithm used to find a path between points. The algorithm uses a grid of nodes that Task Executer objects (travel members) travel through. Each node specifies in which direction travel members can move. The algorithm will look at nodes in the direction of travel and determine which direction is the fastest, including travelling diagonally between nodes. The grid of nodes can be modified by creating barriers restricting where the travel members can move or even influencing them to travel along certain paths.
The General Tab
The General tab has the following properties:
Surround Depth
This number specifies the number of nodes that are placed around the outside of the navigator's outer most barriers. This number must be an integer and be greater than 0.
Smooth Rotations
When checked, travelers will smoothly rotate when turning.
Snap Dividers to Grid
When checked, dividers will snap between points of the A* grid.
Cache Paths
When checked, the A* Navigator will cache paths to be reused in order to save processing time.
Members
The box on the left selects which members lists to view. Clicking the Properties button opens the properties window of the selected member. The box on the right displays all of the objects at the currently selected status.
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Click to sample an object in the model to add as a member. |
 |
Click to open an object selection window and choose objects to add as members. |
 |
Remove the selected member. |
The Behavior Tab
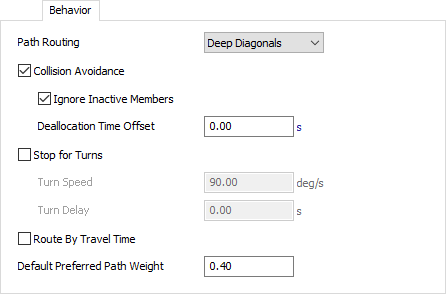
Path Routing
Defines how nodes in the travel grid will be searched. Options are as follows:
- Right Angles Only - The A* path search will only find paths that travel vertically or horizontally. No diagonal travel will be used.
- Diagonals - The A* path search will allow for diagonal travel. Travelers can simultaneously travel one unit vertically and one unit horizontally.
- Deep Diagonals - The A* path search will allow for deep diagonal travel. Travelers can simultaneously travel two units vertically and one unit horizontally, or vice versa.
Collision Avoidance
When checked, travelers will allocate nodes in their path and deallocate them once passed. This prevents two travelers from traveling through the same nodes at the same time.
Ignore Inactive Memebers
When checked, the collision avoidance algorithm will ignore allocations made by inactive travelers. After a traveler has arrived at its destination and ended active travel, the traveler will be essentially invisible to the collision detection algorithm. This means that travelers will run over other travelers that are not actively traveling.
While travelers running over each other is not desirable, it is somewhat complex to figure out what a traveler should do when it is idle to get out of the way of other travelers who need to go to the same spot. In a humans-as-travelers situation, generally people just figure out how to make space for each other without much delay penalty. From this perspective of delay penalties, letting idle travelers ignore each other essentially simulates the same desired behavior as humans naturally getting out of each other's way.
Deallocation Time Offset
Defines an additional time to wait before deallocating a grid node that a traveler is leaving. By default (0.00) a traveler will release its node as soon as it begins to travel to the next node. When this value is greater than zero, the traveler will wait this additional time before releasing the node.
Stop for Turns
When checked, travelers who need to turn to a new direction will stop and rotate to the new direction.
Turn Speed
Defines the turn speed to use when travelers stop and rotate for turns.
Turn Delay
Defines an additional time delay associated with stopping for turns. When the traveler must stop and turn, it will add this delay time to the time it takes to the turn to the new direction.
Route By Travel Time
If checked, the A* search algorithm will use travel time instead of travel distance as the cost function in assessing path desirability. The primary difference in using this is that, when travelers stop for turns, it will calculate the time it takes to turn, and apply that to the cost function.
Default Preferred Path Weight
This is the default path weight for any preferred paths without a custom weight. Setting a path to have a path weight of 0 will revert the path to using this default value.
