content
(node parent)
Commands by Category
AGV
agvaddlistener
(obj agv, node listenernode, num flags[, ...])
Description
Adds a listener event on the agv
Example
agvaddlistener(agv, c, AGV_LISTEN_PRE_ARRIVAL);
agvinfo
(obj agv, num what[, p1, p2, p3, p4])
Description
Deprecated, use AGV class.
Gets various information about an agv, based on the what parameter:
AGV_CURRENT_CP - Returns the agv's current control point
AGV_ORIGIN_CP - Returns the agv's origin control point
AGV_INTERMEDIATE_DEST_CP - Returns the agv's intermediate destination control point
AGV_DEST_CP - Same as AGV_INTERMEDIATE_DEST_CP
AGV_FINAL_DEST_CP - Returns the agv's final destination control point
AGV_DEST - Returns the agv's destination object
AGV_BATTERY_LEVEL - Returns the agv's current battery level as a percentage of battery capacity (0 - 100)
AGV_AMP_HOURS - Returns the agv's current battery level in amp hours
AGV_START_RECHARGE - Starts the agv recharging. Returns the time it will take to recharge to full capacity.
AGV_RECHARGE_TO_LEVEL - Explicitly set's the agv's battery level to p1 (0 - 100).
AGV_ADD_ALLOC_POINT - Should be called from the travel initialization trigger. Manually adds a control point/control area for allocation, i.e. a control point or control area that would not otherwise need to be allocated as part of the agv's current travel path. The control point/control area is passed as p1, and the distance at which it must be allocated is passed as p2. The command will return a reference to a node that represents that allocation. Use AGV_SET_ALLOC_POINT_DEALLOC_DIST and AGV_SET_CAN_STOP_AT_ALLOC_POINT to specify further data on that allocation point.
AGV_SET_ALLOC_POINT_DEALLOC_DIST - For a manual allocation point that's been added, this sets the travel distance at which the agv can deallocate the object. You should call this at some point after adding the allocation, so that the object will be properly deallocated. p1 is a reference to the allocation point node returned by AGV_ADD_ALLOC_POINT, and p2 is the deallocation distance.
AGV_SET_CAN_STOP_AT_ALLOC_POINT - Sets whether or not the agv can stop at a manually added allocation point. The default is no, i.e. the agv will not stop at the stop distance, but will continue to the next stoppable point before attempting to allocate the object. Setting this to 1 will allow the agv to stop at the manual allocation point to allocate ahead. p1 is a reference to the allocation point node returned by AGV_ADD_ALLOC_POINT, and p2 is 1 or 0.
AGV_ATTACH_TRAILER - Manually attaches a trailer to the AGV. p1: the object to attach. p2: the trailer gap to apply. p3: If 1, the trailer will be attached behind the AGV (attach to the AGV's tail), if 0, the trailer be attached ahead of the AGV (attach to the AGV's head). p4: If 1, the trailer will automatically be detached when the object exits the AGV, if 0, the trailer should be manually detached.
AGV_DETACH_TRAILER - Manually detaches a trailer from the AGV. p1: the object that is attached as a trailer.
AGV_SPEED - Returns the agv's current speed
AGV_PROXIMITY_STATE - Returns 1 if the agv is blocked by proximity on an accumulating path, 0 otherwise.
AGV_ACCUM_AHEAD_AGV - Returns the agv ahead of this agv on an accumulating path, if one exists.
Gets various information about an agv, based on the what parameter:
AGV_CURRENT_CP - Returns the agv's current control point
AGV_ORIGIN_CP - Returns the agv's origin control point
AGV_INTERMEDIATE_DEST_CP - Returns the agv's intermediate destination control point
AGV_DEST_CP - Same as AGV_INTERMEDIATE_DEST_CP
AGV_FINAL_DEST_CP - Returns the agv's final destination control point
AGV_DEST - Returns the agv's destination object
AGV_BATTERY_LEVEL - Returns the agv's current battery level as a percentage of battery capacity (0 - 100)
AGV_AMP_HOURS - Returns the agv's current battery level in amp hours
AGV_START_RECHARGE - Starts the agv recharging. Returns the time it will take to recharge to full capacity.
AGV_RECHARGE_TO_LEVEL - Explicitly set's the agv's battery level to p1 (0 - 100).
AGV_ADD_ALLOC_POINT - Should be called from the travel initialization trigger. Manually adds a control point/control area for allocation, i.e. a control point or control area that would not otherwise need to be allocated as part of the agv's current travel path. The control point/control area is passed as p1, and the distance at which it must be allocated is passed as p2. The command will return a reference to a node that represents that allocation. Use AGV_SET_ALLOC_POINT_DEALLOC_DIST and AGV_SET_CAN_STOP_AT_ALLOC_POINT to specify further data on that allocation point.
AGV_SET_ALLOC_POINT_DEALLOC_DIST - For a manual allocation point that's been added, this sets the travel distance at which the agv can deallocate the object. You should call this at some point after adding the allocation, so that the object will be properly deallocated. p1 is a reference to the allocation point node returned by AGV_ADD_ALLOC_POINT, and p2 is the deallocation distance.
AGV_SET_CAN_STOP_AT_ALLOC_POINT - Sets whether or not the agv can stop at a manually added allocation point. The default is no, i.e. the agv will not stop at the stop distance, but will continue to the next stoppable point before attempting to allocate the object. Setting this to 1 will allow the agv to stop at the manual allocation point to allocate ahead. p1 is a reference to the allocation point node returned by AGV_ADD_ALLOC_POINT, and p2 is 1 or 0.
AGV_ATTACH_TRAILER - Manually attaches a trailer to the AGV. p1: the object to attach. p2: the trailer gap to apply. p3: If 1, the trailer will be attached behind the AGV (attach to the AGV's tail), if 0, the trailer be attached ahead of the AGV (attach to the AGV's head). p4: If 1, the trailer will automatically be detached when the object exits the AGV, if 0, the trailer should be manually detached.
AGV_DETACH_TRAILER - Manually detaches a trailer from the AGV. p1: the object that is attached as a trailer.
AGV_SPEED - Returns the agv's current speed
AGV_PROXIMITY_STATE - Returns 1 if the agv is blocked by proximity on an accumulating path, 0 otherwise.
AGV_ACCUM_AHEAD_AGV - Returns the agv ahead of this agv on an accumulating path, if one exists.
Example
agvinfo(agv, AGV_DEST_CP);
agvreassigncp
(obj agv, obj controlpoint)
Description
Deprecated, use AGV class.
Reassigns an agv to the specified control point
Reassigns an agv to the specified control point
Example
agvreassigncp(agv, controlpoint);
agvredirect
(obj agv, obj object/controlpoint, num mode)
Description
Deprecated, use AGV class.
Redirects the agv to the designated object/control point. mode can be one of the following values:
REDIRECT_AND_WAIT - if not redirected before arrival, the agv will wait at the destination until redirected
REDIRECT_AS_FINAL - the destination becomes the new final destination for the agv REDIRECT_AND_CONTINUE_ON_ARRIVAL - the agv will continue to the final destination after arriving at the intermediate destination
REDIRECT_AND_CONTINUE_ON_PRE_ARRIVAL - the agv will continue to the final destination after pre-arriving at the intermediate destination (it will not decelerate to a stop)
Redirects the agv to the designated object/control point. mode can be one of the following values:
REDIRECT_AND_WAIT - if not redirected before arrival, the agv will wait at the destination until redirected
REDIRECT_AS_FINAL - the destination becomes the new final destination for the agv REDIRECT_AND_CONTINUE_ON_ARRIVAL - the agv will continue to the final destination after arriving at the intermediate destination
REDIRECT_AND_CONTINUE_ON_PRE_ARRIVAL - the agv will continue to the final destination after pre-arriving at the intermediate destination (it will not decelerate to a stop)
Example
agvredirect(agv, controlpoint, 1);
cp
(obj/str object_or_name)
Description
Returns a reference to an AGV control point
Example
cp("CP547");
cpaddlistener
(obj rootObj, str connectionPath, node listenerNode, num flags[, ...])
Description
Adds a listener to events on one or more control points
Example
cpaddlistener(current, "Location > LoadPoints", c, CP_LISTEN_EXIT | CP_LISTEN_AVAILABLE);
cpallocate
(obj controlPoint, obj allocator, num force)
Description
Allocates a control point to the claiming object. If successful, a reference to a coupling node
representing the allocation will be returned.
Example
cpallocate(controlPoint, current, 1);
cpconnection
(obj controlpoint/object, num/str connection, num rank)
Description
Returns a control point connection.
Also, if connection is a string and
controlpoint and rank are both 0, then
this command will return the
index of the given connection. This
is for speed, so that you can subsequently
use a number for the connection.
Example
cpconnection(cp, "ForwardTo", 1)
Returns the first ForwardTo connection on cpcpconnection(cp, "LookForWork>NextLookForWork", 1)
Traverses two connections to find an object.
This is the same as cpconnection(cpconnection(cp, "LookForWork", 1), "NextLookForWork", 1)cpconnection(cp, "LookForWork:2>NextLookForWork", 1)
Same as cpconnection(cpconnection(cp, "LookForWork", 2), "NextLookForWork", 1)int connIndex = cpconnection(0, "LookForWork", 0);
treenode obj = cpconnection(cp, connRank, 1);
cpdeallocate
(obj controlPoint, obj allocator)
Description
Deallocates a control point from the claiming object. If successful returns 1, otherwise 0.
Example
cpdeallocate(controlPoint, current);
cpdistance
(obj fromControlPoint, obj toControlPoint)
Description
Returns the agv network distance between two control points
Example
cpdistance(cp1, cp2)
cpisavailable
(obj controlpoint)
Description
Returns 1 if the given control point is available.
byCriterion is not used right now, but is reserved for future use.
Example
if (cpisavailable(cp)) {
...
}
...
}
cpnumconnections
(obj controlpoint, num/str connection)
Description
Returns the number of connections a control point has
Example
cpnumconnections(cp, "ForwardTo")
cptasksequencequeue
(obj controlpoint)
Description
Returns a reference to the task sequence queue associated with the control point
Example
treenode tsQueue = cptasksequencequeue(cp);
Communication
Commands for communicating with external applications such as sockets, database communication, and links with Microsoft Excel.
clientclose
(num socket)
Closes the client socket
Description
This command closes the client socket specified as socket.
It must be called sometime after clientcreate(). Once a socket is closed, nothing can read from it or write to it.
The socket number may be reused again by a later call to clientcreate(). This function returns true if the socket closes correctly.
It must be called sometime after clientcreate(). Once a socket is closed, nothing can read from it or write to it.
The socket number may be reused again by a later call to clientcreate(). This function returns true if the socket closes correctly.
Example
clientclose(1);
clientconnect
(num socket, str hostname, num port)
Attempts to connect the client socket
Description
This command attempts to connect the socket specified by socket to a server running on the machine called hostname, which is listening on the port specified.
The number passed as socket is the number that was previously returned by clientcreate(). The string passed as hostname can be either the computer's name (if it is on the same network as the client) or its IP address. This command should not be called until after a successful call to clientcreate() is made. If the socket does not connect, then it is closed and clientcreate() will have to be called again to reopen it. This functions returns true if the socket connects successfully.
The number passed as socket is the number that was previously returned by clientcreate(). The string passed as hostname can be either the computer's name (if it is on the same network as the client) or its IP address. This command should not be called until after a successful call to clientcreate() is made. If the socket does not connect, then it is closed and clientcreate() will have to be called again to reopen it. This functions returns true if the socket connects successfully.
Example
clientconnect(1,"localhost",1880);
clientcreate
()
Creates a new client socket with TCP/IP protocol
Description
This command creates a new client socket that is set to communicate using the TCP/IP protocol. FlexSim can create up to fifty client sockets at one time.
Each client can be connected to a different server. This function returns a number that must be stored by the model to reference the socket that was created.
If an error occurs, this function returns 0.
Each client can be connected to a different server. This function returns a number that must be stored by the model to reference the socket that was created.
If an error occurs, this function returns 0.
Example
int socknum = clientcreate();
clientreceive
(num socket, str buffer, num buffersize, num noblock[1/0])
Receives data sent to the socket
Description
This command receives data that has been sent to the socket specified as socket. The value of socket is the number that is returned by clientcreate(). This command operates differently in flexscript vs. c++. In c++, buffer must be a valid pointer to a char* destination into which the read bytes will be copied. The return value will be the total number of bytes received. Up to bufsize bytes from the clients message will be read and stored in the preallocated character array called buf. In flexscript, however, buffer should be passed as NULL, and the return value will be the actual string that is received. If noblocking = 1, then this command does not block FlexSim program execution, but if noblocking = 0, FlexSim program execution will block (freeze) until something is received from the client.
Example
c++: int bytes = clientreceive(1,Buf,15,0);
flexscript: string readstr = clientreceive(1, NULL, 15, 0);
flexscript: string readstr = clientreceive(1, NULL, 15, 0);
clientsend
(num socket, str message[, num charlength])
Sends a message across the socket
Description
This command sends a message across the socket specified as socket. The value passed as socket is the number returned by clientcreate(). The charlength is the length of the string being passed and is usually optional. Needed only if the string being sent has NULL characters in it.
Example
clientsend(1,"REQ:service");
excelclose
(num save [1/0])
Close the currently open Excel workbook
Description
This command closes the currently open Excel workbook. If save is 1, the workbook will be saved before it closes. If save is 0, changes made to the workbook will be discarded.
Example
See the example for excelopen().
excelcreatesheet
(str name)
Creates a new worksheet in the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Creates a new worksheet. The new sheet will be given the specified name.
Example
excelcreatesheet("MyNewSheet");
excelcreateworkbook
()
Create an Excel workbook
Description
This command creates a workbook in Excel. Only one workbook can be open at a time. The user must call excelclose() before trying to open or create another workbook, opening a new model, compiling the current model, or closing FlexSim. Before reading from the open file, excelsetsheet() must also be called.
Example
excelcreateworkbook();
excelsetsheet("Sheet1");
excelwritenum(1,1,1);
excelsave("NewWorkBook.xlsx");
excelclose(0);
This first creates a link between FlexSim and a new Excel workbook, sets the active sheet in the workbook to "Sheet1", writes a 1 to row 1 column 1, saves the workbook, then closes the workbook.
excelsetsheet("Sheet1");
excelwritenum(1,1,1);
excelsave("NewWorkBook.xlsx");
excelclose(0);
This first creates a link between FlexSim and a new Excel workbook, sets the active sheet in the workbook to "Sheet1", writes a 1 to row 1 column 1, saves the workbook, then closes the workbook.
exceldeleterange
(str rangename)
Deletes the specified range of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Deletes the specified range. Does not affect the data in the range.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
Example
exceldeleterange("MyRange");
exceldeletesheet
(str name [, int allowwarning])
Delete the worksheet in the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Deletes the specified worksheet. If allowwarning is 1, you will be warned before you delete a sheet with data.
Example
exceldeletesheet("MyNewSheet");
excelexporttable
(str/node/num table, num startrow, num startcol, num numrows, num numcols [, num rowchar, num colchar])
Exports data from a table within FlexSim to the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Exports data from a table within FlexSim to Excel. The table may be referenced by the name of a GlobalTable or by using a treenode reference to a table node. The type of data (string or number) to be exported is determined by the datatype of the cells in the FlexSim table. The user specifies the starting row and column number in Excel, and the total number of rows and columns to export.
Example
excelexporttable("Table1",1,1,5,3);
excelgetrangeparam
(str rangename, num param)
Retrieves a location parameter about the named range of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Retrieves a location parameter about the named range. Valid values for param are:
1 = Starting Row Number
2 = Starting Column Number
3 = Ending Row Number
4 = Ending Column Number
5 = Width
6 = Height
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
1 = Starting Row Number
2 = Starting Column Number
3 = Ending Row Number
4 = Ending Column Number
5 = Width
6 = Height
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
Example
int width = excelgetrangeparam("MyRange",5);
excelgetrangesheet
(str rangename)
Gets the name of the worksheet associated with rangename of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Returns the name of the worksheet where the specified range is located.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
Example
pt(excelgetrangesheet("MyRange"));
excelimporttable
(str/node/num table, num startrow, num startcol, num numrows, num numcols)
Imports data from the currently open Excel workbook to a table in FlexSim
Description
Imports data from Excel to a table in FlexSim. The table may be referenced by the name of a GlobalTable or by using a treenode reference to a table node. The type of data (string or number) to be exported is determined by the datatype of the cells in the FlexSim table. The user specifies the starting row and column number in Excel, and the total number of rows and columns to export.
Example
excelimporttable("MyTable",1,1,5,3);
excellaunch
([str launchdir])
Launch Microsoft Excel
Description
This command opens Microsoft Excel so that it can be accessed by FlexSim. If launchdir is not specified, the path defined in Tools|Excel...|Global Settings will be used. Otherwise, the launchdir must be an accurate path to the location on the hard drive where EXCEL.EXE is located. It is typically something like "C:/Program Files/Microsoft Office/Office10," but may be different depending on the version of Excel installed. It is generally not required to launch Excel before communicating with it. However, if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel via DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), this is not the default behavior) Excel must be running before any communication can be performed. If excellaunch() is called at the beginning of communication, excelquit() must also be called before the user opens a new model, compiles the current model or closes FlexSim.
Example
excellaunch(" C:/Program Files/Microsoft Office/Office10");
excelopen("C:/mybook.xls");
excelsetsheet("Sheet1");
double thenum = excelreadnum(1,1);
excelclose(true);
excelquit();
This starts Excel, opens a workbook called "mybook," stores a value read from row 1, column 1 from that workbook, then closes the file and Excel.
excelopen("C:/mybook.xls");
excelsetsheet("Sheet1");
double thenum = excelreadnum(1,1);
excelclose(true);
excelquit();
This starts Excel, opens a workbook called "mybook," stores a value read from row 1, column 1 from that workbook, then closes the file and Excel.
excelmultitableexport
()
Starts the automatic exporting of data from FlexSim tables to Excel
Description
Starts the automatic exporting of data from FlexSim tables to Excel sheets as setup in the Excel Import/Export tool.
Example
excelmultitableexport()
excelmultitableimport
()
Starts the automatic importing of data from Excel to FlexSim tables
Description
Starts the automatic importing of data from Excel sheets to FlexSim tables as setup in the Excel Import/Export tool.
Example
excelmultitableimport()
excelopen
(str workbook)
Open the Excel workbook
Description
This command opens the file called workbook in Excel. Only one workbook can be open at a time. The user must call excelclose() before trying to open another workbook, opening a new model, compiling the current model, or closing FlexSim. Before reading from the open file, excelsetsheet() must also be called.
Example
excelopen("mydata.xls");
excelsetsheet("Sheet1");
double myvalue = excelreadnum(1,2);
excelclose(0);
This first creates a link between FlexSim and an Excel workbook called "mydata.xls", then sets the active sheet in the workbook to "Sheet1", sets a local variable called myvalue to the number read from row 1 column 2, then closes the workbook without saving.
excelsetsheet("Sheet1");
double myvalue = excelreadnum(1,2);
excelclose(0);
This first creates a link between FlexSim and an Excel workbook called "mydata.xls", then sets the active sheet in the workbook to "Sheet1", sets a local variable called myvalue to the number read from row 1 column 2, then closes the workbook without saving.
excelquit
()
Close Microsoft Excel
Description
This command closes Microsoft Excel if it is open. After this command is called, no other commands to Excel should be called. Any Excel files that were open should be closed before this command is called. You may get an Excel prompt to save changes to any workbooks that were left open. Use excelclose() to avoid this. This command must be called if excellaunch() was called previously.
Example
see excellaunch();
excelrangereadnum
(str rangename, num row, num column)
Read the numeric value from a cell of the specified range of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Reads a numeric value from a cell defined by row and column in the specified named range. The upper-left cell of the range is row 1, column 1.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
Example
excelreadnum("MyRange",5,1)
excelrangereadstr
(str rangename, num row, num column [, num rowchar, num colchar])
Read the text value from a cell of the specified range of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Reads a text value from a cell defined by row and column in the specified named range. The upper-left cell of the range is row 1, column 1.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
Example
excelreadstr("MyRange",5,1)
excelrangewritenum
(str rangename, num row, num column, num value)
Write the numeric value to a cell of the specified range of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Writes a numeric value to a cell defined by row and column in the specified named range. The upper-left cell of the range is row 1, column 1.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting). For writing a whole table of values to Excel, use excelrangewrite.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting). For writing a whole table of values to Excel, use excelrangewrite.
Example
excelwritenum("MyRange",5,1,99.87)
excelrangewritestr
(str rangename, num row, num column, str value)
Write the string value to a cell of the specified range of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Writes string value to a cell defined by row and column in the specified named range. The upper-left cell of the range is row 1, column 1.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting). For writing a whole table of values to Excel, use excelrangewrite.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting). For writing a whole table of values to Excel, use excelrangewrite.
Example
excelwritestr("MyRange",5,1,"My String")
excelreadcell
(num row, num col[, num flags])
Returns the value of a cell in the active worksheet as a variant
Description
Returns the value of a cell in the active worksheet as a variant. Flags can be specified to specify what exactly is returned from Excel.
Those flags are EXCEL_DATA_NUMBER, EXCEL_DATA_STRING, and EXCEL_DATE_AS_NUM.
EXCEL_DATA_NUMBER will read the Excel data as a number.
EXCEL_DATA_STRING will read the Excel data as a string.
EXCEL_DATE_AS_NUM will interpret any Excel dates as a Flexsim readable date number.
EXCEL_DATA_NUMBER will read the Excel data as a number.
EXCEL_DATA_STRING will read the Excel data as a string.
EXCEL_DATE_AS_NUM will interpret any Excel dates as a Flexsim readable date number.
Example
Variant value = excelreadcell(1, 5, EXCEL_DATA_NUMBER | EXCEL_DATE_AS_NUM);
This returns the value of the 5 column in the first row as a number. If it's a date, the number returned will be Flexsim readable as a date.
This returns the value of the 5 column in the first row as a number. If it's a date, the number returned will be Flexsim readable as a date.
excelreadnum
(num row, num column [, num rowchar, num colchar])
Read the numeric value from a cell of the active sheet of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Reads a numeric value from a cell defined by row and column of the active sheet of the currently open Excel workbook.
Example
excelreadnum(5,1)
excelreadstr
(num row, num column [, num rowchar, num colchar])
Read the text value from a cell of the active sheet of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Reads a text value from a cell defined by row and column of the active sheet in the currently open Excel workbook.
Example
excelreadstr(5,1)
excelsave
([str filename])
Saves the currently open Excel file
Description
Saves the currently open Excel file. If a filename is passed to this command, the file will be saved with that name. This is the equivalent of selecting Save As from Excel's File menu. If no parameters are passed to this command, the file will be saved with its current name, and the original file will be overwritten. This is the equivalent of selecting Save from Excel's File menu.
Example
excelsave("runresults_001.xls")
excelsetrange
(str rangename, num startrow, num startcolumn, num endrow, num endcolumn)
Creates or changes a named range of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Creates or changes a named range. The range will be on the active sheet. The range's upper-left cell is defined by startrow and startcolumn. The bottom-right cell is defined by endrow and endcolumn.
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
This command does nothing if FlexSim is set to communicate with Excel using DDE (by calling maintenance(1000,1), not FlexSim's default setting).
Example
excelsetrange("MyRange",5,5,10,15);
excelsetsheet
(str sheetname)
Sets the active worksheet of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
This command sets the active worksheet in the currently open Excel workbook. Whenever excelreadnum() or excelreadstr() are called, the value read will come from the active worksheet. The active worksheet may be set many times for the same open workbook.
Example
See the example for excelopen().
excelversion
()
Gets the version of Microsoft Excel
Description
Returns a string that contains the Excel interface version.
Example
excelversion()
excelwritenum
(num row, num column, num value [, num rowchar, num colchar])
Write the numeric value to a cell of the active sheet of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Writes a numeric value to a cell defined by row and column of the active sheet in the currently open Excel workbook.
Example
excelwritenum(5,1,99.87)
excelwritestr
(num row, num column, str value [, num rowchar, num colchar])
Write the string value to a cell of the active sheet of the currently open Excel workbook
Description
Writes string value to a cell defined by row and column of the active sheet in the currently open Excel workbook.
