Traffic Control
Overview and Key Concepts
The traffic control object is used to control traffic in a given area of a travel network. You build a traffic controlled area by connecting network nodes to the traffic control object. These NetworkNodes then become members of the traffic controlled area. Any path between two nodes that are both members of the same traffic control object is designated as a traffic controlled path, and travelers are only allowed onto that path if given permission by the traffic control object. The traffic control object can be in a mutual exclusion mode, where it only lets a certain number of travelers into the area at any given time, or it can use un-timed traffic modes to only allow travelers onto certain path sections at once.

Events
For information on events, see the Event Listening page.
The traffic control object has the following events:
On Entry
On Entry occurs when a traveller enters the area controlled by this traffic control.
It has the following parameters:
| Event Parameter | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Traveler | treenode | The traveller (or task sequence) entering the control area |
| Network Node | treenode | The traveller's node, an entry to the control area |
| Next Output Port | int | The output port the traveller will use next |
On Entry Request
On Entry Request occurs when a traveller attempts to enter an area controlled by the traffic control.
It has the following parameters:
| Event Parameter | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Traveler | treenode | The traveller (or task sequence) requesting entry the control area |
| Network Node | treenode | The traveller's node, an entry to the control area |
| Next Output Port | int | The output port the traveller will use next |
OnExit
On Exit occurs when a traveller leaves the control area.
It has the following parameters:
| Event Parameter | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Traveler | treenode | The traveller (or task sequence) exiting the control area |
States
The traffic control object does not implement states.
Statistics
The traffic control object does not track any statistics.
Properties
The traffic control object has six tabs with various properties. The last three tabs are common to Travel Network objects. For more information about the properties on those tabs, see:
The remaining three tabs, the TrafficControl tab, the Speeds tab, and NetworkNodes tab are unique to the traffic control object. The properties on these tabs will be explained in more detail in the next three sections.
The TrafficControl Tab
Certain properties on the TrafficControl tab will only appear based on what is selected in the Traffic Control Mode menu. The properties on this tab will be explained in more detail in the following sections.
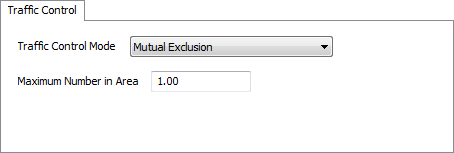
Traffic Control Mode
This menu defines the method by which the object controls traffic. There are two options:
- Mutual Exclusion - Only allows a given number of travelers into the Traffic Control's area, regardless of which paths they are on.
- Untimed Traffic Modes - Used if you want to control traffic based on each individual path in the object's traffic control area.
Mutual Exclusion Properties
Mutual exclusion is used to only allow a given number of travelers into the Traffic Control's area, regardless of which paths they are on. Here you simply specify the maximum number value.
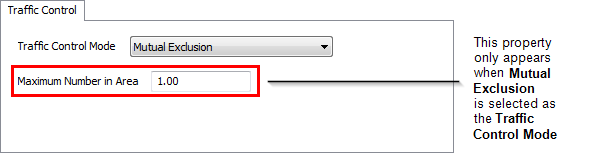
Maximum Number in Area - This property only appears when Mutual Exclusion is selected as the Traffic Control Mode. This value defines the maximum number of travelers that are allowed in the traffic control's area.
Untimed Traffic Modes Properties
Untimed traffic modes are used if you want to control traffic based on each individual path in the object's traffic control area. A mode is defined by one row in the modes table. For each mode you can define a set of paths between nodes in the traffic control area. When the traffic control is in a given mode, travelers are only allowed into the traffic control area if the path they are entering on is one of the paths defined in the current mode. The traffic control will stay in the same mode until there are no travelers left in the traffic control area, after which it will take the first traveler that arrives and find a mode that contains that traveler's requested entry path. This is why it is an un-timed mode. There is no limit on the amount of time that a traffic control may stay in the same mode.
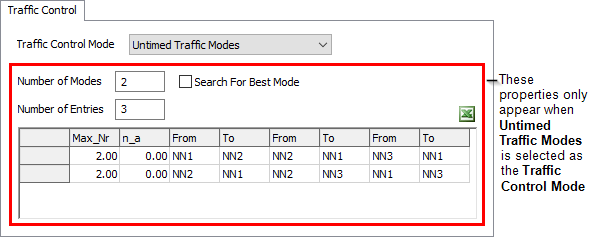
The following properties only appear when Untimed Traffic Mode is selected as the Traffic Mode:
- Number of Modes - This is the number of modes, or rows in the table. Enter the number of modes you want, and click the Apply button, and the appropriate number of rows will be created.
- Number of Entries - This is the maximum number of From/To entries (or columns) that you will need for your modes. If some modes don't need all of the columns, just leave them blank.
- Search for Best Mode - If this box is checked, then whenever the traffic control gets an entry request for an entry path that is not in its current mode, it will search through its modes to see if there are any other modes that include all paths already entered as well as the new path. If so, it will change to that new mode and allow the traveler's entry. Note that this may slow down the model, since the traffic control must search the table every time an entry request is made.
- Mode Table Entries - The mode table has the
following values:
- Max_Nr - This value specifies a maximum number of travelers allowed in when the traffic control is in that given mode. It is much like the maximum number value in mutual exclusion mode.
- n_a - This value is reserved for future development, when timed traffic modes are implemented.
- From/To Entries - For each path of a mode, you specify the node from which the path extends, and the node to which the path extends. Enter the name of the nodes. Note that one entry describes only one direction of a node-to-node connection. Thus to specify both directions of a path, you will need to make two From/To entries, one in each direction.
The Speeds Tab
The Speeds tab has the following properties:
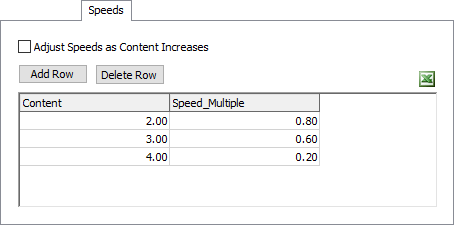
Adjust Speeds as Content Increase
If this option is checked, then the table will be used to adjust speeds of travelers within the traffic control object's area.
Add Row
Click this button to duplicate the selected row. If no row is selected, it will add a row to the end of the table
Delete Row
Click this button to delete the selected row from the table. If no row is selected, it will delete the last row of the table.
The NetworkNodes Tab
The NetworkNodes tab has the following properties:
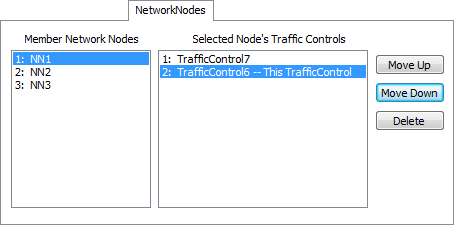
The NetworkNode page of the traffic control object lets you edit a traffic control's connections to network nodes. The panel on the left shows all NetworkNodes that are connected to the traffic control object. Select one of these nodes, and the panel on the right will refresh to a new list of traffic controls. The panel on the right shows all traffic controls that are connected to the NetworkNode you have selected on the left. The traffic control you are editing will have an extra " -- This TrafficControl" text, letting you know how this traffic control is situated among other traffic controls. The ranking of traffic controls in the right panel can have a significant effect on the behavior of the network.