The Visual Tab
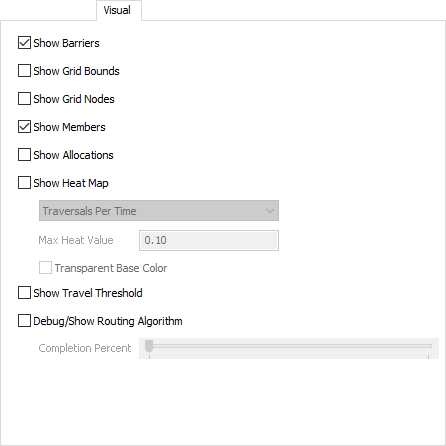
Use these properties to turn on or off the visiblilty of A* features.
Barriers
When checked, Barriers will be visible.
Grid Bounds
When checked, a blue box is drawn indicating the bounds of the grid.
Grid Nodes
When checked, displays the individual nodes of the grid.
Members
When checked, displays a blue circle under travelers and a blue rectangle under Fixed Resources connected to the A* Navigator.
Allocations
When checked, lines are drawn from travelers to the nodes they have allocated.
Heat Map
When checked, a heat map is generated based on the option selected in the dropdown. The Max Heat Value corresponds with the selected dropdown option and defines the threshold for coloring the heatmap.
Travel Threshold
When checked, red and blue diamonds will be displayed around the highlighted object in the 3D view. When a traveler is given a travel task to travel to this object, the A* Navigator will compute the shortest path between the traveler and any of the nodes marked by a red diamond. The traveler will then begin traveling following this shortest path. As soon as the traveler reaches any of the nodes marked by a blue diamond the traveler has arrived at the object and the travel task is complete.
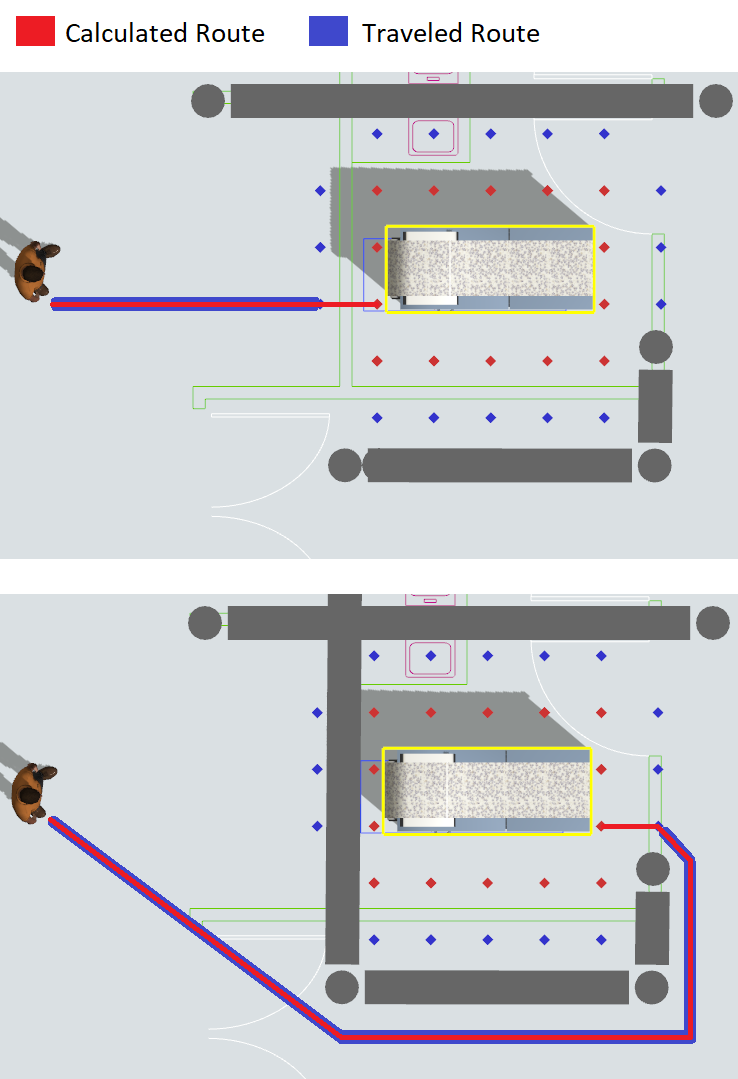
Debug/Show Routing Algorithm
This checkbox is used primarily for debugging purposes. When checked, the A* search algorithm will save additional data that tracks each traveler's last path finding operation. To see this information:
- Check the Debug/Show Routing Algorithm box.