Example
excelwritestr(5,1,"My String")
requestdecision
(str/node/num object)
Description
Request a decision from a ReinforcementLearning object.
When training, this will cause the simulation to return a reward for the previous action, make a new observation, and (if the episode is not done) wait for an action from the algorithm.
When running normally (not training), this will make an observation and execute the On Request Action trigger of the ReinforcementLearning object in order to make a heuristic decision or predict an action using a trained AI model.
Use this command to specify exactly when the AI should make a decision.
When training, this will cause the simulation to return a reward for the previous action, make a new observation, and (if the episode is not done) wait for an action from the algorithm.
When running normally (not training), this will make an observation and execute the On Request Action trigger of the ReinforcementLearning object in order to make a heuristic decision or predict an action using a trained AI model.
Use this command to specify exactly when the AI should make a decision.
Example
requestdecision("ReinforcementLearning1");
rundocument
(str command, str path+filename)
Open a file using the default application for the file type
Description
Opens a file using the default application used for opening files with the specified extension on your computer. The available commands are: edit, explore, find, open, and print. A return value > 32 means success.
Example
rundocument("open","C:/myfile.doc");
Opens myfile.doc with whatever application is default for opening *.doc files on your computer.
Opens myfile.doc with whatever application is default for opening *.doc files on your computer.
runprogram
(str commandline)
Run an external program
Description
Run an external program. This command will issue a command to the operating system. The commandline may contain full program arguments. A return value > 31 means success.
Example
runprogram("c:/myprogram.exe")
serveraccept
(int noblocking)
Gets the server will attempt to accept a client connection
Description
The server will attempt to accept a client connection. If noblocking = 0, the command blocks until a connection is made. It returns an index used to reference the connection made.
The server will attempt to accept a connection from a waiting client. A number will be returned that is the index of the connection established. A return value of 0 indicates that no connection was created. This value will be used in all future server calls. If noblocking = 1, the server will not block FlexSim program execution, but will return a 0 if no client attempts to connect. If noblocking = 0, the server will block (freeze) FlexSim program execution until a client attempts to connect. Connections with clients are only made with this command.
The server will attempt to accept a connection from a waiting client. A number will be returned that is the index of the connection established. A return value of 0 indicates that no connection was created. This value will be used in all future server calls. If noblocking = 1, the server will not block FlexSim program execution, but will return a 0 if no client attempts to connect. If noblocking = 0, the server will block (freeze) FlexSim program execution until a client attempts to connect. Connections with clients are only made with this command.
Example
int client = serveraccept(0);
servercloseconnection
(int connection)
Closes the client connection
Description
The specified connection to a client is closed. Does not close the main server socket. This should be done when the server is completely finished communicating with a client.
Example
servercloseconnection(1);
serverclosemain
()
Closes the main server socket and all open connections
Description
Closes the main server socket and all of the connections that are still open. No more communication can be done until it is created again. All connections should be closed before this is called.
Example
serverclosemain()
servercreatemain
(int port)
Creates a server socket that is listening for connections to the specified port
Description
Creates a server socket that is listening for connections on the specified port. Some ports (called well-known ports) are reserved for special applications. Anything port number over 1024 is usually safe to use.
Example
servercreatemain(1880);
serverreceive
(int connection, char *buffer, int bufsize, int noblocking)
Receives a message from the connection
Description
Receives a message from the specified connection. This command operates differently in flexscript vs. c++. In c++, buffer must be a valid pointer to a char* destination into which the read bytes will be copied. The return value will be the total number of bytes received. Up to bufsize bytes from the clients message will be read and stored in the preallocated character array called buf. In flexscript, however, buffer should be passed as NULL, and the return value will be the actual string that is received. If noblocking = 1, then this command does not block FlexSim program execution, but if noblocking = 0, FlexSim program execution will block (freeze) until something is received from the client.
Example
c++: int bytes = serverreceive(1,Buf,15,0);
flexscript: string readstr = serverreceive(1, NULL, 15, 0);
flexscript: string readstr = serverreceive(1, NULL, 15, 0);
serversend
(int connection, char* message [, num charlength] )
Sends a message to the client connect to connection
Description
Sends the specified text message to the client that is connected to the specified connection. Returns the number of bytes (characters) sent correctly. The text message to be sent must be converted into a char *. The charlength is the length of the string being passed and is usually optional. Needed only if the string being sent has NULL characters in it.
Example
serversend(1,"MadeConnection");
socketend
()
Shuts down the processes started with socketinit()
Description
This command shuts down the processes that were started with socketinit(). It should be called when the model has completely finished working with the sockets that it had open. This function returns true if the shut down is successful. See clientsend() for more information.
Example
socketend();
socketinit
()
Initializes background processes that allow Windows Sockets to be used
Description
This command initializes the background processes that allow Windows Sockets to be used. It must be called before any calls to socket commands will work. This function returns true if the initialization is successful. See clientsend() for more information.
Example
socketinit();
Conversions
Commands for converting units, data types, and spatial coordinate.
apchar
(str string)
Asserts string as a char*
Description
Assert type as C style string (e.g. char*). Alias for stringtopchar
Example
apchar("hello")
cm
(num centimeters)
Gets the number of meters in the number of centimeters
Description
Returns the number of meters in the specified number of centimeters.
Example
cm(3)
convert
(var value, var from, var to)
Converts the given value (a time) from one time format to another
Description
Converts the given value (a time) from one format to another. The from and to arguments only accept the following values:
FS_DATETIME
XL_DATETIME
MODEL_TIME
DATE_STR
TIME_STR
DATETIME_STR
FS_DATETIME - the number of seconds since Jan 1, 1601. getmodelunit(START_TIME) returns a value in FS_DATETIME units.
XL_DATETIME - the serialized day number, where day 1 is Jan 1, 1900. Feb 10, 2025 1:30 PM is 45698.5625 in XL_DATETIME units. This format is used in Microsoft Excel for dates.
MODEL_TIME - the number of model units since the model start time
DATE_STR - a string representing the date portion of a datetime value. The resulting text will depend on the date format specified in the model settings. If converting from this format, the value must be formatted according to those settings.
TIME_STR - a string representing the time portion of a datetime value. The resulting text will depend on the time format specified in the model settings. If converting from this format, the value must be formatted according to those settings.
DATETIME_STR - a string representing the time and date of a datetime value. The resulting text will depend on the time and date formats specified in the model settings. If converting from this format, the value must be formatted according to those settings; the time portion must be first, separated from the date portion by a single space.
Note that year 3000 and beyond are not supported by this command.
FS_DATETIME
XL_DATETIME
MODEL_TIME
DATE_STR
TIME_STR
DATETIME_STR
FS_DATETIME - the number of seconds since Jan 1, 1601. getmodelunit(START_TIME) returns a value in FS_DATETIME units.
XL_DATETIME - the serialized day number, where day 1 is Jan 1, 1900. Feb 10, 2025 1:30 PM is 45698.5625 in XL_DATETIME units. This format is used in Microsoft Excel for dates.
MODEL_TIME - the number of model units since the model start time
DATE_STR - a string representing the date portion of a datetime value. The resulting text will depend on the date format specified in the model settings. If converting from this format, the value must be formatted according to those settings.
TIME_STR - a string representing the time portion of a datetime value. The resulting text will depend on the time format specified in the model settings. If converting from this format, the value must be formatted according to those settings.
DATETIME_STR - a string representing the time and date of a datetime value. The resulting text will depend on the time and date formats specified in the model settings. If converting from this format, the value must be formatted according to those settings; the time portion must be first, separated from the date portion by a single space.
Note that year 3000 and beyond are not supported by this command.
Example
convert(42308, XL_DATETIME, MODEL_TIME) // converts an Excel date to a valid model time
days
(num days)
Gets the number of model time units in the give number of days
Description
Return the number of model time units in the given number of days.
Example
days(1)
Returns 86400 seconds.
Returns 86400 seconds.
fpm
(num feetperminute)
Gets the number of model length/time units in the number of feet/minute
Description
Return the number of model length/time units in the specified number of feet/minute.
Example
fpm(9)
fps
(num feetpersecond)
Gets the number of model length/time units in the number of feet/minute
Description
Return the number of model length/time units in the specified number of feet/second.
Example
fps(9)
ft
(num feet)
Gets the number of model length units in the number of feet
Description
Return the number of model length units in the specified number of feet.
Example
ft(3)
hours
(num hours)
Gets the number of model time units in the number of hours
Description
Return the number of model time units in the given number of hours.
Example
hours(1)
Returns 3600 seconds.
Returns 3600 seconds.
in
(num inches)
Gets the number of model length units in the number of inches
Description
Return the number of model length units in the specified number of inches.
Example
in(8)
minutes
(num minutes)
Gets the number of model time units in the number of minutes
Description
Return the number of model time units in the given number of minutes.
Example
minutes(1);
Returns 60 seconds.
Returns 60 seconds.
mph
(num milesperhour)
Gets the number of model length/time units in the number of miles/hour
Description
Return the number of model length/time units in the specified number of miles/hour.
Example
mph(9)
seconds
(num seconds)
Gets the number of model time units in the number of seconds
Description
Return the number of model time units in the given number of seconds.
Example
seconds(30);
Returns 0.5 minutes.
Returns 0.5 minutes.
tonode
(thing)
Assert type as a node pointer
Description
Assert type as a node pointer. Only serves a real purpose in C++.
Example
tonode(getnodenum(couplingnode))
Converts the numeric value of couplingnode to a treenode
Converts the numeric value of couplingnode to a treenode
tonum
(thing)
Assert type as a number
Description
Assert type as an arithmetic number. Only serves a real purpose in C++.
Example
return tonum(current);
This returns a pointer to the current object, casting it as a number.
This returns a pointer to the current object, casting it as a number.
toptr
(thing)
Description
For developer use. Assert type as pointer. Assert that the argument thing is of type void*. Only serves a real purpose in C++, but is safe to use in flexscript.
Example
toptr(so())
Conveyor
conveyorgetmotor
(obj conveyor)
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor class.
Example
conveyorgetmotor(conveyor);
conveyorinfo
(obj conveyor, num info[, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5])
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor class.
Example
conveyorinfo(conveyor, CONV_INFO_ESTIMATE_CONVEY_TIME);
conveyorresumeitem
(obj item[, num force])
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor class.
Example
conveyorresumeitem(item);
conveyorsenditem
(obj item, obj dest)
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor class.
Example
conveyorsenditem(item, outobject(current, 1));
conveyorsetspeed
(obj conveyor, num toSpeed)
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor class.
Example
conveyorsetspeed(conveyor, 1);
conveyorstopitem
(obj item)
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor class.
Example
conveyorstopitem(item);
mergegetlanestate
(obj mergeController, num laneNum)
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor.MergeController class.
Example
mergegetlanestate(current, 5)
mergegetnumlanes
(obj mergeController)
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor.MergeController class.
Example
mergegetnumlanes(current)
mergeislaneclear
(obj mergeController, num laneNum)
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor.MergeController class.
Example
mergeislaneclear(current, 5)
mergereleaselane
(obj mergeController, num laneNum)
Description
Deprecated, use Conveyor.MergeController class.
Example
mergereleaselane(current, 1)
Deprecated
Commands that are no longer supported, or for which alternative commands have been made. The documentation for these commands has been discontinued, and therefore may be incorrect. Many of the commands still work for backwards compatibility purposes, but we encourage you to use their alternatives instead.
acos
(num ratio)
add
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the + operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the + operator instead.
Addition of value1 to value2. This returns the result of the arithmetic expression value1+value2.
Addition of value1 to value2. This returns the result of the arithmetic expression value1+value2.
Example
double sum = add(1,2);
addfullhistorymoverecord
(num flowitemid, num time, obj origin, obj destination, num itemtype)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Adds a new entry to the Movement table that is recorded when Full History is enabled. The new entry records that the flowitem identified by flowitemid moved from the orgin object to the destination object and the specified time. The entry also records that the flowitem's itemtype at the time of the movement was the itemtype passed as the third parameter. Users should only have to use this command in very rare situations.
Example
addfullhistorymoverecord(getnodenum(uniqueid(item)), time(), current, current.outObjects[1], item.type);
addfullhistorystaterecord
(num time, num state, obj object)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Adds a new entry to the State table that is recorded when Full History is enabled. The new entry records that the specified object passed in as the third parameter changed to the specified state at the time that is entered as the first parameter. This should only need to be called if the object is having its state changed by soem command other than setstate().
Example
addfullhistorystaterecord(time(), STATE_IDLE, current);
addlabel
(obj object, str labelname [, num/str value])
addtablecol
(str/num/node table [, num column, num datatype])
addtablerow
(str/num/node table [, num row, num datatype])
and
(num/node condition1, num/node condition2)
Deprecated, use the && operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the && operator instead..
Example
angle
(num dx, num dy)
Deprecated, use Math.atan2()
Description
Example
double myangle = angle(distx, disty)
anode
(thing)
Deprecated, use tonode()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use tonode() instead.
Assert type as node pointer.
Assert type as node pointer.
Example
anode(so())
anum
(thing)
Deprecated, use tonum()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use tonum() instead.
Assert type as arithmetic number.
Assert type as arithmetic number.
Example
anum(so())
aptr
(thing)
Deprecated, use toptr()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use toptr() instead.
Assert type as pointer
Assert type as pointer
Example
aptr(so())
arraysize
(var array)
asin
(num ratio)
assertattribute
(obj object, str attributename, num datatype)
assertlabel
(obj object, str labelname, num datatype)
assertsubnode
(node containernode, str name[, num datatype])
atan
(num ratio)
atan2
(num dy, num dx)
att
(obj object, num index)
Deprecated, use getvarnode()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use var(), var_s() or getvarnode() instead.
Example
att(current,1)
att_s
(obj object, str name)
Deprecated, use getvarnode()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use getvarnode() instead.
Get the attribute node of an object by name. An attribute node is one which resides inside the "variables" node of the structure of an object. This function will return the pointer to the node called name inside the variables node of object. var_s supercedes this command.
Get the attribute node of an object by name. An attribute node is one which resides inside the "variables" node of the structure of an object. This function will return the pointer to the node called name inside the variables node of object. var_s supercedes this command.
Example
att_s(current,"myatt")
aviadd
(node viewnode)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Video Recorder instead.
Example
avifinish
(node viewnode)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Video Recorder instead.
Example
avistart
(str filename, node viewnode, num fps)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Video Recorder instead.
Example
bcgetitemkinematics
(obj basicconveyor, obj item, num kinematictype {0-main kinematic : 1-time dependent : 2-convey dependent})
Deprecated, legacy conveyors are no longer supported
Description
Deprecated, Legacy conveyors are no longer supported.
This command is used in conjunction with the BasicConveyor object.
The bcgetitemkinematics command is used to obtain a reference to one of the three kinematics associated with a flowitem traveling on a BasicConveyor:
0 = The main convey state kinematics. You may get kinematic information from this, but do not change the kinematic by adding kinematics or initializing it.
1 = A user-definable kinematics that is dependent on simulation time.
2 = A user-definable kinematics that is dependent on the convey position of the flowitem on the conveyor.
The two user-definable kinematics are available for the user to set up customized kinematic motion in addition to traveling down the length of the conveyor. Use bcgetitemkinematics to get a reference to the desired kinematics node, and then use standard initkinematics() and addkinematic() commands as normal. You will need to use the alternative initkinematics parameter list: initkinematics(node, x, y, z, rx, ry, rz, managerots, localcoords). Also, if you add kinematics to the type 2 convey depend kinematic node, bear in mind that all time units for that kinematic no longer apply to actual simulation time units. Instead, they are interpretted as "convey units". For example, a speed of 5 is no longer 5 units per time unit, but is instead 5 units per conveyed unit. Acceleration is not distance per time squared, but distance per conveyed unit squared. Start times are no longer a time to start the kinematic, but a position along the conveyor to start the kinematic at. As an example, let's say you add a kinematic to the convey dependent kinematic node to travel 1 unit in the y direction with "start time" 5 and "max speed" 0.5. What that translates to for the convey dependent kinematic is that the item will start traveling in the y direction once it reaches 5 units along the conveyor. Also, for every unit that it travels down the length of the conveyor, it will travel 0.5 units in the y direction (0.5 y units per convey unit). Thus it will finish the y kinematic once it has travelled 7 units down the conveyor. If the item is blocked in the middle because of accumulation, say at convey position 6, then its y kinematic will also stop, and not resume until the item resumes along the conveyor.
See bcsetitemconveystate command documentation for a general description of the BasicConveyor object.
This command is used in conjunction with the BasicConveyor object.
The bcgetitemkinematics command is used to obtain a reference to one of the three kinematics associated with a flowitem traveling on a BasicConveyor:
0 = The main convey state kinematics. You may get kinematic information from this, but do not change the kinematic by adding kinematics or initializing it.
1 = A user-definable kinematics that is dependent on simulation time.
2 = A user-definable kinematics that is dependent on the convey position of the flowitem on the conveyor.
The two user-definable kinematics are available for the user to set up customized kinematic motion in addition to traveling down the length of the conveyor. Use bcgetitemkinematics to get a reference to the desired kinematics node, and then use standard initkinematics() and addkinematic() commands as normal. You will need to use the alternative initkinematics parameter list: initkinematics(node, x, y, z, rx, ry, rz, managerots, localcoords). Also, if you add kinematics to the type 2 convey depend kinematic node, bear in mind that all time units for that kinematic no longer apply to actual simulation time units. Instead, they are interpretted as "convey units". For example, a speed of 5 is no longer 5 units per time unit, but is instead 5 units per conveyed unit. Acceleration is not distance per time squared, but distance per conveyed unit squared. Start times are no longer a time to start the kinematic, but a position along the conveyor to start the kinematic at. As an example, let's say you add a kinematic to the convey dependent kinematic node to travel 1 unit in the y direction with "start time" 5 and "max speed" 0.5. What that translates to for the convey dependent kinematic is that the item will start traveling in the y direction once it reaches 5 units along the conveyor. Also, for every unit that it travels down the length of the conveyor, it will travel 0.5 units in the y direction (0.5 y units per convey unit). Thus it will finish the y kinematic once it has travelled 7 units down the conveyor. If the item is blocked in the middle because of accumulation, say at convey position 6, then its y kinematic will also stop, and not resume until the item resumes along the conveyor.
See bcsetitemconveystate command documentation for a general description of the BasicConveyor object.
Example
treenode kin = bcgetitemkinematics(current, item, 2);
treenode kin2 = bcgetitemkinematics(current, item, 1);
initkinematics(kin, 0,0,0, 0,0,0, 0,0);
addkinematic(kin, 0,1,1,0.5,1,1,0,0, 5, KINEMATIC_TRAVEL);
initkinematics(kin2, 0,0,0, 0,0,0, 0,0);
addkinematic(kin2, 0,0,720,360,0,0,0,0, time()+5.0, KINEMATIC_ROTATE);
treenode kin2 = bcgetitemkinematics(current, item, 1);
initkinematics(kin, 0,0,0, 0,0,0, 0,0);
addkinematic(kin, 0,1,1,0.5,1,1,0,0, 5, KINEMATIC_TRAVEL);
initkinematics(kin2, 0,0,0, 0,0,0, 0,0);
addkinematic(kin2, 0,0,720,360,0,0,0,0, time()+5.0, KINEMATIC_ROTATE);
bcgetitemposition
(obj basicconveyor, obj item)
Deprecated, legacy conveyors are no longer supported
Description
Deprecated, Legacy conveyors are no longer supported.
This command is used in conjunction with the BasicConveyor object
The bcgetitemposition command returns the current position of an item on a BasicConveyor object. The position is measured along the conveyor's length from the head of the conveyor to the flowitem's edge furthest from the head of the conveyor.
See bcsetitemconveystate command documentation for a general description of the BasicConveyor object.
This command is used in conjunction with the BasicConveyor object
The bcgetitemposition command returns the current position of an item on a BasicConveyor object. The position is measured along the conveyor's length from the head of the conveyor to the flowitem's edge furthest from the head of the conveyor.
See bcsetitemconveystate command documentation for a general description of the BasicConveyor object.
Example
bcgetitemposition(current,current.first);
bcsetdirection
(obj basicconveyor, num direction)
Deprecated, legacy conveyors are no longer supported
Description
Deprecated, Legacy conveyors are no longer supported.
This command is used in conjunction with the BasicConveyor object.
The bcsetdirection command stops all flowitems on the conveyor and sets the direction of travel to 1=forward and 0=reverse. All flowitems will need to have their convey state reset with the bcsetitemconveystate() command before they will begin moving again. The example below shows how to stop the conveyor, and then have all the flowitems accelerate up to a speed of 1 in the reverse direction. Any additional item kinematics will still be active after a direction change.
See bcsetitemconveystate command documentation for a general description of the BasicConveyor object.
This command is used in conjunction with the BasicConveyor object.
The bcsetdirection command stops all flowitems on the conveyor and sets the direction of travel to 1=forward and 0=reverse. All flowitems will need to have their convey state reset with the bcsetitemconveystate() command before they will begin moving again. The example below shows how to stop the conveyor, and then have all the flowitems accelerate up to a speed of 1 in the reverse direction. Any additional item kinematics will still be active after a direction change.
See bcsetitemconveystate command documentation for a general description of the BasicConveyor object.
Example
bcsetdirection(so(),0);
for(int i = 1; i <= so().subnodes.length; i++)
{
treenode item = so().subnodes[i];
bcsetitemconveystate(so(), item, bcgetitemposition(so(), item), 0, 1, 0.2);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= so().subnodes.length; i++)
{
treenode item = so().subnodes[i];
bcsetitemconveystate(so(), item, bcgetitemposition(so(), item), 0, 1, 0.2);
}
bcsetitemconveystate
(obj basicconveyor, obj item, num startpoint, num startspeed, num targetspeed, num accdec)
Deprecated, legacy conveyors are no longer supported
Description
Deprecated, Legacy conveyors are no longer supported.
This command is used in conjunction with the BasicConveyor object.
The BasicConveyor object allows flowitems to be moved in and out of the conveyor at any time and at any location. Each flowitem on the BasicConveyor can be assigned and re-assigned its own kinematic profile defining how the flowitem is to move along the conveyor. When one flowitem overtakes another flowitem on the conveyor which is either stopped or traveling at a slower speed, it will slow down immediately to match that flowitem's speed. Although flowitems may travel in either direction along the conveyor, all flowitems will travel in the same direction at any given time. The travel direction of the conveyor is set with the bcsetdirection() command. As flowitems are moved in and out of the conveyor, other flowitems on the conveyor are aware of the increase or decrease in available space along the conveyor, and will accumulate naturally. After a flowitem enters the conveyor, either indirectly with the receiveitem() command or directly with the moveobject() command; it is necessary to define the flowitem's initial kinematic profile. This profile is refered to as the flowitem's "convey state", and it is set with the bcsetitemconveystate() command. The convey state for a flowitem can be set multiple times if desired. The following are definitions for the parameters used to define the convey state of a flowitem:
basicconveyor = A reference to the conveyor.
item = A reference to the flowitem.
startpoint = The starting location for the flowitem as measured from the beginning of the conveyor, along the conveyor's length to the flowitem's edge furthest from the head of the conveyor (the leading edge if the conveyor's direction is forward, the trailing edge if the conveyor's direction is backward).
startspeed = The initial speed the flowitem will begin traveling at.
targetspeed = The target speed the flowitem will try to achieve. If the targetspeed is greater than the startspeed, then the flowitem will accelerate up to the target speed; otherwise it will decelerate down to the target speed. If both the startspeed and the targetspeed are set to 0, the flowitem will be positioned at the startpoint, and will not move.
accdec = The acceleration or deceleration used to achieve the target speed over time. A value of 0 indicates infinite acceleration/deceleration; or in other words the flowitem will reach it's targetspeed immediately.
