shared resource
Overview and Key Concepts
The shared resource object represents a resource that is shared between multiple objects which are not directly connected. It constrains the total flow through these objects, without those objects being directly related in the flow network. Examples of a shared resource can be an incinerator or a flow valve, which keep separate flows separated but impose a maximum total capacity on the sum.
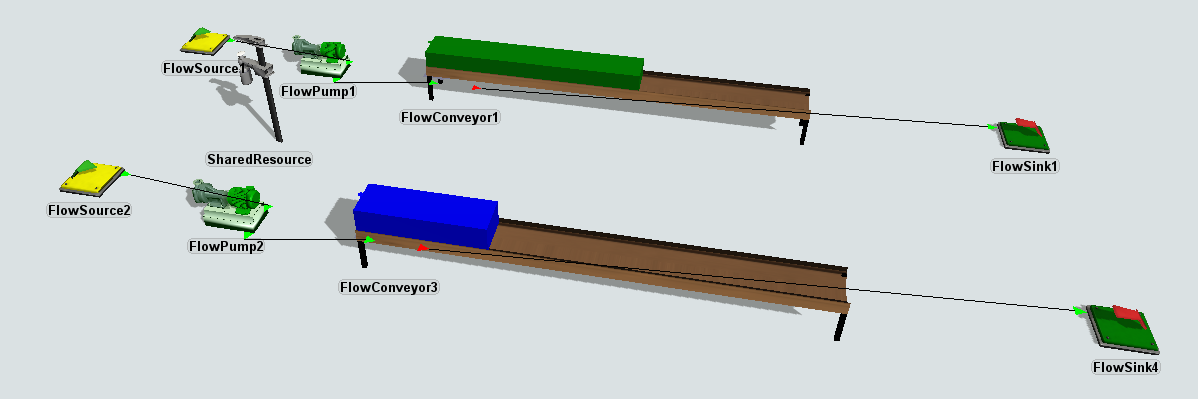
No material flows through the shared resource object itself. Rather, the shared resource is added to the model as a separate object; the objects it restricts (its members) are linked to it through the properties page of the shared resource. All objects for which the inflow and outflow are always equal can be members of the shared resource. This includes pumps, valves, sources and sinks. The sum of all these flows will be enforced to be less than or equal to the maximum capacity of the shared resource object. To be able to do this, all members of the shared resource must be attached to the same flow control. Which flow will be reduced first is determined by the order in which objects are attached to the flow control. In principle this decision is made automatically, however it can be influenced by re-ordering flow ports before recalculation of the flow rates.
Events
For information on events, see the Event Listening page.
The source uses the standard events that are common to all fixed resources. See Fixed Resources - Events for an explanation of these events.
States
The shared resource does not set any states, it will always be in the idle state.
States
The shared resource does not keep track of any statistics.
Properties
The shared resource object uses the following properties panels: