The Travel Panel
The Travel panel controls how task executers travel in the model.
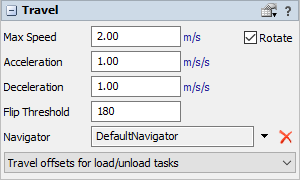
The following properties are on the Travel panel:
Max Speed
This is the fastest that the Task Executer can travel.
Acceleration
This number is how fast the Task Executer gains speed until it reaches its maximum speed or needs to slow down to reach its destination node.
Deceleration
This number is how fast the Task Executer loses speed as it approaches its destination.
Flip Threshold
When the angle between the Task Executer and the destination node meets or exceeds this value, the Task Executer will flip (mirror image) in order to be facing the correct direction. This option will not affect the statistics of the model if checked or unchecked. It is simply for visualization.
Rotate
If this box is checked, the Task Executer will rotate as needed in order to orient itself in the direction of travel. If the box is not checked, it will always face the same direction. This option will not affect the statistics of the model if checked or unchecked. It is simply for visualization.
Navigator
This specifies which Navigator the Task Executer object will use. If Navigator's are
available in the model, they will be displayed in the drop down. To remove the Task
Executer from using any Navigator, press the Remove button
 .
.
Depending on what objects are in your model, various navigators may be available. Below is a list of those navigators and their purpose:
- None - When set to None, the Task Executer will execute travel tasks by moving in a straight line from their current position to the end position. They will also offset travel in a straight line to pickup flow items when necessary.
- DefaultNetworkNavigator - The DefaultNetworkNavigator is available when Network Nodes have been added to the model. Connecting a Task Executer to a NetworkNode using an A connection will automatically set their Navigator to be the DefaultNetworkNavigator. The DefaultNetworkNavigator will build a distance/routing table for all network nodes in the model. When a travel task is given to the Task Executer, the navigator will move the Task Executer from NetworkNode to NetworkNode along the shortest path to the final destination.
- AGVNetwork - The AGVNetwork is available if AGV paths have been added to the model. Task Executers using the AGVNetwork will travel along AGV paths based upon the properties setup in the AGV Network Properties.
- AStarNavigator - The AStarNavigator is available if the AStar Navigator has been added to the model. When connected to the AStarNavigator, the Task Executer will travel the shortest path from the current position to the final destination based upon any dividers or barriers that may be in the way.
Travel offsets for load/unload tasks
This box provides the following options:
- Travel offsets for load/unload tasks - If selected, the Task Executer will move to the exact point where the flow item is being picked up or dropped off.
- Do not travel offsets for load/unload tasks - If selected, the Task Executer will travel to the origin of the destination object and pick up or drop off the flow item there. In the case where the Task Executer is using networknodes to travel to the destination, it will travel to the networknode attached to the destination object and then stop there.
- Do not travel offsets and block space on network - This option only applies when the Task Executer is connected to a network of nonpassing paths. If selected, the Task Executer will arrive at the node, finish its travel, and while it is doing the load/unload operation, it will continue to take up space on the network, and block other transporters/operators traveling on the path.
- Use navigator for offset travel - If selected, the Task Executer will use the assigned Navigator for any offset travel tasks, such as travel-to-loc, travel-relative, and load/unload tasks.