No destination or termination speed is required, because the flowitems continue traveling along the conveyor until they either reach the end of the conveyor, run into another flowitem, or their convey state is changed again. The BasicConveyor allows multiple "Decision Points" to be defined along its length. These trigger points are convenient locations to update the convey state of a flowitem. In addition to the main convey state kinematic assigned to the flowitem with the bcsetitemconveystate() command, a flowitem has two other kinematic structures associated with it that may be used to apply custom kinematic motion (translation or rotation) in addition to the travel motion along the conveyor. One of the kinematic structures is based on simulated time units, and the other is based on distance units along the length of the conveyor. To access these kinematic structures, use the bcgetitemkinematics() command, then use the initkinematics() and addkinematic() commands to create the custom kinematic motion desired. See bcgetitemkinematics() command documentation for more information.
This command is used in conjunction with the BasicConveyor object.
The BasicConveyor object allows flowitems to be moved in and out of the conveyor at any time and at any location. Each flowitem on the BasicConveyor can be assigned and re-assigned its own kinematic profile defining how the flowitem is to move along the conveyor. When one flowitem overtakes another flowitem on the conveyor which is either stopped or traveling at a slower speed, it will slow down immediately to match that flowitem's speed. Although flowitems may travel in either direction along the conveyor, all flowitems will travel in the same direction at any given time. The travel direction of the conveyor is set with the bcsetdirection() command. As flowitems are moved in and out of the conveyor, other flowitems on the conveyor are aware of the increase or decrease in available space along the conveyor, and will accumulate naturally. After a flowitem enters the conveyor, either indirectly with the receiveitem() command or directly with the moveobject() command; it is necessary to define the flowitem's initial kinematic profile. This profile is refered to as the flowitem's "convey state", and it is set with the bcsetitemconveystate() command. The convey state for a flowitem can be set multiple times if desired. The following are definitions for the parameters used to define the convey state of a flowitem:
basicconveyor = A reference to the conveyor.
item = A reference to the flowitem.
startpoint = The starting location for the flowitem as measured from the beginning of the conveyor, along the conveyor's length to the flowitem's edge furthest from the head of the conveyor (the leading edge if the conveyor's direction is forward, the trailing edge if the conveyor's direction is backward).
startspeed = The initial speed the flowitem will begin traveling at.
targetspeed = The target speed the flowitem will try to achieve. If the targetspeed is greater than the startspeed, then the flowitem will accelerate up to the target speed; otherwise it will decelerate down to the target speed. If both the startspeed and the targetspeed are set to 0, the flowitem will be positioned at the startpoint, and will not move.
accdec = The acceleration or deceleration used to achieve the target speed over time. A value of 0 indicates infinite acceleration/deceleration; or in other words the flowitem will reach it's targetspeed immediately.
No destination or termination speed is required, because the flowitems continue traveling along the conveyor until they either reach the end of the conveyor, run into another flowitem, or their convey state is changed again. The BasicConveyor allows multiple "Decision Points" to be defined along its length. These trigger points are convenient locations to update the convey state of a flowitem. In addition to the main convey state kinematic assigned to the flowitem with the bcsetitemconveystate() command, a flowitem has two other kinematic structures associated with it that may be used to apply custom kinematic motion (translation or rotation) in addition to the travel motion along the conveyor. One of the kinematic structures is based on simulated time units, and the other is based on distance units along the length of the conveyor. To access these kinematic structures, use the bcgetitemkinematics() command, then use the initkinematics() and addkinematic() commands to create the custom kinematic motion desired. See bcgetitemkinematics() command documentation for more information.
Example
bcsetitemconveystate(current, item, position, 0, 60, 0);
bitwiseand
(num a, num b)
Deprecated, use & operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use & operator instead.
Returns a bitwise AND operation on the two 32 bit integer values.
Returns a bitwise AND operation on the two 32 bit integer values.
Example
int bwa = bitwiseand(0x460, 0x040);
This example sets bwa to the value 0x020.
This example sets bwa to the value 0x020.
bitwisenot
(num a)
Deprecated, use ~ operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use ~ operator instead.
Returns the bitwise not of the 32 bit integer value
Returns the bitwise not of the 32 bit integer value
Example
int bwn = bitwisenot(0x0);
This example sets bwn to the value 0xffffffff
This example sets bwn to the value 0xffffffff
bitwiseor
(num a, num b)
Deprecated, use | operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use | operator instead.
Returns the bitwise OR of the 32 bit integer values
Returns the bitwise OR of the 32 bit integer values
Example
int bwo = bitwiseor(0x15, 0x01);
This example sets bwo to the value 0x15
This example sets bwo to the value 0x15
bitwisexor
(num a, num b)
Deprecated, use ^ operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use ^ operator instead.
Returns the bitwise XOR of the 32 bit integer values
Returns the bitwise XOR of the 32 bit integer values
Example
int bwxo = bitwisexor(0x15, 0x01);
This example sets bwxo to the value 0x14
This example sets bwxo to the value 0x14
ceil
(num num)
cell
(node table, num col, num row)
cellrc
(obj object, num row, num col)
cellrowcolumn
(node table, num row, num col)
Deprecated, use Table class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Table class instead.
Example
centerobject
(obj object, num centerportnum)
Deprecated, use Object.centerObjects[]
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.centerObjects[] instead.
Reference the object connected to an object's center port.
Reference the object connected to an object's center port.
Example
changeconveyorspeed
(obj conveyor, num newspeed )
Deprecated, use conveyor.targetSpeed
Description
This command is deprecated. Legacy conveyors are no longer supported. Use Conveyor.targetSpeed instead.
Changes the speed of the conveyor to newspeed.
Changes the speed of the conveyor to newspeed.
Example
changeconveyorspeed(current, 4);
This example changes the conveyor's speed to 4.
This example changes the conveyor's speed to 4.
clearconsole
()
Clears the output console
Description
This command clears the output console if it is open. The output console is where output from the pt(), pf(), and pr() commands is printed.
Example
if (v_printerror == 1)
{
clearconsole();
pt("An Error occurred");
}
This clears the output console and prints a simple error message to it if the variable called printerror is equal to 1.
{
clearconsole();
pt("An Error occurred");
}
This clears the output console and prints a simple error message to it if the variable called printerror is equal to 1.
clearcontents
(node thenode)
clearfullhistory
(int resetuniqueid)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Deletes all of the data that has been collected by the Full History system. If resetuniqueid is 1, then the unique IDs of the flowitems that are created after this command is called will being again at 1. Typically, this parameter should be 0, as that will continue numbering so that old flowitems are not confused with new flowitems.
Example
clearfullhistory(0);
clearglobaltable
(str/node/num table)
Deprecated, use Table class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Table class instead.
Example
closeinput
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.input.close()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.input.close() instead.
This command blocks the input of the object. Only the input ports themselves, or the input in general needs to be closed to block entry. When port connections are displayed with sufficient size in the view window, you will see a small red bar drawn across all the input ports (squares) for the object, signifying the input ports are blocked. Individual ports may still be open and drawn in green, but entry to the object is still blocked because of the red bar. Compare this command with stopinput().
This command blocks the input of the object. Only the input ports themselves, or the input in general needs to be closed to block entry. When port connections are displayed with sufficient size in the view window, you will see a small red bar drawn across all the input ports (squares) for the object, signifying the input ports are blocked. Individual ports may still be open and drawn in green, but entry to the object is still blocked because of the red bar. Compare this command with stopinput().
Example
if (current.subnodes.length == getvarnum(current,"maxcontent")
closeinput(current);
This blocks the input ports of current when it has too many objects inside it.
closeinput(current);
This blocks the input ports of current when it has too many objects inside it.
closeoutput
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.output.close()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.output.close() instead.
This command blocks the output of the object. Only the output ports themselves, or the output in general needs to be closed to block the exit. When port connections are displayed with sufficient size in the view window, you will see a small red bar drawn across all the output ports (squares) for the object, signifying the output ports are blocked. Individual ports may still be open and drawn in green, but exit from the object is still blocked because of the red bar. Compare this command with stopoutput().
This command blocks the output of the object. Only the output ports themselves, or the output in general needs to be closed to block the exit. When port connections are displayed with sufficient size in the view window, you will see a small red bar drawn across all the output ports (squares) for the object, signifying the output ports are blocked. Individual ports may still be open and drawn in green, but exit from the object is still blocked because of the red bar. Compare this command with stopoutput().
Example
if (current.subnodes.length == current.mincontent)
closeoutput(current);
This blocks the output ports of current, if current has too few objects inside it.
closeoutput(current);
This blocks the output ports of current, if current has too few objects inside it.
coloraqua
(obj object)
colorarray
(obj object, num colornumber)
colorblack
(obj object)
colorblue
(obj object)
colorbrown
(obj object)
colorgray
(obj object)
colorgreen
(obj object)
colorlightblue
(obj object)
colorlime
(obj object)
colororange
(obj object)
colorpink
(obj object)
colorpurple
(obj object)
colorrandom
(obj object)
colorred
(obj object)
colorrgb
(obj object, num red, num green, num blue)
colorsilver
(obj object)
colorteal
(obj object)
colorwhite
(obj object)
coloryellow
(obj object)
comparetext
(str text1, str text2[, int ignorecase])
Deprecated, use == operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the == operator instead. myStr == "Hello"
Test for string equality.
Test for string equality.
Example
concat
(str text1, str text2 [, str text3, ...])
Deprecated, use + operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the + operator instead. "a" + "b" + "c"
Concatenates strings together.
Concatenates strings together.
Example
connect
(obj object1, num port1, obj object2, num port2)
Deprecated, use contextdragconnection()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use contextdragconnection() instead.
Connect ports of two objects. The two objects are connected by checking whether the ports exist on the objects in question and then connecting them. The output port of the first object will be connected to the input of the second object. If the ports do not exist, or are already connected then the command will abort. To connect two objects by automatically adding ports, see the command objectconnect().
Connect ports of two objects. The two objects are connected by checking whether the ports exist on the objects in question and then connecting them. The output port of the first object will be connected to the input of the second object. If the ports do not exist, or are already connected then the command will abort. To connect two objects by automatically adding ports, see the command objectconnect().
Example
connect(model().subnodes[2],1,model().subnodes[3],2)
containerentry
(obj container, obj item)
Deprecated, use tracked variables or Process Flow
Description
This command is deprecated. Use tracked variables and/or Process Flow to track custom statistics.
Example
containerexit
(obj container, obj item)
Deprecated, use tracked variables or Process Flow
Description
This command is deprecated. Use tracked variables and/or Process Flow to track custom statistics.
Example
contentobj
(obj container)
cos
(num angle)
count
()
Description
The value of the iterator used with several commands such as repeat(), findmatch(), findmin(), and findmax(). The value of count will depend on which iteration is currently being executed.
Example
findmax(Table("MyTable").numRows, Table("MyTable")[count][5])
This example returns the maximum value found in column 5, among all the rows of the table MyTable.
This example returns the maximum value found in column 5, among all the rows of the table MyTable.
cppgettoken
(obj textblock, num tokenindex)
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
cppsettoken
(obj textblock, num tokenindex, str insertiontext)
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
createcopy
(node thenode, node container [, num samename, num inobject, num cached, num replace])
Copies thenode into the specified container
Description
This command is deprecated. Use treenode.copy() instead.
Copy thenode into the node specified as container. This command is different from createinstance() in that it does not attempt to establish any links between thenode and any class. If an instantiation is required, use createinstance() instead.
If samename is 1, the copy will have the same name as thenode.
If samename is 0, the newly created node's name will be thenode's name with a random number added to the end.
If inobject is 1, the copy will be created in the object data portion of the container. If the container does not have object data, the command does nothing.
If cached is 1, a pre-cached version of the node will be copied. This is generally faster.
If replace is 1, the copy will overwrite container, instead of being placed inside it.
If those parameters are not specified, they default to 0.
Copy thenode into the node specified as container. This command is different from createinstance() in that it does not attempt to establish any links between thenode and any class. If an instantiation is required, use createinstance() instead.
If samename is 1, the copy will have the same name as thenode.
If samename is 0, the newly created node's name will be thenode's name with a random number added to the end.
If inobject is 1, the copy will be created in the object data portion of the container. If the container does not have object data, the command does nothing.
If cached is 1, a pre-cached version of the node will be copied. This is generally faster.
If replace is 1, the copy will overwrite container, instead of being placed inside it.
If those parameters are not specified, they default to 0.
Example
createcopy(Model.find("Tools/FlowItemBin/7/1"), current)
createdelaytask
(obj dispatcher, num delaytime, num state, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to pause its current task for delaytime seconds. During the time that it is delayed, it will be in the state specified by state. The task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to pause its current task for delaytime seconds. During the time that it is delayed, it will be in the state specified by state. The task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createdelaytask(current.centerObjects[1], 25, SCHEDULED_DOWN, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createglobaltasksequence
(str name, obj dispatcher [, obj dp1, obj dp2, obj dp3, obj dp4, obj dp5])
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
Creates an instance of the named global task sequence with the given dynamic parameters 1-5 and dispatches it to the specified dispatcher. Returns a reference to the created global task sequence. Note that this does not dispatch the task sequence. You need to dispatch it yourself using dispatchtasksequence().
Creates an instance of the named global task sequence with the given dynamic parameters 1-5 and dispatches it to the specified dispatcher. Returns a reference to the created global task sequence. Note that this does not dispatch the task sequence. You need to dispatch it yourself using dispatchtasksequence().
Example
treenode ts = createglobaltasksequence("GlobalTS", current.centerObjects[1])
dispatchtasksequence(ts)
dispatchtasksequence(ts)
createinstance
(obj class, obj location)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.create() instead.
For developer use.
This command creates an instance of the class specified as class and places it in the object specified as location. The instance will be given a name that is the name of the class followed by a number. The instance will have all of the variables and attributes of class and it's superclasses. Nodes in the behavior node will not be copied into the instance, as they apply to all instances of the class. The object passed as class should be in the library. Generally, location is the model. The library and the model can be easily referenced using the library() and model() commands.
For developer use.
This command creates an instance of the class specified as class and places it in the object specified as location. The instance will be given a name that is the name of the class followed by a number. The instance will have all of the variables and attributes of class and it's superclasses. Nodes in the behavior node will not be copied into the instance, as they apply to all instances of the class. The object passed as class should be in the library. Generally, location is the model. The library and the model can be easily referenced using the library() and model() commands.
Example
createinstance(library().find("?Source"), model());
This creates an instance of the Source class in the model.
This creates an instance of the Source class in the model.
createloadtask
(obj taskexecuter, obj destination, obj flowitem, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to load flowitem. The object will not travel to the flowitem before loading it. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to load flowitem. The object will not travel to the flowitem before loading it. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createloadtask(current.centerObjects[1],current.centerObjects[2],item, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createsendmessagetask
(obj taskexecuter, obj receiver, num priority, num preempting , num param1, num param2, num param3)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence on the object specifies as dispatcher that causes it to send a message to the object specified as receiver. The OnMessage trigger of the receiving object will be executed when the message is sent. The values passed as param1, param2, and param3 will be available in the trigger function using the param() command. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence on the object specifies as dispatcher that causes it to send a message to the object specified as receiver. The OnMessage trigger of the receiving object will be executed when the message is sent. The values passed as param1, param2, and param3 will be available in the trigger function using the param() command. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createsendmessagetask(current, current.centerObjects[1],1,PREEMPT_NOT,5, 6, 7);
createstandardtask
(obj taskexecuter, obj origin, obj destination, obj flowitem, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to origin, load flowitem, travel to destination and unload flowitem. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to origin, load flowitem, travel to destination and unload flowitem. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createstandardtaskcurrent.centerObjects[1],current.centerObjects[2],current.centerObjects[3],item, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createtravelloadtask
(obj taskexecuter, obj destination, obj flowitem, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to destination, and load flowitem. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to destination, and load flowitem. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createtravelloadtask(current.centerObjects[1],current.centerObjects[2],item, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createtraveltask
(obj taskexecuter, obj destination, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to destination. It will travel until its front edge reaches destination. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to destination. It will travel until its front edge reaches destination. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createtraveltask( current.centerObjects[1], current.centerObjects[2], 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createtraveltolocandwaittask
(obj taskexecuter, num relativeloc, num x, num y, num z, num endspeed, num state, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to the point specified by xlox, y, and z. Once the object reaches that point, it will wait in the state specified as state until an endwaittask() command is issued to it. For a list of legal states, see setstate(). If relativeloc is 1, the specified point is relative to the origin of dispatcher. If relativeloc is 0, the specified point is the exact point in
the model that dispatcher will try to travel to. It will travel until its front edge reaches the specified point. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to the point specified by xlox, y, and z. Once the object reaches that point, it will wait in the state specified as state until an endwaittask() command is issued to it. For a list of legal states, see setstate(). If relativeloc is 1, the specified point is relative to the origin of dispatcher. If relativeloc is 0, the specified point is the exact point in
the model that dispatcher will try to travel to. It will travel until its front edge reaches the specified point. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createtraveltolocandwaittask(current.centerObjects[1], 1, 5.15, 2.5, 0, 0, STATE_IDLE, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createtraveltoloctask
(obj dispatcher, num relativeloc, num x, num y, num z, num endspeed, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to the point specified by xlox, y, and z. If relativeloc is 1, the specified point is relative to the origin of dispatcher. If relativeloc is 0, the specified point is the exact point in the model that dispatcher will try to travel to. It will travel until its front edge reaches the specified point. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to the point specified by xlox, y, and z. If relativeloc is 1, the specified point is relative to the origin of dispatcher. If relativeloc is 0, the specified point is the exact point in the model that dispatcher will try to travel to. It will travel until its front edge reaches the specified point. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createtraveltoloctask(current.centerObjects[1], 1, 5.15, 2.5, 0, 0, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createtravelunloadtask
(obj taskexecuter, obj destination, obj flowitem, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to destination, and unload flowitem. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to travel to destination, and unload flowitem. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createtravelunloadtask(current.centerObjects[1],current.centerObjects[2],item, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createunloadtask
(obj dispatcher, obj destination, obj flowitem, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to unload flowitem into the object specified by destination. The object will not travel to the location before unloading. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence for the object specified by dispatcher that causes it to unload flowitem into the object specified by destination. The object will not travel to the location before unloading. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createunloadtask(current.centerObjects[1],current.centerObjects[2],item, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
createwaittask
(obj taskexecuter, num state, num priority, num preempting)
Deprecated, use Process Flow instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead.
This command creates a task sequence on the object specified as dispatcher that causes the object to not perform new task sequences that it is given until it has been released. The object can be released with the endwaittask() command. The object will be in the state specified by state while it is waiting. For a list of possible states, see setstate() command. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
This command creates a task sequence on the object specified as dispatcher that causes the object to not perform new task sequences that it is given until it has been released. The object can be released with the endwaittask() command. The object will be in the state specified by state while it is waiting. For a list of possible states, see setstate() command. This task sequence will be given a priority of priority and a preempting value of preempting. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createwaittask(current.centerObjects[1], STATE_IDLE, 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
current
<no parentheses>
Description
This command is deprecated. This should not be used as a special command with the setcurrent command anymore. Instead, declare a treenode variable type as current, then use current in your code as any other variable type.
Example
treenode current = model().subnodes[3];
pt(current.name);
This sets the object that is ranked 3 in the model to current and prints its name to the output console.
pt(current.name);
This sets the object that is ranked 3 in the model to current and prints its name to the output console.
dbchangetable
(str tablename)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbchangetable("Inventory");
This closes the currently open table and opens a table called Inventory.
This closes the currently open table and opens a table called Inventory.
dbclose
()
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
if (current.donegatheringdata == 1)
dbclose();
If the label donegatheringdata on current is set to 1, the current database is closed.
dbclose();
If the label donegatheringdata on current is set to 1, the current database is closed.
dbexportnode
(obj tablenode, num startrow, num startcol, num numrows, num numcols)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
The starting row and column in the table are specified as well as how many rows and columns
to export.
The starting row and column in the table are specified as well as how many rows and columns
to export.
Example
dbexportnode(so(),1,1,4,5);
dbexporttable
(str tablename, num startrow, num startcol, num numrows, num numcols)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbexportnode("MyTable4",2,2,3,3);
dbgetfieldname
(num column)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
string ColName = dbgetfieldname(1);
This sets ColName to the name of the first column in the current database.
This sets ColName to the name of the first column in the current database.
dbgetmetrics
()
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbgetmetrics()
dbgetmode
()
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
if (dbgetmode() != DBMODE_CLOSED)
ColName = dbgetfieldname(1);
If the database is open, ColName is set to the name of the first column in the database.
ColName = dbgetfieldname(1);
If the database is open, ColName is set to the name of the first column in the database.
dbgetnumcols
()
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
for (int x=1; x<=dbgetnumcols(); x++)
Table("MyTable")[1][x] = stringtonum(dbgettablecell(1,x));
This copies the values from a column in the database to a column in a GlobalTable.
Table("MyTable")[1][x] = stringtonum(dbgettablecell(1,x));
This copies the values from a column in the database to a column in a GlobalTable.
dbgetnumrows
()
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
for (int x=1; x<=dbgetnumrows(); x++)
Table("MyTable")[x][1] = stringtonum(dbgettablecell(x,1));
This copies the values from a row in the database to a row in a GlobalTable.
Table("MyTable")[x][1] = stringtonum(dbgettablecell(x,1));
This copies the values from a row in the database to a row in a GlobalTable.
dbgettablecell
(num row, num col)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
double tablevalue = stringtonum(dbgettablecell(1,1));
This sets tablevalue to the number that is stored in the first row and first column of the database.
This sets tablevalue to the number that is stored in the first row and first column of the database.
dbgettablenum
(num row, num col)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
double val = dbgettablenum(2,3);
dbgettablestr
(num row, num col)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
string val = dbgettablenum(2,3);
dbimportnode
(obj tablenode, num startrow, num startcol, num numrows, num numcols)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbimportnode(so(),1,1,4,5);
dbimporttable
(str tablename, num startrow, num startcol, num numrows, num numcols)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbimportnode("MyTable4",2,2,3,3);
dbopen
(str databasename, str command {SQL string or Tablename}, num usetable [, num showlogin])
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbopen("itemdrive","timetable",1);
This opens a database with the alias "itemdrive" and opens the table called "timetable" in Table mode.
dbopen("warehouse","select * from inventory",0);
This opens a database with the alias "warehouse" and performs a SQL query on it. The database is open in SQL mode.
This opens a database with the alias "itemdrive" and opens the table called "timetable" in Table mode.
dbopen("warehouse","select * from inventory",0);
This opens a database with the alias "warehouse" and performs a SQL query on it. The database is open in SQL mode.
dbsettablecell
(num row, num col, str value)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
for (int x=1; x<= model().subnodes.length; x++)
dbsettablecell(x,1,model().subnodes[x].name);
This places the names of all of the objects in the model into the first column of the current database.
dbsettablecell(x,1,model().subnodes[x].name);
This places the names of all of the objects in the model into the first column of the current database.
dbsettablenum
(num row, num col, num val)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbsettablenum(2,3,56.5);
dbsettablestr
(num row, num col, str val)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbgettablestr(1,1,"John");
dbsqlquery
(str query[, num forwardOnlyCursor])
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbsqlquery("select processtime from timetable where type='1'");
This returns a new table based on the SQL query passed.
dbsqlquery("update timetable set processtime=type*2");
This updates the database based on the query passed.
This returns a new table based on the SQL query passed.
dbsqlquery("update timetable set processtime=type*2");
This updates the database based on the query passed.
dbusername
(str username, str password)
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbusername("user1","abc123XYZ");
This sets the username to "user1" and the password to "abc123XYZ". These values will be used to access a database the next time dbopen() is called.
dbusername("","");
This clears out the last set username and password. The next time dbopen() is called, the database will be accessed without a username or password.
This sets the username to "user1" and the password to "abc123XYZ". These values will be used to access a database the next time dbopen() is called.
dbusername("","");
This clears out the last set username and password. The next time dbopen() is called, the database will be accessed without a username or password.
dbviewtable
()
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbviewtable();
dbwritechanges
()
Deprecated. Use Database.Connection
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Database.Connection instead.
Example
dbwritechanges()
defaultdragconnection
(obj fromobject, obj toobject, char characterpressed)
Deprecated, use contextdragconnection()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use contextdragconnection() instead.
Either connects or disconnects ports between fromobject and toobject according to the specified characterpressed. This command mimics the keyboard and mouse combinations used to connect/disconnect object ports. For instance an 'A' would be as if the letter "A" were held down on the keyboard while click-dragging from the fromobject to the toobject. For 'A' and 'Q' it connects and disconnects output ports to input ports. For 'S' and 'W' it connects and disconnects central ports. Can only be used in C++, not flexscript.
