Using Healthcare 3D Objects
Introduction to Healthcare 3D Objects
FlexSim Healthcare has a variety of 3D objects that you can use to build a simulation model. This topic will explain what these types of objects are and how they differ from standard FlexSim 3D objects.
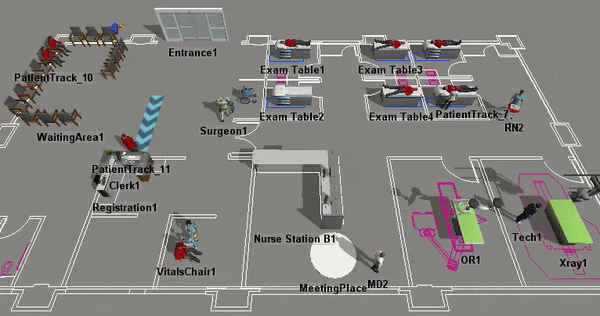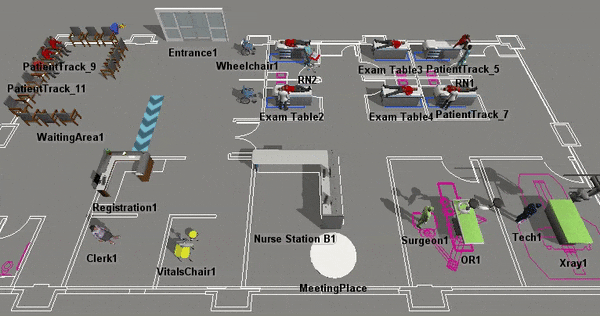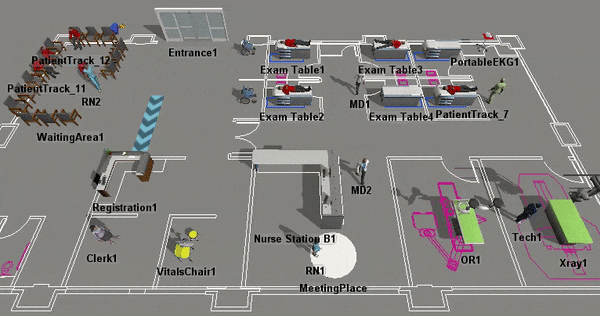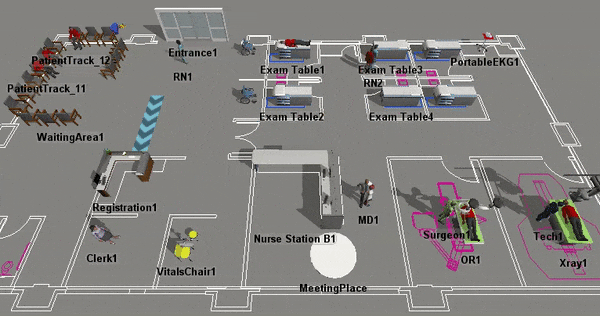
Although there are some important differences between Healthcare 3D objects and standard objects that will be discussed in more detail, they have many similarities too. For example, you will use the same processes to add Healthcare 3D objects to a model, to select the objects, to edit their properties, etc. For that reason, you should consider skimming the chapter about Using 3D Objects for a quick introduction to how the 3D objects work in general, including some tips and tricks. You might find the following topics especially relevant:
Key Concepts about Healthcare 3D Objects
In terms of differences, Healthcare 3D objects are different from standard objects in the following respects:
- The Healthcare 3D objects are available in the Library when you are in the Healthcare environment. The Healthcare environment customizes the look and feel of FlexSim to give prominence to the 3D objects in the Library that will be the most useful when building healthcare simulation models. Make sure you are in the Healthcare environment to ensure ease of access to these 3D objects. Alternatively, the Healthcare 3D objects can be found in the People group if you are in the standard FlexSim environment.
- Healthcare simulation models have patients instead of flow items. In standard FlexSim 3D models, flow items move from one fixed resource to another. By contrast, in healthcare simulation models, patients typically flow from one location to another, assisted by staff members. In this respect, healthcare models are generally patient-centered, which means that most of the system's processes are built around a patient's care from the time they enter the simulation model until they leave.
- Healthcare objects have some additional sub-categories of objects. In standard FlexSim, there are two main categories of 3D objects: fixed resources and task executers. Healthcare models use special classes of these two categories of objects. For example, healthcare models use staff members, which are a special kind of task executer. Healthcare models also include special types of fixed resources called locations and multi-locations. Healthcare models also include transport and equipment objects, which can be moved around the 3D model by staff members. See the following section about Types of Healthcare 3D Objects for more information.
- Healthcare 3D objects are automatically added to groups based on the types of objects they are. When you add a Healthcare object to a 3D model, it is automatically added to the general location, staff, transport, or equipment group depending on what type of object it is. (The exception to this rule are props and visual objects, such as entrances and exits, which have a purely visual function within the model.) In order to make your model's logic scale better, you should consider creating sub-groups for the objects you add to your model. See Using Groups as a Best Practice for more information.
Types of Healthcare 3D Objects
The 3D objects in the FlexSim Healthcare Library are the basic building blocks you will use to build your 3D model. Each object has built-in logic that is commonly used in a variety of healthcare simulation models. You can also easily edit the properties and customize the logic on these objects to adapt any of them to the unique needs of your simulation project. The following sections will provide a high-level overview of the types of Healthcare objects in the Library. Each object has a link to its object reference page for more information. The categories and objects are presented in the same order as they appear in the Library.
Locations
If you're familiar with FlexSim in general, locations are similar to fixed resources in the standard FlexSim environment. Patients will move to these locations and interact with them based on the type of object they are. Usually the interaction will involve changing something about the patient's visuals or animations while they arrive at, use, or exit the location. For example, when patients interact with a chair, it will animate them sitting in a chair.