- Press the Apply button.
- Run the model.
-
Click or shift-select a traveler. When you select the traveler, you'll see a set of
dots on the A* grid that are associated with that traveler's last path finding
operation:
- Green dots represent nodes that are in the A* open set.
- Red dots represent nodes in the closed set.
- The blue dot shows the node that is being resolved from the open set to the closed set.
- Text also appears beside each node showing the formula g + h = f, where g is the cost to get to a node, h is the heuristic calculation to get from the node to the destination, and f is the sum of the two.
- Adjust the Completion Percent tracker to see the routing algorithm as it progresses.
Divider/Path Properties
You can access a Divider or Path's properties by double-clicking on it, or through Quick Properties:
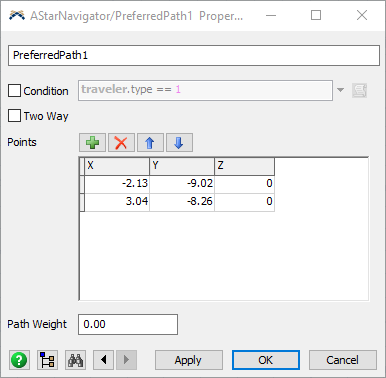
Condition
Check this box to make a barrier conditional, and define the condition that is required for the barrier to be applied. When a barrier is conditional, its condition is reevaluated at the beginning of every travel task. If the condition returns false (0), then the barrier will not be applied in the route calculation algorithm, and the traveler will travel as if the barrier did not exist. Conditional barriers let you define certain barriers as only applicable for certain travelers, or based on certain model conditions.
Two Way
Check this box to make the divider/path apply in two directions instead of just one.
Points (Dividers/One-Way Dividers/Preferred Paths)
Define x,y positions of each point.
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Add a point to the end. |
 |
Remove the selected point. |

 |
Reorder the selected point up or down in the list. |
Path Weight
Preferred Paths only. This is the path weight added to the nodes associated with the path.
Virtual Distance
Bridges only. When checked, this is the distance that will use for traversing the Bridge instead of the actual distance.
Barrier Properties
You can access a Barrier's properties by double-clicking on it, or through Quick Properties:
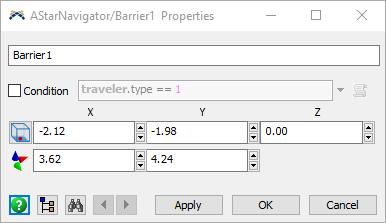
Condition
Check this box to make a barrier conditional, and define the condition that is required for the barrier to be applied. This is the same as the condition described above under Divider/Path Properties.
Position and Size (Barriers)
Specify the size and position of the barrier.
A* Grids
A*'s path search uses grids to resolve travel paths. A grid is a two-dimensional plane that encompasses a travel area. After you've dragged barriers, dividers, etc. into a model, if you reset the model, you will see a grid represented by a blue rectangular border surrounding those objects. The grid is a two-dimensional array of nodes, with a user-defined distance between each node. A* travelers move by traveling from one node in the grid to another. Barriers and dividers determine which adjacent nodes may or may not be traveled to from a given node.
Every A* model has at least one grid. That grid will automatically grow to encompass all the barriers, dividers, preferred paths, etc. that are part of your A* model. Also, you can add additional grids by dragging them from the library on the left. You can move and resize grids in the 3D view as you would any other object. You can also define the node spacing of a grid, as well as its z position, through its Quick Properties pane.
Node Spacing
This is the distance (in model units) between nodes in the grid. Smaller spacing will allow travel members to move more smoothly and direct, however, more nodes will require more processing time to calculate paths.
Set View Grid Z
Sets the current Grid Z of the 3D view to the Z position of this grid.