Either connects or disconnects ports between fromobject and toobject according to the specified characterpressed. This command mimics the keyboard and mouse combinations used to connect/disconnect object ports. For instance an 'A' would be as if the letter "A" were held down on the keyboard while click-dragging from the fromobject to the toobject. For 'A' and 'Q' it connects and disconnects output ports to input ports. For 'S' and 'W' it connects and disconnects central ports. Can only be used in C++, not flexscript.
Example
defaultdragconnection(model().subnodes[count], model().subnodes[2], 'A')
degreestoradians
(num degrees)
deletetablecol
(str/num/node table, num column)
deletetablerow
(str/num/node table, num row)
dellabel
(obj object, str/num label)
Deprecated, use treenode.labels["LabelName"].destroy()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use treenode.labels["LableName"].destroy() instead.
Deletes the specified label from the node called "labels" on the specified object.
The specified label can either be the labelname as a string or the label's rank as a number.
If the label does not exist in that node, this command does nothing.
Deletes the specified label from the node called "labels" on the specified object.
The specified label can either be the labelname as a string or the label's rank as a number.
If the label does not exist in that node, this command does nothing.
Example
dellabel(current,"MyLabel")
destroyobject
(node thenode)
diffsign
(num value1, num value2)
div
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the / operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the / operator instead.
Division of value1 by value2. If value2 is zero, the calculation is aborted and zero is returned.
Division of value1 by value2. If value2 is zero, the calculation is aborted and zero is returned.
Example
div(10,2)
divide
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the / operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use / operator instead.
This is an alias for div().
This is an alias for div().
Example
divide(10,2)
dumpquery
(node dumpNode[, num asTable])
enablefullhistory
(num on/off)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Turns Full History collection on and off. If the parameter passed in is 1, Full History will be turned on. If it is 0, it will be turned off. This command should not be called directly. Instead, use the Enable Full History menu option to turn Full History on or off.
Example
enablefullhistory(1); // Turns Full History collection on
endwaittask
(obj taskexecuter)
Deprecated, use Process Flow or freeoperators()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Process Flow instead or the freeoperators() command instead.
This command releases the object specified as dispatcher from a wait task issued by the createwaittask(). Once the object is released, it will return to the state that it was previously in, and it will begin to perform any task sequences that are in its tasksequence queue.
This command releases the object specified as dispatcher from a wait task issued by the createwaittask(). Once the object is released, it will return to the state that it was previously in, and it will begin to perform any task sequences that are in its tasksequence queue.
Example
endwaittask(current.centerObjects[1]);
eq
(num/node value1, num/node value2)
Deprecated, use the == operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the == operator instead..
Example
excelexportnode
(node table, num startrow, num startcol, num numrows, num numcols [, num rowchar, num colchar])
Deprecated, use excelexporttable()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use excelexporttable() instead.
Example
excelexportnode(reftable("Table1"),1,1,5,3);
excelimportnode
(obj node, num startrow, num startcol, num numrows, num numcols [, num rowchar, num colchar])
Deprecated, use excelimporttable()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use excelimporttable() instead
Example
excelimportnode(so(),1,1,5,3);
excelmacro
(str macro)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. This command allows the user to send an Excel 4.0 macro command to Excel. This language is no longer maintained by Microsoft and may be removed from future versions of Excel.
Example
excelmacro("select(\"r1c1:r5c5\")");
This selects the section of the workbook beginning at row 1, column 1 to row 5, column 5.
This selects the section of the workbook beginning at row 1, column 1 to row 5, column 5.
excelrangeread
(str rangename[treenode target], num row, num col[, num numRows, num numCols, num flags])
Reads an Excel range and dumps it to a treenode
Description
This function is overloaded so that it has two functions depending on which arguments you pass in.
The first (where you pass in a string) is deprecated. Use excelrangereadnum() and excelrangereadstr() instead.
The second (where you pass in a treenode) will read a range in Excel and assign all of the data in that range to the target treenode. If the treenode has bundle data, the excel data will be set on the bundle. Otherwise, subnodes will be inserted under the target treenode that will have the Excel data set on them as either string or number data, in the same format as Global Tables.
The origin of the range is specified by the row and col passed in, and the second pair of numbers will specify the size of the range. If 0 is passed in for any one of these, Flexsim will automatically choose the boundary in that direction of the Excel range that has data.
Flags can be passed in to change exactly what is read from Excel. Those flags are EXCEL_DATA_AUTOMATIC, EXCEL_DATA_NUMBER, EXCEL_DATA_STRING, EXCEL_DATE_AS_NUM, EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS and EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS.
EXCEL_DATA_AUTOMATIC will assign string or number data based on what the datatype of the Excel cell is. This is the default behavior.
EXCEL_DATA_NUMBER will force all Excel data to be read as a number.
EXCEL_DATA_STRING will force all Excel data to be read as a string.
EXCEL_DATE_AS_NUM will read any Excel dates as numbers readable by Flexsim as dates. Otherwise, the data will come in as a string.
EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS will take the first row of data and use it as names for the table columns instead of data.
EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS will take the first column of data and use it as names for the table rows instead of data.
The second (where you pass in a treenode) will read a range in Excel and assign all of the data in that range to the target treenode. If the treenode has bundle data, the excel data will be set on the bundle. Otherwise, subnodes will be inserted under the target treenode that will have the Excel data set on them as either string or number data, in the same format as Global Tables.
The origin of the range is specified by the row and col passed in, and the second pair of numbers will specify the size of the range. If 0 is passed in for any one of these, Flexsim will automatically choose the boundary in that direction of the Excel range that has data.
Flags can be passed in to change exactly what is read from Excel. Those flags are EXCEL_DATA_AUTOMATIC, EXCEL_DATA_NUMBER, EXCEL_DATA_STRING, EXCEL_DATE_AS_NUM, EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS and EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS.
EXCEL_DATA_AUTOMATIC will assign string or number data based on what the datatype of the Excel cell is. This is the default behavior.
EXCEL_DATA_NUMBER will force all Excel data to be read as a number.
EXCEL_DATA_STRING will force all Excel data to be read as a string.
EXCEL_DATE_AS_NUM will read any Excel dates as numbers readable by Flexsim as dates. Otherwise, the data will come in as a string.
EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS will take the first row of data and use it as names for the table columns instead of data.
EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS will take the first column of data and use it as names for the table rows instead of data.
Example
treenode myTable = node ("Tools/GlobalTables/GlobalTable1>variables/data", model());
excelrangeread(myTable, 1, 1, 5, 0, EXCEL_DATA_AUTOMATIC | EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS);
This will read data from the active sheet starting at cell A1. It will read the first five rows, and read as many columns as have data in them. The first row will be used as names for the columns of the Global Table we're writing to. Therefore, if the Excel sheet has 10 columns with data in them, a total of 40 nodes will be inserted under the data variable of the Global Table. Each of those nodes will have the datatype of their corresponding Excel cell.
excelrangeread(myTable, 1, 1, 5, 0, EXCEL_DATA_AUTOMATIC | EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS);
This will read data from the active sheet starting at cell A1. It will read the first five rows, and read as many columns as have data in them. The first row will be used as names for the columns of the Global Table we're writing to. Therefore, if the Excel sheet has 10 columns with data in them, a total of 40 nodes will be inserted under the data variable of the Global Table. Each of those nodes will have the datatype of their corresponding Excel cell.
excelrangewrite
(treenode source, num row, num col, num flags)
Reads data from a source table node and writes it to the active Excel sheet
Description
This function will write all the of the data from the source table node to the active Excel sheet. If the treenode has bundle data,
this will read the bundle and write it to the sheet, otherwise it will look for child nodes with data on them, like a Global Table. The row and col passed in
specify where on the Excel sheet to begin writing the data. All of the data on the source node will always be written. Flags can be passed in to change the use
of headers. Those flags are EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS and EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS.
EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS will write any existing column headers as a separate row in the Excel table.
EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS will write any existing row headers as a separate column in the Excel table.
EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS will write any existing column headers as a separate row in the Excel table.
EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS will write any existing row headers as a separate column in the Excel table.
Example
treenode myTable = node("Tools/GlobalTables/GlobalTable1>variables/data", model());
excelrangewrite(myTable, 1, 1, EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS | EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS);
This will take all of the data in GlobalTable1 and write it to the active Excel sheet, starting at cell A1. Before it writes any of the actual data, there will be a row of column headers and column of row headers.
excelrangewrite(myTable, 1, 1, EXCEL_USE_ROWHEADERS | EXCEL_USE_COLUMNHEADERS);
This will take all of the data in GlobalTable1 and write it to the active Excel sheet, starting at cell A1. Before it writes any of the actual data, there will be a row of column headers and column of row headers.
excelread
(num row, num col)
Deprecated, use excelreadnum(), excelreadstr() or excelreadcell()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use excelreadnum(), excelreadstr() or excelreadcell() instead.
Example
excelwrite
(str data, num row, num col)
Deprecated, use excelwritenum() and excelwritestr()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use excelwritenum() and excelwritestr() instead.
Example
executetablecell
(str/node/num table, num row, num column)
Deprecated, use Table.executeCell() or the Table's [] operators
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Table.executeCell() or the Table class's [] operators instead.
Executes the table cell's text as Flexscript.
Executes the table cell's text as Flexscript.
Example
exp
(num value)
exportfullhistory
([str filename, num scenario, num replication])
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Writes to a database (.mdb file) the Full History data that was collected during a run. If a file name is passed to this command, that name willbe used for the database. If no file name is passed in, the user will be prompted for a file to save the data to. If the file (either passed in or selected from a dialog) does not exist, it will be created.
Example
exportfullhistory("myrundata.mdb");
fabs
(num value)
factorial
(num value)
familycreate
(obj familycontainer, str name)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Group class instead.
Create a new family (a list of nodes used for organizing relational information).
Create a new family (a list of nodes used for organizing relational information).
Example
familycreate(item,"family1")
familydelete
(obj familycontainer, str name)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Group class instead.
Delete a family.
Delete a family.
Example
familydelete(item,"family1")
familymember
(obj familycontainer, str name, num index)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Group class instead.
Returns a pointer to a member of the specified family.
Returns a pointer to a member of the specified family.
Example
familymember(item,"family1",2)
familymemberadd
(obj familycontainer, str name, obj member)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Group class instead.
Adds a new family member to the specified familycontainer.
Adds a new family member to the specified familycontainer.
Example
familymemberadd(item,"family1",item.subnodes[1])
familymemberdel
(obj familycontainer, str name, obj member)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Group class instead.
Removes a family member from the specified familycontainer.
Removes a family member from the specified familycontainer.
Example
familymemberdel(item,"family1",item.subnodes[2])
familymemberqty
(obj familycontainer, str name)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Group class instead.
Returns the size of the specified family.
Returns the size of the specified family.
Example
familymemberqty(item,"family1")
fillarray
(array thearray, num/treenode/string val1[, num/treenode/string val2, ...])
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Array class to construct the array using an array literal: Array arr = [1, 2, 3];
Fill a local array with values.
Fill a local array with values.
Example
findmatch
(num nr, num matchexpression[, returnexpression = count, num reverseorder = 0])
Description
Performs a matching test a defined number of times, and when a match is found, returns a user-definable value
associated with that match. Within the match expression and return expression, "count" can be used to determine
which iteration your are on in the check. This can be used to search in a list of things for a matching item or criterion. If returnexpression is not included in the call, then findmatch() will return the count associated
with the matching expression. If no matches are found, findmatch() will return 0. If reverseorder is 1, then
it will go backwards, assigning count to nr first, then nr - 1, etc. down to 1. If
returnexpression is left out, then findmatch will return the count associated with the
found match.
Example
int portNr = findmatch(current.outObjects.length, current.outObjects[count].subnodes.length < 5);
This example will return the output port number that corresponds to the first object it finds connected to current's output ports that has a content less than 5.
treenode object = findmatch(current.outObjects.length, current.outObjects[count].subnodes.length < 5, current.outObjects[count]);
This example is similar to the previous example except it will return the object itself instead of the associated port number.
int item2Rank = findmatch(current.subnodes.length, current.subnodes[count].type == 2);
This example will return the rank number of the first item found in current's queue that has an item type of 2.
This example will return the output port number that corresponds to the first object it finds connected to current's output ports that has a content less than 5.
treenode object = findmatch(current.outObjects.length, current.outObjects[count].subnodes.length < 5, current.outObjects[count]);
This example is similar to the previous example except it will return the object itself instead of the associated port number.
int item2Rank = findmatch(current.subnodes.length, current.subnodes[count].type == 2);
This example will return the rank number of the first item found in current's queue that has an item type of 2.
findmax
(num nr, num valueexpression[, returnexpression = maxvalue, num criterion = true, num reverseorder = 0])
Description
Iteratively evaluates an expression, and then returns the maximum value found, or a user-definable return value
associated with that maximum value. Within the value expression, return expression and criterion, "count" can be used to determine
which iteration you are on in the check. If the return expression is not defined, the maximum value found will be returned.
Additionally, you can specify a criterion to filter out values as invalid. If criterion is defined and nothing meets the
criterion, 0 will be returned.
Example
double latestCreation = findmax(current.subnodes.length, getcreationtime(current.subnodes[count]));
This example will return the maximum creation time of all items in current.
int largestQueuePortNr = findmax(current.inObjects.length, current.inObjects[count].subnodes.length;
This example will return the input port number associated with the object with the largest queue of items.
int largestQueuePortNr = findmax(current.inObjects.length, current.inObjects[count].subnodes.length, count, getitemstate(current.inObjects[count].first) == FR_STATE_READY);
This example is the same as the previous example, but additionally in includes a criterion that the first item in the upstream object must also have been released.
This example will return the maximum creation time of all items in current.
int largestQueuePortNr = findmax(current.inObjects.length, current.inObjects[count].subnodes.length;
This example will return the input port number associated with the object with the largest queue of items.
int largestQueuePortNr = findmax(current.inObjects.length, current.inObjects[count].subnodes.length, count, getitemstate(current.inObjects[count].first) == FR_STATE_READY);
This example is the same as the previous example, but additionally in includes a criterion that the first item in the upstream object must also have been released.
findmin
(num nr, num valueexpression[, returnexpression = maxvalue, num criterion = true, num reverseorder = 0])
Description
Iteratively evaluates an expression, and then returns the minimum value found, or a user-definable return value
associated with that minimum value. findmin() is the same as findmax() except it finds the minimum value instead
of the maximum value. For more information, refer to the documentation for findmax().
Example
Refer to findmax()
first
(node container)
floor
(num num)
fmod
(num value1, num value2)
forobjecthighlightedin
(obj view) { }
Description
This command is deprecated. Use selectedobject() instead.
Iterate on the node that is both selected (red) and highlighted (yellow) in the selected view. Reference the selected and highlighted node by using "a" within the loop.
Iterate on the node that is both selected (red) and highlighted (yellow) in the selected view. Reference the selected and highlighted node by using "a" within the loop.
Example
forobjecthighlightedin(sv())
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of the selected, highlighted node in the first level of the model.
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of the selected, highlighted node in the first level of the model.
forobjectlayerunder
(node container) { }
Description
This command is deprecated. Use for() or while() commands instead.
Execute a block of code for each node that is in the tree layer directly under the node specified as container. To access the node that is currently active in the loop, the "a" command is used. The forobjectlayerunder() command can only be used in flexscript, not C++.
Execute a block of code for each node that is in the tree layer directly under the node specified as container. To access the node that is currently active in the loop, the "a" command is used. The forobjectlayerunder() command can only be used in flexscript, not C++.
Example
forobjectlayerunder(model())
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of every object in the first level of the model.
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of every object in the first level of the model.
forobjectsbefore
(node thenode) { }
Description
This command is deprecated. Use for() or while() commands instead.
Execute a block of code for each node that is in the same layer and has a rank value less than or equal to the rank of the object specified as thenode. To access the node that is currently active in the loop, the "a" command is used. The forobjectsbefore() command can only be used in flexscript, not C++.
Execute a block of code for each node that is in the same layer and has a rank value less than or equal to the rank of the object specified as thenode. To access the node that is currently active in the loop, the "a" command is used. The forobjectsbefore() command can only be used in flexscript, not C++.
Example
forobjectsbefore(model.subnodes[5]))
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of the first 5 objects in the model.
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of the first 5 objects in the model.
forobjectsbehind
(node thenode) { }
Description
This command is deprecated. Use for() or while() commands instead.
Execute a block of code for each node that is in the same layer and has a rank value greater than the rank of the object specified as thenode. To access the node that is currently active in the loop, the "a" command is used. The forobjectsbehind() command can only be used in flexscript, not C++.
Execute a block of code for each node that is in the same layer and has a rank value greater than the rank of the object specified as thenode. To access the node that is currently active in the loop, the "a" command is used. The forobjectsbehind() command can only be used in flexscript, not C++.
Example
forobjectsbehind(model.subnodes[5])
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of the objects in the model starting with the sixth one.
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of the objects in the model starting with the sixth one.
forobjectselectionset
(node container) { }
Description
This command is deprecated. Instead use:
for(int i =1; i<= container.subnodes.length; i++)
{
if(switch_selected(container.subnodes[i]))
{
pt(container.subnodes[i].name); pr();
}
}
The block following the command will be iterated upon once for each selected object in the container. The value of the "a" command will return the pointer to the object being iterated upon. This command is not available in C++.
for(int i =1; i<= container.subnodes.length; i++)
{
if(switch_selected(container.subnodes[i]))
{
pt(container.subnodes[i].name); pr();
}
}
The block following the command will be iterated upon once for each selected object in the container. The value of the "a" command will return the pointer to the object being iterated upon. This command is not available in C++.
Example
forobjectselectionset(library()) { pt(a.name); pr(); }
This prints to the outputconsole the name of every object currently selected in the library tree.
This prints to the outputconsole the name of every object currently selected in the library tree.
frac
(num value)
ge
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the >= operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the >= operator instead.
Example
get
(node thenode)
getcolorcomponent
(obj object, num index)
getdatatype
(thing)
getinput
(obj involved)
getitemtype
(obj object)
Deprecated, use labels
Description
This command is deprecated. Use labels instead.
Returns the itemtype value of a flow item.
Returns the itemtype value of a flow item.
Example
getitemtype(so())
getlabel
(obj node, str/num label)
Deprecated, use treenode.LabelName
Description
This command is deprecated. Use treenode.labelProperties instead.
Gets the value of an object's label.
Gets the value of an object's label.
Example
getlabelnum
(obj node, str/num label)
Deprecated, use treenode.LabelName
Description
This command is deprecated. Use treenode.labelProperties instead.
Gets the number value of an object's label.
Gets the number value of an object's label.
Example
getlabelstr
(obj node, str/num label)
Deprecated, use treenode.LabelName
Description
This command is deprecated. Use treenode.labelProperties instead.
Gets the string value of an object's label
Gets the string value of an object's label
Example
getmodelunitnum
(num querytype)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use getmodelunit() instead.
Example
getmodelunitstr
(num querytype)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use getmodelunit() instead.
Returns a name or abbreviation of the current model's units.
Returns a name or abbreviation of the current model's units.
Example
getmoverecord
(num record)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Returns a movement record that has been recorded for the Full History Report. A movement record is created every time a flowitem moves from one object to another if Full History is enabled. The parameter passed to this function is the number of the record (beginning at 1) that the user wishes to retrieve. If this command is called in C++, the return value is a MoveRecord*. If this command is called in FlexScript, the return value can be assigned to an int.
Example
See the example for getnummoverecords().
getmoverecordvalue
(num record, num value)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Returns one of the values from the movement record that is passed in as the first parameter to the function. This record is the return value from a call to getmoverecord(). The value passed to this function as the second parameter indicates which value from the movement record the user wishes to retrieve:
0 = The record ID. This is the record\'s row number in the movement table.
1 = The ItemID of the flowitem whose movement is recorded by the record.
2 = The time the flowitem moved.
3 = The object that the flowitem moved from. This is returned as an int and should be converted to a treenode using tonode().
4 = The object that the flowitem moved to. This is returned as an int and should be converted to a treenode using tonode();
5 = The itemtype of the flowitem at the time it moved.
0 = The record ID. This is the record\'s row number in the movement table.
1 = The ItemID of the flowitem whose movement is recorded by the record.
2 = The time the flowitem moved.
3 = The object that the flowitem moved from. This is returned as an int and should be converted to a treenode using tonode().
4 = The object that the flowitem moved to. This is returned as an int and should be converted to a treenode using tonode();
5 = The itemtype of the flowitem at the time it moved.
Example
See the example for getnummoverecords().
getname
(node thenode)
getnodename
(node thenode)
getnodenum
(node thenode)
getnodestr
(node thenode)
getnummoverecords
()
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Returns the number of movement records that have been collected for the Full History Report. The records are deleted when a model is reset, so this will return 0 before a model run. If Full History is not enabled, this will return 0.
Example
// Print the move records that have been recorded
for (int rec = 1; rec <= getnummoverecords(); rec++)
{
int record = getmoverecord(rec);
pd(getmoverecordvalue(record,0)); pt(" ");
pd(getmoverecordvalue(record,1)); pt(" ");
pf(getmoverecordvalue(record,2)); pt(" ");
pt(getmoverecordvalue(record,3).name); pt(" ");
pt(getmoverecordvalue(record,4).name); pt(" ");
pd(getmoverecordvalue(record,5)); pt(" ");
}
for (int rec = 1; rec <= getnummoverecords(); rec++)
{
int record = getmoverecord(rec);
pd(getmoverecordvalue(record,0)); pt(" ");
pd(getmoverecordvalue(record,1)); pt(" ");
pf(getmoverecordvalue(record,2)); pt(" ");
pt(getmoverecordvalue(record,3).name); pt(" ");
pt(getmoverecordvalue(record,4).name); pt(" ");
pd(getmoverecordvalue(record,5)); pt(" ");
}
getnumstaterecords
()
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Returns the number of state change records that have been collected for the Full History Report. The records are deleted when a model is reset, so this will return 0 before a model run. If Full History is not enabled, this will return 0.
Example
// Print the state change records that have been recorded
for (int rec = 1; rec <= getnumstaterecords(); rec++)
{
int record = getstaterecord(rec);
pd(getstaterecordvalue(record,0)); pt(" ");
pf(getstaterecordvalue(record,1)); pt(" ");
pd(getstaterecordvalue(record,2)); pt(" ");
pt(getstaterecordvalue(record,3).name); pr();
}
for (int rec = 1; rec <= getnumstaterecords(); rec++)
{
int record = getstaterecord(rec);
pd(getstaterecordvalue(record,0)); pt(" ");
pf(getstaterecordvalue(record,1)); pt(" ");
pd(getstaterecordvalue(record,2)); pt(" ");
pt(getstaterecordvalue(record,3).name); pr();
}
getobjectimageindex
(obj object)
Deprecated, do not use.
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Returns the index number of the bmp or jpeg image currently assigned to the base of the object.
Returns the index number of the bmp or jpeg image currently assigned to the base of the object.
Example
getobjectimageindex(item);
getquerycolcount
()
getquerymatchcount
()
getquerymatchtablerow
(str/num table, num matchRow)
Deprecated, use Table.query()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Table.query() instead.
Returns the source table's row number associated with a matched row in the last query() result.
table - If a string, it is the name of the table as defined in the FROM statement. If you used an alias, it should be the table's alias. If a number, it should be the 1-based index of the table in the FROM statement. If there is only one table in the query, this should be 1. For multiple tables, the first table in the FROM is 1, the second is 2, etc.
matchRow - The 1-based row of the result table of the query.
Note that this command will not work if you use aggregator functions such as MIN(), MAX(), AVG(), etc. in the SELECT clause. When aggregators are used, this command just returns the number of rows in the source table.
Returns the source table's row number associated with a matched row in the last query() result.
table - If a string, it is the name of the table as defined in the FROM statement. If you used an alias, it should be the table's alias. If a number, it should be the 1-based index of the table in the FROM statement. If there is only one table in the query, this should be 1. For multiple tables, the first table in the FROM is 1, the second is 2, etc.
matchRow - The 1-based row of the result table of the query.