Staff
Staff objects are people that will move around the 3D model assisting patients and perform various tasks throughout the simulation model. They can interact with patients, locations, transports, and equipment as needed. For example, staff can travel, escort or transport patients, move equipment, and perform many other simulation tasks.

Transports
Transport objects can move around the simulation model carrying patients from one location to another. They will typically require a staff member to operate them.

Equipment
Equipment objects can also move around the simulation model and can be acquired to help care for a patient. They will also typically require a staff member to operate them.
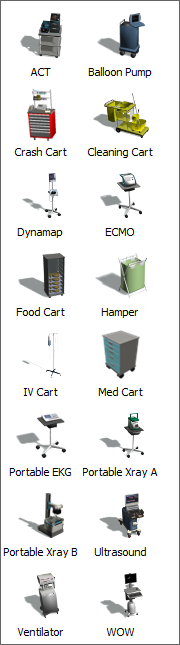
Multi-Locations
A multi-location is a location that contains a group of related locations. When a patient attempts to acquire the multi-location, any of the individual locations in this group could be acquired. The most typical multi-location you'll use is a set of chairs to represent a waiting room area. Each individual chair can potentially be acquired by the patients, but you don't need to add each chair to the model; you can simply add the group of chairs.

Waiting Lines
Waiting line objects can be used anywhere in the model where patients need to form a queue for service.
Elevators
Elevators can be used for staff and patients to travel to other floors in simulation models that have more than one floor.
Props
Props generally have a purely visual function within the 3D model. For that reason, they generally don't have any special logic built into their functionality.
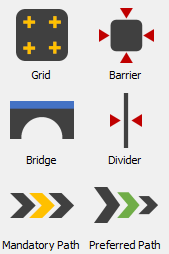
A* Navigation
A* Navigation objects are either objects or tools that can be used to control patient and staff movement throughout a model. See Working With A* Navigation" for more information about working with A* Navigation objects and tools.
Using Groups as a Best Practice
By default, all Healthcare locations, staff, equipment, and transports are automatically added to one of the main object groups. For example, all locations are added to the Locations object group, all staff are added to the Staff object group, and so forth.
However, you also have the ability to create additional groups or sub-groups to better organize your model. When a staff member is required to help a patient, you can assign any member of the group to help the patient (as opposed to assigning a specific staff member). When needed, the process flow will select the first available member of this group to work on a task.
Using object groups will help your model scale well as it becomes more complex. It makes it so that you can add extra chairs, clerks, nurses, etc. as needed without having to change the model's logic. When you add new objects to the 3D model, all you will have to do is add the new members to the group and FlexSim Healthcare will take care of the rest of the logic. These object groups also make it possible to easily study the impact of adding additional staff or location resources to your model to find the most efficient use of resources.