Note that this command will not work if you use aggregator functions such as MIN(), MAX(), AVG(), etc. in the SELECT clause. When aggregators are used, this command just returns the number of rows in the source table.
Example
getqueryvalue
(num row, num/str col)
Deprecated, use Table.query()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Table.query() instead.
Returns a value in the result table for the last call to query()
row - The 1-based row number of the result table
col - The 1-based column number of the result table, or the name of the result column. If you have defined aliases in the select statement, the column name should be the alias.
Returns a value in the result table for the last call to query()
row - The 1-based row number of the result table
col - The 1-based column number of the result table, or the name of the result column. If you have defined aliases in the select statement, the column name should be the alias.
Example
getrank
(node thenode)
gets
(node thenode)
getstatenum
(obj object [, num stateprofilenr])
getstaterecord
(num record)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Returns a state change record that has been recorded for the Full History Report. A state change record is created every time an object changes state if Full History is enabled. The parameter passed to this function is the number of the record (beginning at 1) that the user wishes to retrieve. If this command is called in C++, the return value is a StateRecord*. If this command is called in FlexScript, the return value can be assigned to an int.
Example
See the example for getnumstaterecords().
getstaterecordvalue
(num record, num value)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Returns one of the values from the state change record that is passed in as the first parameter to the function. This record is the return value from a call to getstaterecord(). The value passed to this function as the second parameter indicates which value from the state change record the user wishes to retrieve:
0 = The record ID. This is the record\'s row number in the movement table.
1 = The time of the state change.
2 = The state that the object changed to.
3 = The object that changed state. This is returned as an int and should be converted to a treenode using tonode().
0 = The record ID. This is the record\'s row number in the movement table.
1 = The time of the state change.
2 = The state that the object changed to.
3 = The object that changed state. This is returned as an int and should be converted to a treenode using tonode().
Example
See the example for getnumstaterecords().
getstatestr
(obj object)
gettablecell
(str/node/num table, num row, num column)
gettablecols
(str/node/num table)
gettableheader
(string/num/node table, num row/col, num rowcolnr)
Deprecated, use Table.getColHeader() or Table.getRowHeader()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Table.getColHeader()
or Table.getRowHeader() instead.
Gets the value of the header field of a table.
Gets the value of the header field of a table.
Example
gettablenum
(str/node/num table, num row, num col)
Deprecated, use the Table's [] operators
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Table class's [] operators instead.
Gets the number value in a table cell.
Gets the number value in a table cell.
Example
gettablerows
(str/node/num table)
gettablestr
(str/node/num table, num row, num col)
Deprecated, use the Table's [] operators
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Table class's [] operators instead.
Gets the text value in a table cell.
Gets the text value in a table cell.
Example
gettrackedvariable
(str/node trackedvar [, num valtype] )
Deprecated, use Tracked Variable class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TrackedVariable class instead.
Example
getvartype
(var)
glBegin
(num primitive)
Deprecated, use the mesh() API
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use. Use the mesh() API instead.
Example
glColor3d
(num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1})
Deprecated, use fglColor()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglColor() instead.
Example
glColor4d
(num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1}, num alpha {0-1})
Deprecated, use fglColor()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglColor() instead.
Example
glDisable
(num setting)
Deprecated, use fglDisable()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglDisable() instead.
Example
glEnable
(num setting)
Deprecated, use fglEnable()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglEnable() instead.
Example
glEnd
()
Deprecated, use the mesh() API
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use. Use the mesh() API instead.
Example
glLoadIdentity
()
Deprecated, use fglLoadIdentity()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglLoadIdentity() instead.
Example
glMatrixMode
(num mode)
Deprecated, use fglMatrixMode()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglMatrixMode() instead.
Example
glNormal3d
(num x, num y, num z)
Deprecated, use fglNormal()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglNormal() instead.
Example
glNormal3d(1,0,0);
globallist
(str listName)
Deprecated, use List("GlobalListName")
Description
This command is deprecated. Use List("GlobalListName") instead.
References a global list by name.
References a global list by name.
Example
glPopAttrib
()
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
glPopMatrix
()
Deprecated, use fglPopMatrix()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglPopMatrix() instead.
Example
glPushAttrib
(num attribsetting)
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
glPushMatrix
()
Deprecated, use fglPushMatrix()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglPushMatrix() instead.
Example
glRotated
(num degrees, num x, num y, num z)
Deprecated, use fglRotate()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglRotate() instead.
Example
glScaled
(num x, num y, num z)
Deprecated, use fglScale()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglScale() instead.
Example
glTexCoord2d
(num x 0-1, num y 0-1)
Deprecated, use the mesh() API
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use. Use the mesh() API instead.
Example
glTranslated
(num x, num y, num z)
Deprecated, use fglTranslate()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglTranslate() instead.
Example
glVertex3d
(num x, num y, num z)
Deprecated, use the mesh() API
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use. Use the mesh() API instead.
Example
groupaddmember
(str group, obj member)
groupmember
(str group, num member)
Deprecated, use Group[]
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Group[] instead.
Gets a reference to a group member.
Gets a reference to a group member.
Example
groupnummembers
(str group)
groupremovemember
(str group, num/obj member)
Deprecated, use Group.removeMember()
Description
Example
gt
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the > operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the > operator instead..
Example
helpcommands
(node destnode, num what, str command)
Description
For developer use. Used to get information about a command. Enter the command name in parameter 3.
The return value will be copied into the string data of destnode.
"what" defines what information is needed, as follows:
1 - returns the xml fragment string that contains the documentation for that command
"what" defines what information is needed, as follows:
1 - returns the xml fragment string that contains the documentation for that command
Example
helpcommands(
hidelabel
(obj object[, num off/on])
Deprecated, use switch_hidelabel()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use switch_hidelabel() instead.
This command sets the specified object to show or hide its name and basic statistics on the screen. A value of 1 is show and a value of 0 is hide. If the name and statistics are hidden for an object, they will not be visible in any view window. View windows also have an attribute that controls this connector display of all objects in the view.
This command sets the specified object to show or hide its name and basic statistics on the screen. A value of 1 is show and a value of 0 is hide. If the name and statistics are hidden for an object, they will not be visible in any view window. View windows also have an attribute that controls this connector display of all objects in the view.
Example
hidelabel(current,0);
This sets the object referenced by current so that its name and statistics will not be drawn.
This sets the object referenced by current so that its name and statistics will not be drawn.
hideports
(obj object[, num off/on])
Deprecated, use switch_hideconnectors()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use switch_hideconnectors() instead.
This command sets the specified object to show or hide its ports and connections. A value of 1 is show and a value of 0 is hide. If the ports and connections are hidden, they will not be visible in any view window.
This command sets the specified object to show or hide its ports and connections. A value of 1 is show and a value of 0 is hide. If the ports and connections are hidden, they will not be visible in any view window.
Example
hideports(current,1);
This sets the current object to show its ports and connections in all view windows.
This sets the current object to show its ports and connections in all view windows.
inc
(node thenode, num amount)
Deprecated, use += operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use += operator instead. myNode.value += 2;
Increments the value of a node by a defined amount.
Increments the value of a node by a defined amount.
Example
inc(current.mylabel,1)
inittrackedvariable
(node theNode, num type[, num startValue, num flags])
Deprecated, use Tracked Variable class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TrackedVariable class instead.
Example
inobject
(obj object, num inputportnum)
installpackage
(str path+filename)
Deprecated, use user libraries
Description
This command is deprecated. Use user libraries instead.
Install a service pack (.fpk).
Install a service pack (.fpk).
Example
installpackage("C:/mypak.fpk")
item
<no parentheses>
Description
This command is deprecated. This should not be used as a special command with the setitem command anymore. Instead, declare a treenode variable type as item, then use item in your code as any other variable type.
Example
treenode item = model().subnodes[3];
pt(item.name);
This sets the object that is ranked 3 in the model to item and prints its name to the output console.
pt(item.name);
This sets the object that is ranked 3 in the model to item and prints its name to the output console.
iterate
(num start, num end, num step) {}
Deprecated, use for() or while() commands
Description
This command is deprecated. Use for() or while() commands instead.
Repeatedly execute the following block {} with counter value traversing from start to end being incremented by step. The count command can be used to access the current counter value on each iteration. The return value of count will depend on which iteration is currently being executed.
Repeatedly execute the following block {} with counter value traversing from start to end being incremented by step. The count command can be used to access the current counter value on each iteration. The return value of count will depend on which iteration is currently being executed.
Example
iterate(1,9,2)
{
pd(count);pr();
}
Prints the following numbers to the outputconsole: 1,3,5,7,9
{
pd(count);pr();
}
Prints the following numbers to the outputconsole: 1,3,5,7,9
label
(obj object, str/num label)
last
(node container)
le
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the <= operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the <= operator instead.
Example
listbackorders
(obj list[, var partitionId])
Deprecated, use List.backOrders()
Description
Example
listentries
(obj list[, var partitionId])
listinlist
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Array class instead.
Index of occurrence of value in list. The list, of length qty, is searched and the position in the list of the value val is returned by this function.
Index of occurrence of value in list. The list, of length qty, is searched and the position in the list of the value val is returned by this function.
Example
listinlist(5,3,2,1,2,3,4)
This returns the index number 4 because 3 is the fourth number in the list of 5 numbers.
This returns the index number 4 because 3 is the fourth number in the list of 5 numbers.
listmax
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Array class instead.
Index of highest value. The list, of length qty, is searched and the position in the list of the highest value is returned by this function.
Index of highest value. The list, of length qty, is searched and the position in the list of the highest value is returned by this function.
Example
listmax(5,2,1,2,3,4)
This returns a 5 because 4 is the largest value and it is fifth in the list of five numbers.
This returns a 5 because 4 is the largest value and it is fifth in the list of five numbers.
listmaximum
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Array class instead.
Highest value. The list, of length qty, is searched and the value of the highest value is returned by this function.
Highest value. The list, of length qty, is searched and the value of the highest value is returned by this function.
Example
listmaximum(5,2,1,2,3,4)
This returns a 4 because it is the highest value in the list.
This returns a 4 because it is the highest value in the list.
listmean
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Array class instead.
Average of values. The mean of the values in the list, of length qty, is returned by this function.
Average of values. The mean of the values in the list, of length qty, is returned by this function.
Example
listmean(5,2,1,2,3,4)
This returns 2.5.
This returns 2.5.
listmin
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Array class instead.
Index of lowest value. The list, of length qty, is searched and the position in the list of the lowest value is returned by this function.
Index of lowest value. The list, of length qty, is searched and the position in the list of the lowest value is returned by this function.
Example
listmin(5,2,1,2,3,4)
This returns 2 because 1 is the lowest value and it is second in the list.
This returns 2 because 1 is the lowest value and it is second in the list.
listminimum
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Array class instead.
Lowest value. The list, of length qty, is searched and the value of the lowest value is returned by this function.
Lowest value. The list, of length qty, is searched and the value of the lowest value is returned by this function.
Example
listminimum(5,2,1,2,3,4)
This returns 1 because that is the lowest value in the list.
This returns 1 because that is the lowest value in the list.
listmul
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the * operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the * operator instead.
Product of list. The product of all the values in the list, of length qty, is returned by this function.
Product of list. The product of all the values in the list, of length qty, is returned by this function.
Example
listmul(5,2,1,2,3,4)
This returns the value 48.
This returns the value 48.
listpull
(str/obj list, str/node query, num requestNum [, num requireNum, str/node/num puller, str/node/num partitionId, num flags])
listpush
(str/obj list [, str/node/num pushVal, str/node/num partitionId, ...])
listremove
(obj entryOrBackOrder)
Deprecated, use List.backOrders()[backOrderNum].remove() or List.entries()[enterNum].remove()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use List.backOrders()[backOrderNum].remove()
or List.entries()[entryNum].remove() instead.
Removes an entry or back order from its owning list.
Removes an entry or back order from its owning list.
Example
listsub
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the - operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the - operator instead.
Subtraction of list. The list, of length qty, is traversed and the first value has all subsequent values subtracted from it and then is returned by this function.
Subtraction of list. The list, of length qty, is traversed and the first value has all subsequent values subtracted from it and then is returned by this function.
Example
listsub(5,2,1,2,3,4)
listsum
(num qty, num val [, num a,...])
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the + operator instead.
Sum of values. The sum of all the values in the list, of length qty, is returned by this function.
Sum of values. The sum of all the values in the list, of length qty, is returned by this function.
Example
listsum(5,2,1,2,3,4)
loadsound
(str path+filename)
Deprecated, use soundload()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use soundload() instead.
A sound file on disk will be loaded into FlexSim and recorded in the Media List. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded sounds. Each sound has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the loaded sound. The sound must be a .wav file.
A sound file on disk will be loaded into FlexSim and recorded in the Media List. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded sounds. Each sound has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the loaded sound. The sound must be a .wav file.
Example
int applauseindex = loadsound("c:/My Music/APPLAUSE.WAV");
local
(num index)
Deprecated, use local variables
Description
This command is deprecated. Use local variables like treenode, int, double, string instead.
Gets a reference to an indexed local variable as a treenode. You must use localarray() to define how many local variables are used and what data type they should have. Can only be used in flexscript.
Gets a reference to an indexed local variable as a treenode. You must use localarray() to define how many local variables are used and what data type they should have. Can only be used in flexscript.
Example
setnodenum(local(1),4);
Sets the 1st variable in the localarray to 4.
Sets the 1st variable in the localarray to 4.
localarray
(num qty[, num datatype])
Deprecated, use Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Array class instead.
Allocate general purpose local array with the given quantity of local variables.
Type can be: 1 = num, 2 = str, 3 = coupling, 4 = obj. May only be used in flexscript.
Allocate general purpose local array with the given quantity of local variables.
Type can be: 1 = num, 2 = str, 3 = coupling, 4 = obj. May only be used in flexscript.
Example
localarray(1,4)
log
(num value)
log10
(num value)
lognormal
(num location, num normalmean, num normalstdev[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a lognormal distribution
Description
lognormal() and lognormal2() are similar functions, but with different parameter definitions. lognormal() uses parameter definitions as defined on wikipedia and other sites. lognormal2() uses parameters as defined in the latest versions of Expertfit. Essentially, the parameters can be converted as follows:
lognormal( location, normalmean, normalstdev ) = lognormal2( location, Math.exp( normalmean ), normalstdev )
lognormal2( location, scale, shape ) = lognormal( location, Math.log( scale ), shape ) (Math.exp(x) is e raised to the x power, and Math.log(x) is the natural logarithm of x.)
Please make sure you use the right distribution. Using the wrong distribution could result in bad simulation results.
lognormal( location, normalmean, normalstdev, stream ) is a continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
location : ( - ∞, ∞ )
normalmean such that ( Math.exp( normalmean ) > 0 )
normalstdev such that ( normalstdev > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( location , ∞ )
mean = location + Math.exp( normalmean + normalstdev²⁄ 2)
variance = Math.exp( 2*normalmean + normalstdev² ) [ Math.exp( normalstdev² ) − 1 ]
Probability Density Functions:
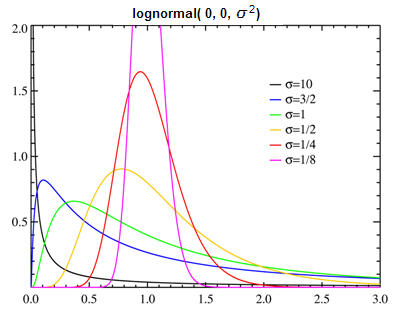
Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to perform some task, and to model quantities that are the product of a large number of other quantities. It can also be used as a rough model in the absence of data.
Comments:
The probability density for the lognormal distribution takes on shapes similar to gamma( normalstdev, normalmean ) and weibull( normalstdev, normalmean ) densities for normalstdev > 1, but can have a large spike close to x=0 that is often useful.
lognormal( location, normalmean, normalstdev ) = lognormal2( location, Math.exp( normalmean ), normalstdev )
lognormal2( location, scale, shape ) = lognormal( location, Math.log( scale ), shape ) (Math.exp(x) is e raised to the x power, and Math.log(x) is the natural logarithm of x.)
Please make sure you use the right distribution. Using the wrong distribution could result in bad simulation results.
lognormal( location, normalmean, normalstdev, stream ) is a continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
location : ( - ∞, ∞ )
normalmean such that ( Math.exp( normalmean ) > 0 )
normalstdev such that ( normalstdev > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( location , ∞ )
mean = location + Math.exp( normalmean + normalstdev²⁄ 2)
variance = Math.exp( 2*normalmean + normalstdev² ) [ Math.exp( normalstdev² ) − 1 ]
Probability Density Functions:

Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to perform some task, and to model quantities that are the product of a large number of other quantities. It can also be used as a rough model in the absence of data.
Comments:
The probability density for the lognormal distribution takes on shapes similar to gamma( normalstdev, normalmean ) and weibull( normalstdev, normalmean ) densities for normalstdev > 1, but can have a large spike close to x=0 that is often useful.
Example
lognormalmeanstdev
(num mean, num stdev[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a lognormal distribution
Description
This command is an alternative to the lognormal2 command, used in the absence of data. You can specify the
mean and standard deviation, and the command will calculate from those parameters the proper location, scale, and shape
parameters for the lognormal2 command, and return a sample from that distribution. Note that the shape of the distribution
is pre-defined to be a bell-shaped curve with a reasonably long right tail. Hence this command isn't as flexible as the
lognormal2 command. This command, similar to the triangular distribution, should be used in the absence of
data, where you know the mean and standard deviation of the distribution, and you assume that the distribution is right-skewed
(it has a longer right tail), but you do not have a real data set to fit to a distribution. Refer to lognormal2
for more information. Relating to the diagram describing the lognormal2 distribution, the lognormalmeanstdev command uses a
normalstdev/shape value of 0.75 to define its shape. Note that since the shape of the
distribution is hard-set, depending on the mean and standard deviation values, this may return a negative value.
Example
double cycletime = lognormalmeanstdev(10, 2);
This example will return a random value that follows a right-skewed lognormal distribution with a mean of 10 and standard deviation of 2.
This example will return a random value that follows a right-skewed lognormal distribution with a mean of 10 and standard deviation of 2.
lt
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the < operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the < operator instead.
Example
main
()
Deprecated, use maintree()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use maintree() instead.
Get the main tree node. This is one of the two primary databases of FlexSim. Also called the "Project Tree". The other primary database is the views tree node also called the "View Layout Tree"
Get the main tree node. This is one of the two primary databases of FlexSim. Also called the "Project Tree". The other primary database is the views tree node also called the "View Layout Tree"
Example
main()
makearray
(num qty)
Deprecated, use the Array class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Array(qty) instead. Array array = Array(4);
Initializes a local array.
Initializes a local array.
Example
max
(num value1, num value2)
maxof
(num value1, num value2)
min
(num value1, num value2)
minof
(num value1, num value2)
module
(num type, node libnode)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the DLL functionality provided with version 4 instead.
Used with dll plugins. The type can be:
MOD_LOAD (1)
MOD_UNLOAD (2)
MOD_GETFUNCTION (3)
MOD_RUNFUNCTION (4)
Used with dll plugins. The type can be:
MOD_LOAD (1)
MOD_UNLOAD (2)
MOD_GETFUNCTION (3)
MOD_RUNFUNCTION (4)
Example
module(MOD_UNLOAD,main.find("project/exec/dll/1"))
movetablecol
(str/num/node table, num column, num newcolumn)
movetablerow
(str/num/node table, num row, num newrow)
mul
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the * operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the * operator instead.
Product of a and b. This returns the result of the arithmetic expression value1*value2.
Product of a and b. This returns the result of the arithmetic expression value1*value2.
Example
double product = mul(3,4);
multisorttable
(str/node/num table, num col1[, num col2, num col3, ...])
ncols
(node thenode)
ne
(num/node value1, num/node value2)
Deprecated, use the != operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the != operator instead.
Example
next
(obj object)
node
(str relativepath[, obj startnode])
nodeadddata
(node thenode, num type:num/str/ptr/obj)
nodedeldata
(node thenode)
nodepoint
(node a, node b)
nodetomodelpath
(node thenode [, num nameflag=1])
nodetopath
(node thenode [, num nameflag=0])
not
(num/node value1)
Deprecated, use the ! operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the ! operator instead.
Example
nrcp
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.centerObjects.length
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.centerObjects.length instead.
Number of center ports of object.
Number of center ports of object.
Example
nrip
(obj object)
nrop
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.outObjects.length
Description
Example
nrows
(node thenode)
ntravelto
(obj traveler, obj spline, num endx, num endy, num endz, num vmax, num acc, num dec, num startspeed, num endspeed)
Deprecated, use kinematics instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use kinematics instead.
Causes the object to travel to a given rz and return the simulation time that it will arrive. Similar to the travelto command, but includes a start and end speed definition. Used in the development of the TaskExecuter.
Causes the object to travel to a given rz and return the simulation time that it will arrive. Similar to the travelto command, but includes a start and end speed definition. Used in the development of the TaskExecuter.
Example
ntravelto(current, 0, 5, 8, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1)
ntraveltoupdate
(obj object)
Deprecated, use kinematics instead
Description
This command is deprecated. Use kinematics instead.
Updates the rz of an object after a ntravelto() command was called on it. Used in the OnPreDraw of the TaskExecuter to update it's position.
Updates the rz of an object after a ntravelto() command was called on it. Used in the OnPreDraw of the TaskExecuter to update it's position.
Example
ntraveltoupdate(current)
numtostring
(num value[, num width, num precision])
objectconnect
(obj object1, obj object2)
Deprecated, use contextdragconnection()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use contextdragconnection() instead.
Connect two objects, adding needed ports. Object1 will have an output port added, and object2 will have an inport added as needed. Then the ports are connected.
Connect two objects, adding needed ports. Object1 will have an output port added, and object2 will have an inport added as needed. Then the ports are connected.
Example
connect(so(),so().next)
objectshapecode
(obj object)
Deprecated, use getshapeindex()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use getshapeindex() instead.
Get the index of the object's default shape. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded shapes. Each shape has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the objects default shape.
Get the index of the object's default shape. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded shapes. Each shape has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the objects default shape.
Example
objectshapecode(so())
objecttexcode
(obj object)
Deprecated, use getobjecttextureindex()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use getobjecttextureindex() instead.
Gets the index of the object's default image. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded textures (images). Each texture has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the objects default texture (image).
Gets the index of the object's default image. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded textures (images). Each texture has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the objects default texture (image).
Example
objecttexcode(current)
openflexsimchart
([str filename1] [,str filename2])
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated.
Example
openglcolor
(num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1}, num opacity {0-1})
Deprecated, use fglColor()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglColor() instead.
Example
opengllighting
(num on/off)
Deprecated, use fglEnable(GL_LIGHTING) and fglDisable(GL_LIGHTING)
Description
This command is deprecated. Use fglEnable(GL_LIGHTING) and fglDisable(GL_LIGHTING) instead.
Example
openinput
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.input.open()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.input.open() instead.
This command unblocks the input of the object after it has been previously blocked with the closeinput() command. It is necessary that both the input ports themselves, and the input in general, are open before entry will be allowed. It is advised that modelers never use this command in any field other than the OnMessage field which has been triggered with the senddelayedmessage() command, because commands which open ports often spawn several other activities that shouldn't be performed during transitional events. Compare this command with resumeinput().
This command unblocks the input of the object after it has been previously blocked with the closeinput() command. It is necessary that both the input ports themselves, and the input in general, are open before entry will be allowed. It is advised that modelers never use this command in any field other than the OnMessage field which has been triggered with the senddelayedmessage() command, because commands which open ports often spawn several other activities that shouldn't be performed during transitional events. Compare this command with resumeinput().
Example
if (current.subnodes.length < maxcontent)
openinput(current);
openinput(current);
openoutput
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.output.open()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.output.open() instead.
This command unblocks the output of the object after it has been previously blocked with the closeoutput() command. It is necessary that both the output ports themselves, and the output in general, are open before exiting is allowed. It is advised that modelers never use this command in any field other than the OnMessage field which has been triggered with the senddelayedmessage() command, because commands which open ports often spawn several other activities that shouldn't be performed during transitional events. Compare this command with resumeoutput().
This command unblocks the output of the object after it has been previously blocked with the closeoutput() command. It is necessary that both the output ports themselves, and the output in general, are open before exiting is allowed. It is advised that modelers never use this command in any field other than the OnMessage field which has been triggered with the senddelayedmessage() command, because commands which open ports often spawn several other activities that shouldn't be performed during transitional events. Compare this command with resumeoutput().
Example
if (current.subnodes.length > mincontent)
openoutput(current);
openoutput(current);
or
(num/node condition1, num/node condition2)
Deprecated, use the || operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the || operator instead.
Example
outobject
(obj object, num outputportnum)
Deprecated, use Object.outObjects[]
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.outObjects[] instead.
Reference the downstream object connected to an upstream object's output port.
Reference the downstream object connected to an upstream object's output port.
Example
parg
()
Description
This command is deprecated.
Example
parg()
parnode
(num index)
Deprecated, use param()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use param instead.
This command is used inside a function that is called by the nodefunction() command. It returns the parameter passed to nodefunction specified by index as a node (or treenode). The first additional parameter passed to nodefunction() is parameter 1, the second is parameter 2, etc. Parameters can also be retrieved using parval() and parstr() for casting them as numbers and strings respectively.
This command is used inside a function that is called by the nodefunction() command. It returns the parameter passed to nodefunction specified by index as a node (or treenode). The first additional parameter passed to nodefunction() is parameter 1, the second is parameter 2, etc. Parameters can also be retrieved using parval() and parstr() for casting them as numbers and strings respectively.
Example
If a trigger/field is called with:
nodefunction(thefuncnode, item)
then within the trigger/field, getting access to the item passed as the first additional parameter would be done with:
treenode item = parnode(1);
nodefunction(thefuncnode, item)
then within the trigger/field, getting access to the item passed as the first additional parameter would be done with:
treenode item = parnode(1);
parstr
(num index)
Deprecated, use param()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use param instead.
This command is used inside a function that is called by the nodefunction() command. It returns the parameter passed to nodefunction specified by index as a string. The first additional parameter passed to nodefunction() is parameter 1, the second is parameter 2, etc. Parameters can also be retrieved using the param() command.
This command is used inside a function that is called by the nodefunction() command. It returns the parameter passed to nodefunction specified by index as a string. The first additional parameter passed to nodefunction() is parameter 1, the second is parameter 2, etc. Parameters can also be retrieved using the param() command.
Example
If a trigger/field is called with:
nodefunction(thefuncnode, passingstr)
then within the trigger/field, getting access to the passingstr string passed as the first additional parameter would be done with:
string passedstr = parstr(1);
nodefunction(thefuncnode, passingstr)
then within the trigger/field, getting access to the passingstr string passed as the first additional parameter would be done with:
string passedstr = parstr(1);
particleset
()
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Used to set values on a "particle" object, which is no longer supported.
Example
parval
(num index)
Deprecated, use param()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use param instead.
This command is used inside a function that is called by the nodefunction() command. It returns the parameter passed to nodefunction specified by index as a number. The first additional parameter passed to nodefunction() is parameter 1, the second is parameter 2, etc. Parameters can also be retrieved using parnode() and parstr() for casting them as a treenode and string respectively.
This command is used inside a function that is called by the nodefunction() command. It returns the parameter passed to nodefunction specified by index as a number. The first additional parameter passed to nodefunction() is parameter 1, the second is parameter 2, etc. Parameters can also be retrieved using parnode() and parstr() for casting them as a treenode and string respectively.
Example
If a trigger/field is called with:
nodefunction(thefuncnode, passingval)
then within the trigger/field, getting access to the passingval passed as the first additional parameter would be done with:
double passedval = parval(1);
nodefunction(thefuncnode, passingval)
then within the trigger/field, getting access to the passingval passed as the first additional parameter would be done with:
double passedval = parval(1);
pc
(num asciivalue)
Deprecated, use print()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the print() command instead.
Print an ASCII character to the output console.
Print an ASCII character to the output console.
Example
pd
(num value)
Deprecated, use print()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the print() command instead.
Print an integer to the output console.
Print an integer to the output console.
Example
pf
(num value)
Deprecated, use print()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the print() command instead.
Print a floating point number to the output console.
Print a floating point number to the output console.
Example
pi
()
port
<no parentheses>
Description
This command is deprecated. This should not be used as a special command with the setport command anymore. Instead, declare an int variable type as port, then use port in your code as any other variable type.
Example
int port = param(3);
pd(port);
This sets port to param(3) and then prints the value to the output console.
pd(port);
This sets port to param(3) and then prints the value to the output console.
pow
(num num1, num num2)
pr
()
Deprecated, use print()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the print() command instead.
Print a new line to the output console.
Print a new line to the output console.
Example
prev
(obj object)
pt
(str text)
Deprecated, use print()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the print() command instead.
Print text to the output console.
Example
query
(str query[, node/num/str p1, node/num/str p2, ...])
Deprecated, use Table.query()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Table.query() instead.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > SQL Queries for more information.
Example
radianstodegrees
(num value)
rank
(obj parent, num index)
rankobj
(obj container, num rank)
reftable
(str/num globaltable)
Deprecated, use Table("GlobalTableName")
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Table class instead.
Gets a reference to a global table.
Gets a reference to a global table.
Example
Table table = reftable("GlobalTable1")
relloc
(obj object, obj containerobj, num coordinate)
Deprecated, use Vec3.project()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Vec3.project() instead.
This command returns the x, y, or z location of an object relative to an object that contains it. The containerobj does not need to be the immediate container, but does need to eventually be a container of the object. Use a coordinate value of 1,2,3 for x,y,z respectively.
This command returns the x, y, or z location of an object relative to an object that contains it. The containerobj does not need to be the immediate container, but does need to eventually be a container of the object. Use a coordinate value of 1,2,3 for x,y,z respectively.
Example
double x = relloc(current,model(),1);
double y = relloc(current,model(),2);
double z = relloc(current,model(),3);
Sets x, y and z to the x,y,z positions of the current object relative to the model space.
double y = relloc(current,model(),2);
double z = relloc(current,model(),3);
Sets x, y and z to the x,y,z positions of the current object relative to the model space.
repeat
(num nr, expression)
Description
Executes expression the specified number of times. The expression can use "count" to get the 1-based number of the iteration being executed.
Example
repeat(current.outObjects.length, current.outObjects[count].input.close);
This example will close the input of all objects connected to the output ports of current.
This example will close the input of all objects connected to the output ports of current.
reset
()
Deprecated, use resetmodel()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use resetmodel() instead.
For developer use. This command resets the model. The simulation clock is set to 0, and the OnReset event function is called for every object in the model. The OnReset events generally call the ResetTrigger functions that the users define. The model must be compiled before it can be reset. The resetmodel() command should typically be used instead of reset().
For developer use. This command resets the model. The simulation clock is set to 0, and the OnReset event function is called for every object in the model. The OnReset events generally call the ResetTrigger functions that the users define. The model must be compiled before it can be reset. The resetmodel() command should typically be used instead of reset().
Example
reset();
go();
This resets then runs the model.
go();
This resets then runs the model.
resumeinput
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.input.resume()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.input.resume() instead.
This command opens the input of an object just like openinput() does, but because it keeps track of previous stopinput() commands called on the object, it will only open input after all stops have been resumed. Refer to openinput() documentation for additional information.
This command opens the input of an object just like openinput() does, but because it keeps track of previous stopinput() commands called on the object, it will only open input after all stops have been resumed. Refer to openinput() documentation for additional information.
Example
resumeinput(current.centerObjects[1]);
resumeobject
(obj object [, num id, num stateprofile ] )
Deprecated, use Object.resume()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.resume() instead.
Tells the object that it may resume whatever it was doing before stopobject() was called on it.
The id value is optional and is for matching stop requests with resume requests. Refer to the stopobject()
documentation for more information on this.
Tells the object that it may resume whatever it was doing before stopobject() was called on it.
The id value is optional and is for matching stop requests with resume requests. Refer to the stopobject()
documentation for more information on this.
Example
resumeobject(current.centerObjects[1]);
resumeoutput
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.output.resume()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.output.resume() instead.
This command opens the output of an object just like openoutput() does, but because it keeps track of previous stopoutput() commands called on the object, it will only open output after all stops have been resumed. Refer to openoutput() documentation for additional information.
This command opens the output of an object just like openoutput() does, but because it keeps track of previous stopoutput() commands called on the object, it will only open output after all stops have been resumed. Refer to openoutput() documentation for additional information.
Example
resumeoutput(current.centerObjects[1]);
richeditaddtext
(obj richedit, str text, num protected (0/1))
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
richedittoken
(obj richedit, num tokenindex)
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
round
(num value[, num precision])
savefpk
(node servicepackhead)
Deprecated, use user libraries
Description
This command is deprecated. Use user libraries instead.
This saves the node to disk as a service pack file (.fpk).
A save file dialog box will appear, allowing you to define the path and name of the file. A service pack is nothing more than a node with subnodes. The first subnode is assumed to be toggled flexscript and contain string data with code. When the service pack is loaded using File | Install Service Pack, the first subnode of you service pack will execute automatically. The code will usually copy the other subnodes into the MAIN and VIEW trees.
This saves the node to disk as a service pack file (.fpk).
A save file dialog box will appear, allowing you to define the path and name of the file. A service pack is nothing more than a node with subnodes. The first subnode is assumed to be toggled flexscript and contain string data with code. When the service pack is loaded using File | Install Service Pack, the first subnode of you service pack will execute automatically. The code will usually copy the other subnodes into the MAIN and VIEW trees.
Example
savefpk(so());
senddelayedmessage
(obj toobject, num delaytime, obj fromobject [, num par1, num par2, num par3])
Send a delayed message to an object, firing its OnMessage trigger after the delay time has transpired
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.message() instead. Causes a message to be sent to the toobject from the fromobject after the delaytime has transpired. When the toobject receives the message, its OnMessage trigger will fire.
In the code of the OnMessage trigger, you may refer to the fromobject as msgsendingobject, and the three numeric par values passed in as msgparam(1), msgparam(2) and msgparam(3).
This is a very usefuly command for creating your own time events during a model run.
In the code of the OnMessage trigger, you may refer to the fromobject as msgsendingobject, and the three numeric par values passed in as msgparam(1), msgparam(2) and msgparam(3).
This is a very usefuly command for creating your own time events during a model run.
Example
senddelayedmessage(current.outObjects[1], 25, current, 0, 0, 0);
Sends a message from the current object to the object connecte to output port 1 of the current object 25 time units after this command is executed. Zeros are passed for all three of the user-defined parameters.
Sends a message from the current object to the object connecte to output port 1 of the current object 25 time units after this command is executed. Zeros are passed for all three of the user-defined parameters.
sendmessage
(obj toobject, obj fromobject [, var par1, var par2, var par3])
Send a message to an object, firing its OnMessage trigger
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.message() instead. Causes a message to be sent immediately to the toobject from the fromobject as in a direct function call. When the toobject receives the message, its OnMessage trigger will fire.
In the code of the OnMessage trigger, you may refer to the fromobject as msgsendingobject, and the three par values passed in as msgparam(1), msgparam(2) and msgparam(3). These message parameters are Variants, meaning they can be numbers, strings, treenode references or arrays.
In the code of the OnMessage trigger, you may refer to the fromobject as msgsendingobject, and the three par values passed in as msgparam(1), msgparam(2) and msgparam(3). These message parameters are Variants, meaning they can be numbers, strings, treenode references or arrays.
Example
sendmessage(current.centerObjects[1], current, item, 10);
This sends a message to the object connected to current's first center port. A reference to item is passed as par1 and the number 10 as par2.
This sends a message to the object connected to current's first center port. A reference to item is passed as par1 and the number 10 as par2.
set
(node thenode, num value)
setcenter
(obj object, num x, num y, num z)
Deprecated, use Object.setLocation()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.setLocation() instead.
Sets the x, y, and z location of the object's rotational center, relative to its container.
Sets the x, y, and z location of the object's rotational center, relative to its container.
Example
setcolor
(obj object, num red, num green, num blue)
setcurrent
(thing)
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
setitem
(thing)
Deprecated do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
setitemtype
(obj object, num value)
Deprecated, use labels
Description
This command is deprecated. Use labels instead.
This command sets the itemtype attribute of the object to value. If the object does not have the itemtype attribute, this command does nothing. The attribute itemtype is typically used to distinguish between different types of flowitems that may be of the same class.
This command sets the itemtype attribute of the object to value. If the object does not have the itemtype attribute, this command does nothing. The attribute itemtype is typically used to distinguish between different types of flowitems that may be of the same class.
Example
setitemtype(item,duniform(1,3));
This sets the itemtype attribute of the flowitem referenced by item to a random integer between 1 and 3.
This sets the itemtype attribute of the flowitem referenced by item to a random integer between 1 and 3.
setlabel
(obj node, str/num label, num/str/node value)
Deprecated, use treenode.LabelName
Description
This command is deprecated. Use treenode.labelProperties instead.
Sets the value of an object's label.
Sets the value of an object's label.
Example
setlabelnum
(obj object, str/num label, num value)
Deprecated, use treenode.LabelName
Description
Example
setlabelstr
(obj object, str/num label, str value)
Deprecated, use treenode.LabelName
Description
Example
setloc
(obj object, num x, num y, num z[, num xFactor, num yFactor, num zFactor])
setname
(obj object, str value)
setnodename
(obj/node object, str value)
setnodenum
(node thenode, num value)
setnodestr
(node thenode, str value)
setobjectimageindex
(obj object, num index)
Deprecated, do not use.
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Sets the index number of the bmp or jpeg image to be assigned to the base of the object (2D shape and base image). For the new index to take effect, the imagebase node of the object must be removed or renamed, so this command renames the imagebase node to "_imagebase" for you. The index number must be a valid index number of a currently imported bmp or jpeg image. To view currently imported images, or to import another bmp or jpeg image, use the Import Media option in the ToolBox.
Sets the index number of the bmp or jpeg image to be assigned to the base of the object (2D shape and base image). For the new index to take effect, the imagebase node of the object must be removed or renamed, so this command renames the imagebase node to "_imagebase" for you. The index number must be a valid index number of a currently imported bmp or jpeg image. To view currently imported images, or to import another bmp or jpeg image, use the Import Media option in the ToolBox.
Example
setobjectimageindex(item,gettextureindex("fs3d\\BBsphere.bmp"));
setport
(thing)
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
setquerynode
(node queryNode)
Deprecated, use Table.query()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Table.query() instead.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > SQL Queries for more information.
Example
setrank
(obj/node object, num index)
setrot
(obj object, num rx, num ry, num rz)
sets
(node thenode, str value)
setsize
(obj object, num sx, num sy, num sz)
setstate
(obj object, num state [, num profilenr])
setstate_s
(obj object, str statename)
settable
(node table, num sx, num sy[, num type, num overwrite])
Deprecated, use Table class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Table class instead.
Example
settableheader
(string/num/node table, num row/col, num rowcolnr, string value)
Deprecated, use Table.setColHeader() or Table.setRowHeader()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Table.setColHeader()
or Table.setRowHeader() instead.
Sets the value of the header field of a table
Sets the value of the header field of a table
Example
settablenum
(str/node/num table, num row, num col, num value)
Deprecated, use the Table's [] operators
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Table class's [] operators instead.
Sets the number value in a table cell.
Sets the number value in a table cell.
Example
settablesize
(str/num/node table, num rows, num cols [, num datatype, num overwrite y/n])
settablestr
(str/node/num table, num row, num col, str value)
Deprecated, use the Table's [] operators
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Table class's [] operators instead.
Sets the text value in a table cell.
Sets the text value in a table cell.
Example
settrackedvariable
(str/node trackedvar, num value[, num rate])
Deprecated, use Tracked Variable class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TrackedVariable class instead.
Example
setundos
(num maxundos)
Deprecated
Description
This command is deprecated. This command is currently deprecated because a faster leaner implementation of the undo functionality has been developed that does not use this command.
Sets the maximum number of allowable undos. A copy of the entire model will be saved each time a mouse is clicked or a key is pressed. Using the setundos command, you specify the maximum number of model copies that will be remembered for undoing. This command first requires creating a node in the main tree named undo and giving it number data.
Sets the maximum number of allowable undos. A copy of the entire model will be saved each time a mouse is clicked or a key is pressed. Using the setundos command, you specify the maximum number of model copies that will be remembered for undoing. This command first requires creating a node in the main tree named undo and giving it number data.
Example
setundos(2);
showgraphicinfo
(num showhide, str filename)
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use.
Example
sign
(num value)
sin
(num angle)
sorttable
(str/node/num table, num column)
spaceglobal
()
Deprecated, use drawtomodelscale()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use drawtomodelscale() instead.
Set the OpenGL space to the global matrix.
Set the OpenGL space to the global matrix.
Example
spaceglobal()
spaceobject
()
Deprecated, use drawtoobjectscale()
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use. Use drawtoobjectscale() instead.
Example
spaceobject()
sqr
(num value)
sqrt
(num value)
startanimation
(obj object, num/str animation[, num speedtype, num speedvalue, num repeattype, num repeatvalue])
Deprecated, use Animation class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Animation class instead.
Starts an animation on an object.
Starts an animation on an object.
Example
startanimation(current, "Stand");
statisticaltime
()
Deprecated, use the Model class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Model.statisticalTime instead.
Returns the current simulation time with respect to when stats were last reset, such as since the warmup time has passed in an experiment or since resetstats() was executed.
Returns the current simulation time with respect to when stats were last reset, such as since the warmup time has passed in an experiment or since resetstats() was executed.
Example
item.TimeIn = statisticaltime();
This sets the label called "TimeIn" on the object referenced by item to the current simulation clock time.
This sets the label called "TimeIn" on the object referenced by item to the current simulation clock time.
stopanimation
(obj object, num/str animation)
Deprecated, use Animation class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Animation class instead.
Stops an animation on an object.
Stops an animation on an object.
Example
stopanimation(current, "Walk");
stopinput
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.input.stop()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.input.stop() instead.
This command closes the input of the object just like closeinput() does, but it also keeps track of consecutive stopinput() commands, and will only open input after all stops have been resumed. Refer to closeinput() documentation for additional information.
This command closes the input of the object just like closeinput() does, but it also keeps track of consecutive stopinput() commands, and will only open input after all stops have been resumed. Refer to closeinput() documentation for additional information.
Example
stopinput(current.centerObjects[1]);
stopobject
(obj object, num state [, num id, num priority, num stateprofile] )
Deprecated, use Object.stop()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.stop() instead.
Tells the object to stop whatever it is doing, go into the state specified (in the state profile if specified), and waits for resumeobject() to be called. Stopobject commands are accumulated, meaning if stopobject is called twice on the same object, the object will not resume its operations until resumeobject has been called twice as well. Stopping an object depends on the type of object that is being stopped.
For FixedResources, generally events are delayed indefinitely, input and output is stopped, and all operations going into and out of the object are stopped. This means that TaskExecuters trying to load/unload to or from the object will have to wait until the object has been resumed.
For TaskExecuters, events are not delayed, but rather a preempting task sequence with priority of 100,000 is created for the TaskExecuter, with one TE_STOP task in it.
Be aware that, if there are several stop requests for the same object, the state for each stop request is not remembered. If an object is requested to stop by entity A with state 12, and then is later requested to stop by entity B for state 14, it will go into state 14 and forget state 12. Even if entity B resumes the object before entity A, the object will remain in state 14 until all stop requests have resumed.
The last two parameters, id and priority, are optional and have recently been added to fix the problem in the previous paragraph. If you specify these parameters, then it will store a record of the stop request, instead of just incrementing a value for the number of stops requested. The id is like a key for that stop request. The priority allows the object to prioritize its stop requests. For example, if you have a stop request for the scheduled down state, and another for the breakdown state at the same time, technically the object should be in two states at once, but since a FlexSim object can only be in one state at a time, the priority value breaks the tie and goes into the state of the highest priority stop request.
The id value should match an id value that is added to a resumeobject() command later on. This is for matching stop requests with their appropriate resume requests. For example, if you stop an object for scheduled maintenance with and id of 1, once the scheduled maintenance is finished, you will need to resume the object with the same id of 1.
Tells the object to stop whatever it is doing, go into the state specified (in the state profile if specified), and waits for resumeobject() to be called. Stopobject commands are accumulated, meaning if stopobject is called twice on the same object, the object will not resume its operations until resumeobject has been called twice as well. Stopping an object depends on the type of object that is being stopped.
For FixedResources, generally events are delayed indefinitely, input and output is stopped, and all operations going into and out of the object are stopped. This means that TaskExecuters trying to load/unload to or from the object will have to wait until the object has been resumed.
For TaskExecuters, events are not delayed, but rather a preempting task sequence with priority of 100,000 is created for the TaskExecuter, with one TE_STOP task in it.
Be aware that, if there are several stop requests for the same object, the state for each stop request is not remembered. If an object is requested to stop by entity A with state 12, and then is later requested to stop by entity B for state 14, it will go into state 14 and forget state 12. Even if entity B resumes the object before entity A, the object will remain in state 14 until all stop requests have resumed.
The last two parameters, id and priority, are optional and have recently been added to fix the problem in the previous paragraph. If you specify these parameters, then it will store a record of the stop request, instead of just incrementing a value for the number of stops requested. The id is like a key for that stop request. The priority allows the object to prioritize its stop requests. For example, if you have a stop request for the scheduled down state, and another for the breakdown state at the same time, technically the object should be in two states at once, but since a FlexSim object can only be in one state at a time, the priority value breaks the tie and goes into the state of the highest priority stop request.
The id value should match an id value that is added to a resumeobject() command later on. This is for matching stop requests with their appropriate resume requests. For example, if you stop an object for scheduled maintenance with and id of 1, once the scheduled maintenance is finished, you will need to resume the object with the same id of 1.
Example
stopobject(current.centerObjects[1], STATE_BLOCKED);
stopoutput
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.output.stop()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.output.stop() instead.
This command closes the output of the object just like closeoutput() does, but it also keeps track of consecutive stopoutput() commands, and will only open output after all stops have been resumed. Refer to closeoutput() documentation for additional information.
This command closes the output of the object just like closeoutput() does, but it also keeps track of consecutive stopoutput() commands, and will only open output after all stops have been resumed. Refer to closeoutput() documentation for additional information.
Example
stopoutput(current.centerObjects[1]);
store
()
Description
This command is deprecated. This command is currently deprecated because a faster leaner implementation of the undo functionality has been developed that does not use this command.
It explicitly stores an archived copy of the current model inside the undo folder of the main tree. Refer to undos() command documentation for more information.
It explicitly stores an archived copy of the current model inside the undo folder of the main tree. Refer to undos() command documentation for more information.
Example
store();
stringcopy
(str string, num start, num length)
stringlen
(str string)
stringpart
(str string, num start, num length)
Deprecated, use string.substr()
Description
Example
stringpart("Hello",2,3) returns the sub string "llo".
stringreplace
(str stringtosearch, str searchfor, str replacewith)
stringreturn
(str returnstring, ptr callpoint)
Description
This command is deprecated. You can simply return strings from C++ user commands with the return statement.
Prior to FlexSim 7.7, this command was used to return a string from a C++ implementation of a user command. This command was only needed in C++. In FlexScript user commands, you can simply return the string with the return statement.
Prior to FlexSim 7.7, this command was used to return a string from a C++ implementation of a user command. This command was only needed in C++. In FlexScript user commands, you can simply return the string with the return statement.
Example
C++: stringreturn(result, callpoint); return 0;
stringsearch
(str stringtosearch, str searchfor, int startindex[, int flags])
stringtonum
(str string)
stringtopchar
(str string)
Deprecated, use apchar()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use apchar() instead.
This command returns the string as a pointer to a C++ character. This is used to convert variables of type string to type char* for some C++ commands which only take char*'s. It is not needed in Flexscript.
This command returns the string as a pointer to a C++ character. This is used to convert variables of type string to type char* for some C++ commands which only take char*'s. It is not needed in Flexscript.
Example
setname(current,stringtopchar("ThisObjectName"));
This sets the name of the object referenced by current to "ThisObjectName". The stringtopchar() command may not be mandatory here, but it is legal.
This sets the name of the object referenced by current to "ThisObjectName". The stringtopchar() command may not be mandatory here, but it is legal.
strquote
(str string)
Deprecated, use \"
Description
This command is deprecated. Use \" instead to include quotation marks within a string.
Example
strquote("hello")
sub
(num value1, num value2)
Deprecated, use the - operator
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the - operator instead.
operator instead. of value1 and value2. This returns the result of the arithmetic expression value1-value2.
operator instead. of value1 and value2. This returns the result of the arithmetic expression value1-value2.
Example
double operator instead. = sub(10,4);
swaptablecols
(str/num/node table, num column, num column2)
swaptablerows
(str/num/node table, num row, num row2)
switch_hidebase
(obj object[, num off/on])
Deprecated, do not use
Description
This command is deprecated. Do not use. Get or set the "Show 2D Shape" flag of the object. A value of 1 is hide, a value of 0 is show, and a value of -1 gets the current value. The 2D shape (base) of an object is visible in the Planar view window. Note that view windows also have an attribute named hideallbases that controls the display of 2D shapes (bases) for ALL objects in their view.
Example
switch_hidebase(so(),1)
tan
(num angle)
time
()
trackedvariable
(str name)
Deprecated, use Tracked Variable class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TrackedVariable class instead.
Example
transfernode
(node movenode, node container)
Deprecated, use treenode.up
Description
Example
transfernode(current.labels["inactivequeue"].first, current.labels["activequeue"]);
travelto
(obj object, obj spline, num x, num y, num z, num vmax, num acc, num dec)
Deprecated, use kinematics
Description
This command is deprecated. Use kinematics instead.
Calculate current travel parameters for the object. A travel path will be calculated. Once set, the object's position will be calculated based on the travel path as defined by this command. This function returns the time of travel end. This function can be used in conjunction with a spline to create curved travel paths.
Calculate current travel parameters for the object. A travel path will be calculated. Once set, the object's position will be calculated based on the travel path as defined by this command. This function returns the time of travel end. This function can be used in conjunction with a spline to create curved travel paths.
Example
travelto(traveler,NULL,100,100,0,5,1,6)
traveltoupdate
(obj object [, obj spline])
Deprecated, use kinematics
Description
This command is deprecated. Use kinematics instead.
Update the object's position based on it's current travel parameters. Explicitly set an object's position based on the time and travel path parameters as calculated from the travelto() command on object, using spline as the path geometry if desired.
Update the object's position based on it's current travel parameters. Explicitly set an object's position based on the time and travel path parameters as calculated from the travelto() command on object, using spline as the path geometry if desired.
Example
traveltoupdate(current)
Updates the current object's position based on the travel parameters set earlier by the traveto() command. This command is usually executed from the Custom Draw Code field.
Updates the current object's position based on the travel parameters set earlier by the traveto() command. This command is usually executed from the Custom Draw Code field.
trunc
(num value)
undos
(num off/on)
Description
This command is deprecated. This command is currently deprecated because a faster leaner implementation of the undo functionality has been developed that does not use this command.
This command is used to turn on (1) and off (0) the automatic saving of model copies each time there is a mouse click or key press. Use the setundos command, to specify the maximum number of model copies that will be remembered for undoing. To function correctly, this command requires first creating a node in the main tree named undo and giving it number data.
This command is used to turn on (1) and off (0) the automatic saving of model copies each time there is a mouse click or key press. Use the setundos command, to specify the maximum number of model copies that will be remembered for undoing. To function correctly, this command requires first creating a node in the main tree named undo and giving it number data.
Example
undos(1);
up
(obj object)
updateanimation
(obj object [, num updatetime, num animationnr])
Deprecated, use Animation class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Animation class instead.
Updates an animation on an object.
Updates an animation on an object.
Example
updateanimation(current);
userfunction_n
(obj object, num index [, num param_a,...])
Deprecated, use nodefunction()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use nodefunction() instead because it will work on any node.
Executes code associated with a node found in the object's userfunctions group having the specified rank index. Use param() within the called function node to retrieve the arguments passed into the function.
Executes code associated with a node found in the object's userfunctions group having the specified rank index. Use param() within the called function node to retrieve the arguments passed into the function.
Example
userfunction_s(current,4,1,2,3)
Executes the code associated with a node ranked 4th in the userfunctions group of the current object.
Executes the code associated with a node ranked 4th in the userfunctions group of the current object.
userfunction_s
(obj object, str name [, num param_a,...])
Deprecated, use nodefunction()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use nodefunction() instead, because it will work on any node.
Executes code associated with a node found in the object's userfunctions group having the specified name. Use param() within the called function node to retrieve the arguments passed into the function.
Executes code associated with a node found in the object's userfunctions group having the specified name. Use param() within the called function node to retrieve the arguments passed into the function.
Example
userfunction_s(current,"myfunc",1,2,3)
Executes the code associated with a node named "myfunc" in the userfunctions group of the current object.
Executes the code associated with a node named "myfunc" in the userfunctions group of the current object.
var
(obj object, num index)
Deprecated, use getvarnode()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use getvarnode() instead.
Get the node of an object in 'variables' by index.
Get the node of an object in 'variables' by index.
Example
var(so(),1)
var_s
(obj object, str name)
Deprecated, use getvarnode()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use getvarnode() instead.
Get the node of an object in 'variables' by name.
Get the node of an object in 'variables' by name.
Example
var_s(current,"myatt")
vectorprojectx
(obj projectfrom, num fromx, num fromy, num fromz, obj projectonto)
vectorprojecty
(obj projectfrom, num fromx, num fromy, num fromz, obj projectonto)
vectorprojectz
(obj projectfrom, num fromx, num fromy, num fromz, obj projectonto)
xcenter
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.getLocation()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.getLocation().
Gets the x location of the rotational center of the object within its container.
Gets the x location of the rotational center of the object within its container.
Example
xloc
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.location or Object.getLocation()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.location
or Object.getLocation().
Gets the x location of an object.
Gets the x location of an object.
Example
xrot
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.rotation or Object.setRotation()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.rotation
or Object.setRotation() instead.
Gets the x rotation of an object (rotation about the x-axis).
Gets the x rotation of an object (rotation about the x-axis).
Example
xsize
(obj object)
ycenter
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.getLocation()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.getLocation() instead.
Gets the y location of the rotational center of the object within its container.
Gets the y location of the rotational center of the object within its container.
Example
yloc
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.location or Object.getLocation()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.location
or Object.getLocation() instead.
Gets the y location of an object.
Gets the y location of an object.
Example
yrot
(obj object)
ysize
(obj object)
zcenter
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.getLocation()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.getLocation() instead.
Gets the z location of the rotational center of the object within its container.
Gets the z location of the rotational center of the object within its container.
Example
zloc
(obj object)
Deprecated, use Object.location or Object.getLocation()
Description
This command is deprecated. Use Object.location
or Object.getLocation() instead.
Gets the z location of an object.
Gets the z location of an object.
Example
zrot
(obj object)
zsize
(obj object)
Development
High-level development commands not typically intended for end users.
addcommand
(obj codenode, str commandname, str description, str parameters, str example [, str cppprefix, str shortdescription])
Description
For developer use. Adds a Flexscript command to the current list of available commands. The new command is available until the next compile. The Tools | User Commands menu is for end-users to create their own commands.
Example
addcommand(...)
backupfile
(str filepath)
Description
For developer use. Backs up the file by appending a ! onto the specified file's name. Note that this doesn't copy the file. You would do this before an overwrite of a file.
Example
backupfile(modeldir() + "mydocument.htm");
buildall
()
Description
For developer use. This command builds Flexscript trees for all of the nodes in the tree that are designated as Flexscript nodes. A Flexscript node must have a Flexscript tree made before it can run. This option is available in the main menu under Build -> Build All Flexscript. This must be done before running a model with Flexscript written anywhere in it. It should also be done after making any changes to GUIs.
Example
buildall();
This builds Flexscript trees for all Flexscript nodes in the tree.
This builds Flexscript trees for all Flexscript nodes in the tree.
buildnodeflexscript
(node codenode)
Description
For developer use. This command builds Flexscript trees for the node specified as node if it is designated as a Flexscript node. A Flexscript node must have a Flexscript tree made before it can run.
Example
buildnodeflexscript(Table("mytable").cell(1,2));
This builds a Flexscript tree for the node at row 1 column 2 of the GlobalTable named "mytable", if it is a Flexscript node.
This builds a Flexscript tree for the node at row 1 column 2 of the GlobalTable named "mytable", if it is a Flexscript node.
changedisplay
(num width, num height, num depth, num fullscreen, num test)
Change resolution
Description
Change resolution
Example
changedisplay(1024,768,0,0,0)
cleannodeflexscript
(node startnode)
Description
For developer use. This command recursively deletes Flexscript trees starting at the node specified.
Example
cleannodeflexscript(model());
This cleans all the Flexscript nodes in the model.
This cleans all the Flexscript nodes in the model.
cmdcompile
()
Description
For developer use.
Compile the project.
Compile the project.
Example
cmdcompile()
cmddelete
(node thenode)
Description
For developer use. Use destroyobject().
Delete thenode.
Delete thenode.
Example
cmddelete(model().subnodes[4]))
cmdexit
()
Description
For developer use.
Closes FlexSim.
Closes FlexSim.
Example
cmdexit()
cmdloadbyextension
(str filename, num silent)
Description
For developer use.
Load a file by name and extension. Recognizes: Project (fsp), Session (fss), Model (fsm), View Layout (fsv). If silent is 0, the user will be asked to confirm that they are opening the correct file.
Load a file by name and extension. Recognizes: Project (fsp), Session (fss), Model (fsm), View Layout (fsv). If silent is 0, the user will be asked to confirm that they are opening the correct file.
Example
cmdloadbyextension("c:/mysession.fss",0)
cmdloadsession
(str filename)
Description
For developer use.
Load a session by name.
Load a session by name.
Example
cmdloadsession("c:/mysession.fss")
cmdloadtree
(obj desttree, str filename [, num nobuild])
Description
For developer use.
Load a tree by file path into desttree. By default, after loading, all flexscript will be built. If nobuild is 1, flexscript will not be built. Set nobuild to 1 if you are executing this command from a script node that is toggled as flexscript, or else your script will not finish properly.
Load a tree by file path into desttree. By default, after loading, all flexscript will be built. If nobuild is 1, flexscript will not be built. Set nobuild to 1 if you are executing this command from a script node that is toggled as flexscript, or else your script will not finish properly.
Example
cmdloadtree(node("MAIN:/project/model/2"),"c:/mytree.t"))
cmdnew
()
Description
For developer use.
Start a new model. This command will clear the contents of the model by deleting all objects in the model.
Start a new model. This command will clear the contents of the model by deleting all objects in the model.
Example
cmdnew()
cmdopen
()
Description
For developer use.
Open a new model. This command will cause an Open Model Dialog box to appear from which a model file can be selected for opening.
Open a new model. This command will cause an Open Model Dialog box to appear from which a model file can be selected for opening.
Example
cmdopen()
cmdsaveas
()
Description
For developer use.
Save the model. This command will cause an SaveAs Model Dialog box to appear from which a model file name can be specified for saving.
Save the model. This command will cause an SaveAs Model Dialog box to appear from which a model file name can be specified for saving.
Example
cmdsaveas()
cmdsavesession
(str filename)
Description
For developer use.
Save a session by name.
Save a session by name.
Example
cmdsavesession("c:/mysession.fss")
cmdsavetree
(obj tree, str filename)
Save a Tree by name
Description
Save a Tree by name
Example
cmdsavetree(node("MAIN:/project/library/1"),"c:\\mytree.t"))
consoleexecutefs
(HWND input, HWND output)
Description
For developer use.
Execute the console code as Flexscript.
Execute the console code as Flexscript.
Example
copyattributes
(obj destination, obj source, num mask)
Description
For developer use. Copy the attributes from one object to another. Use mask parameter to enable specific groups (from least significant):
ATTCOPY_ALL
ATTCOPY_SPATIAL
ATTCOPY_OFFSETS
ATTCOPY_VISUAL
ATTCOPY_MEDIA ATTCOPY_LABELS
ATTCOPY_VARIABLES
ATTCOPY_DESCRIPTIVE
ATTCOPY_TABLES
Use the OR operator (|) to combine these values into a single value for the mask parameter.
ATTCOPY_ALL
ATTCOPY_SPATIAL
ATTCOPY_OFFSETS
ATTCOPY_VISUAL
ATTCOPY_MEDIA ATTCOPY_LABELS
ATTCOPY_VARIABLES
ATTCOPY_DESCRIPTIVE
ATTCOPY_TABLES
Use the OR operator (|) to combine these values into a single value for the mask parameter.
Example
copyattributes(library().subnodes[1],model().subnodes[1],ATTCOPY_SPATIAL | ATTCOPY_VISUAL)
copycolor
(obj highlightedobj)
Description
For developer use. Copies the color of the highlighted object to all of the selected objects
Example
copycolor(current)
copylabel
(obj highlightedobject, str/obj labelnamenode)
Description
For developer use. Copies the label with the name specified by parameter 2 or stored on the string data of the node in parameter 2 from the parameter 1 object to all selected objects in the model.
Example
copylabel(selectedobject(ownerview(c)), c.find(">labelname"))
copylabels
(obj highlightedobj[, num mode])
Description
For developer use. Copies all labels from the parameter 1 object to all selected objects in the model. By default it clears out all existing
labels and replaces them with the labels on the parameter 1 object. If mode is 1, existing labels will be overwritten by any incoming labels with the same name,
but will otherwise be left alone. If mode is 2, only labels that the selected objects do not already have will be copied.
Example
copylabels(selectedobject(ownerview(c)), c.find(">labelname"))
copyvariable
(obj fromobject, obj variablenamenode)
Description
For developer use. Copies the variable with the name held by the node in parameter 2 from the parameter 1 object to all selected objects in the model.
Example
copyvariable(selectedobject(ownerview(c)), c.find(">variablename"))
copyvariables
(obj fromobject)
Description
For developer use. Copies all variables from the parameter 1 object to all selected objects in the model.
Example
copyvariables(selectedobject(ownerview(c)))
copyvisuals
(obj highlightedobj [, num copyshapefactorsalso])
Description
For developer use. Copies all visuals from the parameter 1 object to all selected objects in the model.
Example
copyvisuals(selectedobject(ownerview(c)),1)
daemonstate
(num thing)
Description
For developer use.
Returns the stats of:
1 - clock
2 - flythrough
3 - ticker
Returns the stats of:
1 - clock
2 - flythrough
3 - ticker
Example
daemonstate(1)
documentusercommands
()
Description
For developer use. Accesses the current model's command documenation and updates a file called usercommands.xml so that the user commands are included in the command documentation
Example
documentusercommands();
excelupdatepreferences
()
SYSTEM USE ONLY
Description
SYSTEM USE ONLY - used to update global variables to match preferences. Called in startupRT.txt and in OnSelect of Excel Preferences GUI.
Example
excelupdatepreferences()
fgldebuglevel
(num level [0-3])
Description
For developer use. Set the OpenGL debug level. The higher the number, the more scrutiny is put on the system, and the more reporting is done. 0 is none, 3 is maximum.
Example
fgldebuglevel(3)
fileisreadonly
(str filename)
Description
For developer use (Dynamo). Looks for the string "READONLY" in the PROPERTY_COMMENTS of the specified file.
Example
fileisreadonly(pdir() + "\\flexsim.exe")
fillwithatts
(obj object, num attgroup)
Description
For developer use. Fill an object with attribute from an attribute group.
Example
fillwithatts(so(),1)
fscheckall
(node startingnode)
Description
For developer use. This command checks for errors in all flexscript nodes under and including the specified startingnode and outputs the results to the compiler console if it finds atleast one error.
Example
fscheckall(main());
function_n
(obj object, num index [, num param_a,...])
Description
For developer use. Executes code associated with a node found in the object's eventfunctions group having the specified event code. The event code is not the rank of the node in the eventfunctions group, but it corresponds to one of the following pre-defined FlexSim event :
OnReset 1
OnMessage 2
OnEvent 3
OnDraw 4
OnInopen 5
OnOutopen 6
OnReceive 7
OnSend 8
OnEntering 9
OnExiting 10
OnCompile 11
OnCreate 12
OnDestroy 13
OnLoad 14
OnCollision 15
OnClick 16
OnRunend 17
OnRunstart 18
OnInterrupted 19
OnCaptured 20
OnListen 21
OnPredraw 22
OnDrawplanar 23
OnPredrawplanar 24
OnPreListen 25
OnReset 1
OnMessage 2
OnEvent 3
OnDraw 4
OnInopen 5
OnOutopen 6
OnReceive 7
OnSend 8
OnEntering 9
OnExiting 10
OnCompile 11
OnCreate 12
OnDestroy 13
OnLoad 14
OnCollision 15
OnClick 16
OnRunend 17
OnRunstart 18
OnInterrupted 19
OnCaptured 20
OnListen 21
OnPredraw 22
OnDrawplanar 23
OnPredrawplanar 24
OnPreListen 25
Example
function_n(current,1,1,2,3)
Executes the OnReset event function defined on the current object.
Executes the OnReset event function defined on the current object.
function_s
(obj object, str name [, num param_a,...])
Description
For developer use. Executes code associated with the node found in the object's eventfunctions group having the specified name. For a list of the pre-defined system level events in FlexSim refer to function_n() command documentation.
Example
function_s(current,"OnReset",1,2,3)
Executes the OnReset event function defined on the current object.
Executes the OnReset event function defined on the current object.
getapplicationtitle
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the current application's title as a string.
Example
msg(getapplicationtitle(),"Hello world.");
getnextparametersobject
(obj startobject, str guifocus, num doguifocusclass, num searchforward)
Description
For developer use. Used in parameters window to access the next object when the "Next" button on the parameters window is pressed.
Example
Refer to object parameters properties windows in the view tree
getproperty
(str filename, num property)
Description
For developer use. Gets the value for the specified property in the specified file.
Example
getproperty(modeldir() + "MyModel.fsm",1);
gettreedrawposition
(node destnode, node roottree)
Description
For developer use.
Example
groupconnectfrom
(obj object, str character)
Description
For developer use. Connects the object passed in as param(1) to every selected object in the model using the letter passed in as param(2).
Typically used in GUIs.
Typically used in GUIs.
Example
groupconnectfrom(selectedobject(ownerview(c)),"A");
groupconnectto
(obj object, str character)
Description
For developer use. Connects every selected object in the model to the object passed in as param(1) using the letter passed in as param(2).
Typically used in GUIs.
Typically used in GUIs.
Example
groupconnectto(selectedobject(ownerview(c)),"A");
groupcopyconnections
(obj object)
Description
For developer use. Copies the connections on the object passed in as param(1) onto every selected object in the model.
Typically used in GUIs
Typically used in GUIs
Example
groupcopyconnections(selectedobject(ownerview(c)));
help
()
Description
For developer use. Display the help system window.
Example
help()
howmanyattributes
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the number of attributes.
Example
howmanyattributes()
howmanycommands
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the number of commands.
Example
howmanycommands()
license
()
Gets the current license type
Description
Get the current license type
Example
licenseactivation
(num operation[, str buffer, var p1, node callback])
Description
For developer use. Do various licensing operations.
Example
licenseactivation(LA_SET_ACTIVATION_SERVER_PARAMS,"@localhost",0);
maintenance
(num command[, num state, str strparam])
Description
For developer use. Set a maintenance switch.
The first parameter designates the operation. The second parameter designates a state to set it to.
Maintenance switches:
0. print this list
1. deadlinks
2. atttrbute bind method (0=names, 1=indices, 2=bootstrap)
3. numberprecision
4. display binding report
5. usercollisions
6. post-onsend
7. loadsavemode
8. disablefscheck
9. disablefspreprocess
10. splinetension
11. streamalizer
12. immediately load extended docs
13. save reps at experiment end
14. suppress object library compile
15. suppress global compile
16. set runtime info
17. get runtime info
18. bind c++ functions
19. autorebind c++ functions onoff
20. get presentation mode
21. refresh main menu
22. is optquest enabled
23. flypaths in seconds units
24. chached ports on/off
25. bind on reset on/off
26. set category name (user command group is 22, other 23, 24+ is available)
27. object sizermode 0. default 1. 3-axis
28. show hidden nodes in tree
29. hide 3d cursor
30. supress simclock redraw
31. use parser two
32. grid draw settings: bitwise field: 0x1-auto expand grid, 0x2-show grid axes, 0x4-show grid origin
1000. DDE
The first parameter designates the operation. The second parameter designates a state to set it to.
Maintenance switches:
0. print this list
1. deadlinks
2. atttrbute bind method (0=names, 1=indices, 2=bootstrap)
3. numberprecision
4. display binding report
5. usercollisions
6. post-onsend
7. loadsavemode
8. disablefscheck
9. disablefspreprocess
10. splinetension
11. streamalizer
12. immediately load extended docs
13. save reps at experiment end
14. suppress object library compile
15. suppress global compile
16. set runtime info
17. get runtime info
18. bind c++ functions
19. autorebind c++ functions onoff
20. get presentation mode
21. refresh main menu
22. is optquest enabled
23. flypaths in seconds units
24. chached ports on/off
25. bind on reset on/off
26. set category name (user command group is 22, other 23, 24+ is available)
27. object sizermode 0. default 1. 3-axis
28. show hidden nodes in tree
29. hide 3d cursor
30. supress simclock redraw
31. use parser two
32. grid draw settings: bitwise field: 0x1-auto expand grid, 0x2-show grid axes, 0x4-show grid origin
1000. DDE
Example
maintenance(0)
modeleditmode
(num/str mode)
Description
For developer use. Sets the current model edit mode. You can query the current mode with -1.
Example
modeleditmode("AConnect");
postclosewindowmessage
(obj view)
Posts a Windows Message to close the window
Description
Posts a message onto the Windows message queue to close the window. This allows you to finish any scripting code before the window is actually closed.
Example
postclosewindowmessage(ownerview(c));
postmovewindowupdate
(obj view)
Description
For developer use. Do not use.
Example
postwindowmessage
(HWND window, num msg[, num/str/node wParam, num/str/node lParam])
Description
For developer use. This gives direct access to the Windows API PostMessage() command, posting a message to a window. Use windowfromnode() or getviewhwnd() to get access to the window handle. Refer to Windows API documentation for more information. Not that you cannot use a message that uses lParam or wParam as an [out] parameter, or one that you pass in as a pointer to a struct. You should be able to pass strings into lParam or wParam, but again thay cannot be [out] parameters. FlexSim does not include all possible WM_ messages in its flexscript macros, so if you want to use one in flexscript, you will need to find the definition in the windows header files and add the definition to your flexscript code.
Example
postwindowmessage(windowfromnode(view), WM_COPY, 0,0);
rebindobjectattributes
(node thenode)
Rebinds object attributes
Description
Rebinds object attributes for the given node. If you delete or add an attribute to an object, the object's attribute cache will not immediately reflect that change, so you can call rebindobjectattributes to update the object's attribute cache. This is the same as right-clicking on the object and selecting Edit|Rebind Object Attributes.
Example
rebindobjectattributes(c)
recover
(num phase)
Load recovery files
Description
Load recovery files. phase: 1 or 2
Example
recover(1)
refreshcommandlist
()
Description
For developer use. Refreshes the command list.
Example
refreshcommandlist()
refreshglobalvariables
()
Description
For developer use. Refreshes all global variables to their initial values.
Example
refreshglobalvariables()
refreshmodelcommands
()
Description
System command. Do not use.
Example
runexpertfit
()
Description
For developer use. Starts the expertfit program automatically if licensed.
Example
runexpertfit()
sendwindowmessage
(HWND window, num msg[, num/str/node wParam, num/str/node lParam])
Description
For developer use. This gives direct access to the Windows API SendMessage() command, sending a message to a window. Use windowfromnode() or getviewhwnd() to get access to the window handle. Refer to Windows API documentation for more information. Not that you cannot use a message that uses lParam or wParam as an [out] parameter, or one that you pass in as a pointer to a struct. You should be able to pass strings into lParam or wParam, but again thay cannot be [out] parameters. FlexSim does not include all possible WM_ messages in its flexscript macros, so if you want to use one in flexscript, you will need to find the definition in the windows header files and add the definition to your flexscript code.
Example
sendwindowmessage(windowfromnode(view), WM_COPY, 0,0);
setapplicationtitle
(str title)
Description
For developer use. Sets the current application's title.
Example
setapplicationtitle("Custom Application Title");
setmessageloopsleep
(num interval, num sleeptime)
Description
For developer use. Set a sleep time for each cycle of the message loop to decrease cpu load. Use carefully because a large value can make FlexSim unresponsive to user input. Every interval milliseconds, FlexSim will pause for a period of sleeptime milliseconds. This command may help certain laptops that tend to overheat due to excessive cpu usage.
Example
setmessageloopsleep(1)
setproperty
(str filename, num property, str newvalue)
Description
For developer use. Sets the value for the specified property in the specified file to the newvalue.
Example
setproperty(modeldir() + "MyModel.fsm",1,"Custom Title");
setticker
(node thenode[, num tickspersecond])
Description
For developer use. Set the ticker script node. If tickspersecond is specified, the code will be executed that many times per second, otherwise the code associated with the node will be executed at each iteration of the windows event loop. The node must be toggled FlexScript or C++. No model events are created in association with the ticker node execution. To turn off ticker execution, use setticker(0).
Example
setticker(so())
statsenablemask
(num mask)
Description
For developer use. Enable or disable aspects of stats collection. Set a 32 bit enable mask: Sum of flags. Bits: 0 = State; 1 = Flow; 2 = Inside Ports.
Example
statsenablemask(add(1,2))
stick
(num stickno, num command [, HWND/num win, var/num p])
Description
For developer use. This command queries the joystick or controller state or sets functionality for a joystick or controller.
stickno defines an id for the joystick or gamepad you want to query. This is a number between 0 and 32. Usually you will only have one joystick connected to your computer, so in this case you should use the value 1 as stickno. If you are using a gamepad, you might need to use stickno 2. For Xbox controllers, stickno will be a value between 0 and 3. For VR controllers, stickno will be either 0 or 1. For Oculus touch controllers, stickno 0 is the left hand and stickno 1 is the right hand. Use stickno -1 to get the status, position, or rotation of a connected VR headset.
command defines the operation that the command should perform. This should be one of the macros below:
STICK_JOY_STATUS - Queries the connectivity of the joystick. If the joystick is connected properly, then this command will return 0. If the return value is non-zero, then there is some error with the joystick's connectivity, and you can view the system console to see what the error is. The following errors apply:
MMSYSERR_NODRIVER - The joystick driver is not present.
MMSYSERR_INVALPARAM - Invalid joystick ID or hwnd is NULL.
JOYERR_NOCANDO - Cannot capture joystick input because a required service (such as a Windows timer) is unavailable.
JOYERR_UNPLUGGED - The specified joystick is not connected to the system.
JOYERR_PARMS - Invalid joystick ID or hwnd is NULL.
STICK_JOY_XPOS - Current X-coordinate of the joystick. This is a number between 0 and 65535. 0 means the joystick is pushed all the way to the left, 65535 means it is pushed all the way to the right, and 32768 is exactly in the center. If you are using a gamepad, then this is the x position of the left side joystick.
STICK_JOY_YPOS - Current Y-coordinate of the joystick. Again this is a number between 0 and 65535. 0 is up, 65535 is down. If you are using a gamepad, this is the position of the gamepad's left joystick.
STICK_JOY_ZPOS - Current Z-coordinate of the joystick. If you are using a joystick, this will usually be the current setting of the joystick's throttle. Again it is a value between 0 and 65535. If you are using a gamepad, this represents the y position of the right side joystick.
STICK_JOY_BUTTONS - Current state of the 32 joystick buttons. This is bitwise integer with each bit representing the state of a given button. For a joystick, the main trigger button is usually represented by the 0x00000001 bit, other buttons on the stick are 0x00000002 and 0x00000004, and buttons on the base of the joystick are then higher order bits. You will need to test these out on your own as each joystick is a little different.
STICK_JOY_SET_CAPTURE - This command sets the joystick capture to a FlexSim window that you specify. This command requires the win and p parameters to be passed in. By executing this command, joystick messages will be sent to the OnStick attribute of the view. For example, if you have an ortho view that you would like to listen to joystick events, you would call this command, passing the ortho view's HWND handle (use windowfromnode()), and a polling period. The period specifies a time interval in milliseconds to repeatedly call the OnStick event. If p is 0, then the OnStick event will only be called when the joystick's state changes. If p is greater than 0, then the OnStick event will simply be called at the end of each sample period interval. Example: stick(1,5, windowfromnode(sv()), 200); This will cause the OnStick event to be called every 200 milliseconds. In order for this to work, you need to add an OnStick attribute to the view (you may also need to rebind the view's attributes after adding it: right-click->Edit|Rebind Object Attributes).
STICK_JOY_RELEASE_CAPTURE - This command releases the joystick capture for the window that was previously captured with the 5 command. You need to pass in the win parameter as with command 5.
STICK_JOY_RPOS - Current position of the rudder or fourth joystick axis of the joystick. For a joystick, this is usually the rotation of the joystick if your joystick can rotate around its z axis. Again it is a number between 0 and 65535. If you are using a gamepad, it is the x position of the right side joystick.
STICK_JOY_UPOS - Current fifth axis position of the joystick.
STICK_JOY_VPOS - Current sixth axis position of the joystick.
STICK_JOY_POV - Current position of the point-of-view control of the joystick. It is a number between 0 and 35900 and represents the number of degrees times 100. For a gamepad, this represents the directional pad on the left of the gamepad. Up is 0, right is 9000, down is 18000, left is 27000. If the directional pad is not pressed, the value will be 65535. If you are using a joystick, there may be a directional thumb controller on the stick itself that you can press up, down, right, or left, and this will get the setting of that controller.
STICK_JOY_CURRENT_BUTTON - Current button number that is pressed.
STICK_JOY_FLAGS - Flags indicating the valid information returned about the joystick.
STICK_XBOX_STATUS - Queries the connectivity of the Xbox controller. If the controller is connected properly, this returns 0.
STICK_XBOX_BUTTONS - Bitmask of the device digital buttons. A set bit indicates that the corresponding button is pressed.
STICK_XBOX_LEFT_THUMB_X - Left thumbstick x-axis value. Each of the thumbstick axis members is a signed value between -32768 and 32767 describing the position of the thumbstick. A value of 0 is centered. Negative values signify down or to the left. Positive values signify up or to the right.
STICK_XBOX_LEFT_THUMB_Y - Left thumbstick y-axis value. The value is between -32768 and 32767.
STICK_XBOX_RIGHT_THUMB_X - Right thumbstick x-axis value. The value is between -32768 and 32767.
STICK_XBOX_RIGHT_THUMB_Y - Right thumbstick y-axis value. The value is between -32768 and 32767.
STICK_XBOX_LEFT_TRIGGER - The current value of the left trigger analog control. The value is between 0 and 255.
STICK_XBOX_RIGHT_TRIGGER - The current value of the right trigger analog control. The value is between 0 and 255.
STICK_VR_STATUS - Returns 1 if an Oculus Rift controller is active. Returns 2 if an HTC Vive controller is active. Returns 0 if the controller is inactive. Returns nullvar if the controller is not attached.
STICK_VR_THUMB_X - Thumbstick or trackpad x-axis value between -1 and 1.
STICK_VR_THUMB_Y - Thumbstick or trackpad y-axis value between -1 and 1.
STICK_VR_INDEX_TRIGGER - Index trigger value between 0 and 1.
STICK_VR_GRIP_TRIGGER - Grip trigger value between 0 and 1. On HTC Vive, grip button is pressed.
STICK_VR_BUTTON_1 - The first button is pressed. A or X on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_BUTTON_2 - The second button is pressed. B or Y on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_BUTTON_3 - The third button is pressed. Enter or Home on Oculus Rift. Menu on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_BUTTON_4 - The fourth button is pressed. Thumbstick on Oculus Rift. Trackpad on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_BUTTON_1 - The first button is touched. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_BUTTON_2 - The second button is touched. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_BUTTON_3 - The third button is touched. Unused on Oculus Rift.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_BUTTON_4 - The fourth button is touched.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_THUMB_REST - The thumb rest sensor is touched on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_INDEX_TRIGGER - The index trigger sensor is touched.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_POINTING - The hand gesture is pointing on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_THUMB_UP - The hand gesture is thumbs-up on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_HAND_POSITION - The controller position in VR space.
STICK_VR_HAND_ROTATION - The controller rotation in VR rotation coordinates.
STICK_VR_HAND_WORLD_POSITION - The controller position in FlexSim world space.
STICK_VR_HAND_WORLD_ROTATION - The controller rotation in FlexSim rotation coordinates.
STICK_VR_HAND_OFFSET_POSITION - The controller's position in FlexSim world space, but with an offset applied based on the controller's rotation. Pass an array as the offset vector in the p parameter. You can use this option to get a point relative to the controller, such as a finger position or where the controller is pointing.
STICK_VR_TARGET_FLOOR_POSITION - The target position on the floor that the controller is pointing towards. Pass a value in the p parameter for the maximum distance away from the controller.
STICK_VR_SET_VIBRATION - Causes the controller to vibrate. On Oculus Rift, pass an array for the p parameter where the first element is a value between 0 and 1 for the frequency and the second element is a value between 0 and 1 for the amplitude. On HTC Vive, pass a duration in microseconds for the p parameter.
STICK_VR_SUBMIT_VIBRATION - Causes the controller to subtly vibrate. On original Oculus Touch controllers, pass an array of amplitudes (0 - 255) for the p parameter to be queued up and executed. Unused on HTC Vive or Oculus Rift S controllers.
stickno defines an id for the joystick or gamepad you want to query. This is a number between 0 and 32. Usually you will only have one joystick connected to your computer, so in this case you should use the value 1 as stickno. If you are using a gamepad, you might need to use stickno 2. For Xbox controllers, stickno will be a value between 0 and 3. For VR controllers, stickno will be either 0 or 1. For Oculus touch controllers, stickno 0 is the left hand and stickno 1 is the right hand. Use stickno -1 to get the status, position, or rotation of a connected VR headset.
command defines the operation that the command should perform. This should be one of the macros below:
STICK_JOY_STATUS - Queries the connectivity of the joystick. If the joystick is connected properly, then this command will return 0. If the return value is non-zero, then there is some error with the joystick's connectivity, and you can view the system console to see what the error is. The following errors apply:
MMSYSERR_NODRIVER - The joystick driver is not present.
MMSYSERR_INVALPARAM - Invalid joystick ID or hwnd is NULL.
JOYERR_NOCANDO - Cannot capture joystick input because a required service (such as a Windows timer) is unavailable.
JOYERR_UNPLUGGED - The specified joystick is not connected to the system.
JOYERR_PARMS - Invalid joystick ID or hwnd is NULL.
STICK_JOY_XPOS - Current X-coordinate of the joystick. This is a number between 0 and 65535. 0 means the joystick is pushed all the way to the left, 65535 means it is pushed all the way to the right, and 32768 is exactly in the center. If you are using a gamepad, then this is the x position of the left side joystick.
STICK_JOY_YPOS - Current Y-coordinate of the joystick. Again this is a number between 0 and 65535. 0 is up, 65535 is down. If you are using a gamepad, this is the position of the gamepad's left joystick.
STICK_JOY_ZPOS - Current Z-coordinate of the joystick. If you are using a joystick, this will usually be the current setting of the joystick's throttle. Again it is a value between 0 and 65535. If you are using a gamepad, this represents the y position of the right side joystick.
STICK_JOY_BUTTONS - Current state of the 32 joystick buttons. This is bitwise integer with each bit representing the state of a given button. For a joystick, the main trigger button is usually represented by the 0x00000001 bit, other buttons on the stick are 0x00000002 and 0x00000004, and buttons on the base of the joystick are then higher order bits. You will need to test these out on your own as each joystick is a little different.
STICK_JOY_SET_CAPTURE - This command sets the joystick capture to a FlexSim window that you specify. This command requires the win and p parameters to be passed in. By executing this command, joystick messages will be sent to the OnStick attribute of the view. For example, if you have an ortho view that you would like to listen to joystick events, you would call this command, passing the ortho view's HWND handle (use windowfromnode()), and a polling period. The period specifies a time interval in milliseconds to repeatedly call the OnStick event. If p is 0, then the OnStick event will only be called when the joystick's state changes. If p is greater than 0, then the OnStick event will simply be called at the end of each sample period interval. Example: stick(1,5, windowfromnode(sv()), 200); This will cause the OnStick event to be called every 200 milliseconds. In order for this to work, you need to add an OnStick attribute to the view (you may also need to rebind the view's attributes after adding it: right-click->Edit|Rebind Object Attributes).
STICK_JOY_RELEASE_CAPTURE - This command releases the joystick capture for the window that was previously captured with the 5 command. You need to pass in the win parameter as with command 5.
STICK_JOY_RPOS - Current position of the rudder or fourth joystick axis of the joystick. For a joystick, this is usually the rotation of the joystick if your joystick can rotate around its z axis. Again it is a number between 0 and 65535. If you are using a gamepad, it is the x position of the right side joystick.
STICK_JOY_UPOS - Current fifth axis position of the joystick.
STICK_JOY_VPOS - Current sixth axis position of the joystick.
STICK_JOY_POV - Current position of the point-of-view control of the joystick. It is a number between 0 and 35900 and represents the number of degrees times 100. For a gamepad, this represents the directional pad on the left of the gamepad. Up is 0, right is 9000, down is 18000, left is 27000. If the directional pad is not pressed, the value will be 65535. If you are using a joystick, there may be a directional thumb controller on the stick itself that you can press up, down, right, or left, and this will get the setting of that controller.
STICK_JOY_CURRENT_BUTTON - Current button number that is pressed.
STICK_JOY_FLAGS - Flags indicating the valid information returned about the joystick.
STICK_XBOX_STATUS - Queries the connectivity of the Xbox controller. If the controller is connected properly, this returns 0.
STICK_XBOX_BUTTONS - Bitmask of the device digital buttons. A set bit indicates that the corresponding button is pressed.
STICK_XBOX_LEFT_THUMB_X - Left thumbstick x-axis value. Each of the thumbstick axis members is a signed value between -32768 and 32767 describing the position of the thumbstick. A value of 0 is centered. Negative values signify down or to the left. Positive values signify up or to the right.
STICK_XBOX_LEFT_THUMB_Y - Left thumbstick y-axis value. The value is between -32768 and 32767.
STICK_XBOX_RIGHT_THUMB_X - Right thumbstick x-axis value. The value is between -32768 and 32767.
STICK_XBOX_RIGHT_THUMB_Y - Right thumbstick y-axis value. The value is between -32768 and 32767.
STICK_XBOX_LEFT_TRIGGER - The current value of the left trigger analog control. The value is between 0 and 255.
STICK_XBOX_RIGHT_TRIGGER - The current value of the right trigger analog control. The value is between 0 and 255.
STICK_VR_STATUS - Returns 1 if an Oculus Rift controller is active. Returns 2 if an HTC Vive controller is active. Returns 0 if the controller is inactive. Returns nullvar if the controller is not attached.
STICK_VR_THUMB_X - Thumbstick or trackpad x-axis value between -1 and 1.
STICK_VR_THUMB_Y - Thumbstick or trackpad y-axis value between -1 and 1.
STICK_VR_INDEX_TRIGGER - Index trigger value between 0 and 1.
STICK_VR_GRIP_TRIGGER - Grip trigger value between 0 and 1. On HTC Vive, grip button is pressed.
STICK_VR_BUTTON_1 - The first button is pressed. A or X on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_BUTTON_2 - The second button is pressed. B or Y on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_BUTTON_3 - The third button is pressed. Enter or Home on Oculus Rift. Menu on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_BUTTON_4 - The fourth button is pressed. Thumbstick on Oculus Rift. Trackpad on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_BUTTON_1 - The first button is touched. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_BUTTON_2 - The second button is touched. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_BUTTON_3 - The third button is touched. Unused on Oculus Rift.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_BUTTON_4 - The fourth button is touched.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_THUMB_REST - The thumb rest sensor is touched on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_INDEX_TRIGGER - The index trigger sensor is touched.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_POINTING - The hand gesture is pointing on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_TOUCH_THUMB_UP - The hand gesture is thumbs-up on Oculus Rift. Unused on HTC Vive.
STICK_VR_HAND_POSITION - The controller position in VR space.
STICK_VR_HAND_ROTATION - The controller rotation in VR rotation coordinates.
STICK_VR_HAND_WORLD_POSITION - The controller position in FlexSim world space.
STICK_VR_HAND_WORLD_ROTATION - The controller rotation in FlexSim rotation coordinates.
STICK_VR_HAND_OFFSET_POSITION - The controller's position in FlexSim world space, but with an offset applied based on the controller's rotation. Pass an array as the offset vector in the p parameter. You can use this option to get a point relative to the controller, such as a finger position or where the controller is pointing.
STICK_VR_TARGET_FLOOR_POSITION - The target position on the floor that the controller is pointing towards. Pass a value in the p parameter for the maximum distance away from the controller.
STICK_VR_SET_VIBRATION - Causes the controller to vibrate. On Oculus Rift, pass an array for the p parameter where the first element is a value between 0 and 1 for the frequency and the second element is a value between 0 and 1 for the amplitude. On HTC Vive, pass a duration in microseconds for the p parameter.
STICK_VR_SUBMIT_VIBRATION - Causes the controller to subtly vibrate. On original Oculus Touch controllers, pass an array of amplitudes (0 - 255) for the p parameter to be queued up and executed. Unused on HTC Vive or Oculus Rift S controllers.
Example
stick(1, STICK_JOY_YPOS); This gets the y position of the joystick id 1
suspenddraw
(num bitmask)
Description
For developer use. Bit mask. Disables draw in window types. Bits: 0 - TREE; 1 - PLANAR; 2 - SPATIAL
Example
suspenddraw(1)
switch_variable
(obj object, str var[, num off/on])
Description
For developer use. Add and set; or remove a dynamic switch variable to/from an object. When set to on, a node called var will be added to the structure of object and have a numerical value of 1 assigned to it. When set to off, a node called var, if present will be removed from the structure of object. Used in model update code.
Example
switch_variable(so(),"arrivalmode",1);
toggleallcodestates
(node startpoint, num ascpp)
Toggles all code nodes under startpoint as either C++ or flexscript
Description
Traverses the tree starting at start point and toggles all code nodes to either c++ or flexscript. 1 toggles to c++, 0 toggles to flexscript. This will only change nodes that have not been locked to their code state. This is the same as using the menu option Build|Make all code C++ or Build|Make all code flexscript.
Example
toggleallcodestates(model(), 1);
tracemaskevents
(num mask)
Description
For developer use. Set a 32 bit trace mask: Sum of Math.pow(2,N1)+Math.pow(2,N2)... where Nx are the event numbers to be reported in the trace. See View|Trace Debugger...
Example
tracemaskevents(listsum(Math.pow(2,1),Math.pow(2,2),Math.pow(2,3)))
tracemaskobject
(obj object)
Description
For developer use. Set an object to be included in the event reporting in the trace debugger. See View|Trace Debugger...
Example
tracemaskobject(Model.find("Processor3"))
tracemasktime
(num start, num end)
Description
For developer use. Define a start and end time for event reporting in the trace debugger. See View|Trace Debugger...
Example
tracemasktime(100,200)
uselisteners
(num mask)
Description
Enable or disable listening.
Example
uselisteners(1)
Drawing
Commands associated with drawing graphics in the planar, orthographic, or perspective views. Draw commands are designed for use in OnDraw events such as the "Custom Draw Code" field found in an object's Properties window.
bindtexture
(num textureid)
Description
This function is used in an OpenGL call sequence. When OpenGL commands are being used to draw a scene, this command will bind the texture loaded into FlexSim with the index textureid. Once bound, a texture will be used to render any polygons drawn subsequently. Texture mapping is the application (or mapping) of an image (or texture) to the surface of a polygon or other graphics primitive.
Example
bindtexture(10)
Use loaded texture with index number 10 for rendering any subsequent polygons
Use loaded texture with index number 10 for rendering any subsequent polygons
draw3dtext
(str text[, num asBitmap])
Draws text in a 3d view
Description
This command is similar to drawtext(), but can only be used in a 3D view, and its parameter set is stripped down to
provide direct access to the text rendering procedure. Whereas drawtext() does some automatic scaling based on the current object,
as well as some OpenGL state changes, etc., draw3dtext() calls the text drawing procedure directly, so any positioning, scaling,
color settings, etc., should be done with OpenGL commands, i.e. glTranslated(), glScaled(), glColor3d(), etc.
Example
draw3dtext(current.name);
drawbox
(num x, num y, num z, num sx, num sy, num sz, num glbegin)
Draws a simple box
Description
Draws a simple box. If glbegin is 1, then it will call glBegin before drawing.
This command is a shortcut way to draw an OpenGL type cube that allows more control over lighting,
coloring, and texturing than the drawcube() command.
Example
drawbox(5,0,0, 2,1,3, 1);
drawcolumn
(num x, num y, num z, num totalsides, num baseradius, num topradius, num height, num rx, num ry, num rz, num red {0-255}, num green {0-255}, num blue {0-255} [, num opacity {0-1}, num textureindex, num textureXrepeat, num textureYrepeat])
Draws a 3D column
Description
A very versatile command that can draw anything with multiple sides and a height such as a square, a pentagon, a pyramid, and even a cylinder (if the total number of sides is large).
Draws a column with its origin (center of base) positioned at x, y, z. The column is then defined by the number of sides, a base radius, a top radius, and a height. The column can be rotated in degrees about each axis with rx, ry, rz. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 255.
An optional opacity parameter will change the column from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be repeated textureXrepeat and textureYrepeat times on each face of the column.
The location, size and rotation of the column are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
Draws a column with its origin (center of base) positioned at x, y, z. The column is then defined by the number of sides, a base radius, a top radius, and a height. The column can be rotated in degrees about each axis with rx, ry, rz. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 255.
An optional opacity parameter will change the column from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be repeated textureXrepeat and textureYrepeat times on each face of the column.
The location, size and rotation of the column are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
Example
drawcolumn(0,0,0, 5 ,4,2, 6 ,0,0,0, 175,175,175, .6, 3, 5,1);
drawcube
(num x, num y, num z, num sx, num sy, num sz, num rx, num ry, num rz, num red {0-255}, num green {0-255}, num blue {0-255} [, num opacity {0-1}, num textureindex, num textureXrepeat, num textureYrepeat])
Draws a 3D cube
Description
Draws a cube with its origin (bottom left corner) positioned at x, y, z. Its length, width, and height is defined by sx, sy, and sz respectively. It can be rotated in degrees about the x, y, and z axis by rx, ry, and rz. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 255.
An optional opacity parameter will change the cube from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be repeated textureXrepeat and textureYrepeat times on each face of the cube.
The location, size and rotation of the cube are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
An optional opacity parameter will change the cube from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be repeated textureXrepeat and textureYrepeat times on each face of the cube.
The location, size and rotation of the cube are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
Example
drawcube(0,0,0, 5,3,2, 0,0,0, 175,175,175, .6, 3, 1,1);
drawcylinder
(num x, num y, num z, num baseradius, num topradius, num height, num rx, num ry, num rz, num red {0-255}, num green {0-255}, num blue {0-255} [, num opacity {0-1}, num textureindex])
Draws a 3D clyinder
Description
This command draws a hollow cylinder with its origin (center of base) positioned at x, y, z. The cylinder's dimensions are defined by a base radius, a top radius and a height. Use the drawdisk() command to cap off the ends of the cylinder. The cylinder can be rotated in degrees about the x, y, and z axis by rx, ry, and rz. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 255.
An optional opacity parameter will change the cylinder from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be used as texturing around the outside circumference of the cylinder.
The location, size and rotation of the cylinder are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
An optional opacity parameter will change the cylinder from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be used as texturing around the outside circumference of the cylinder.
The location, size and rotation of the cylinder are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
Example
drawcylinder(0,0,0, 1,1, 5, 0,0,0, 175,175,175, .6,3);
drawdisk
(num x, num y, num z, num innerradius, num outerradius, num startangle, num sweepangle, num rx, num ry, num rz, num red {0-255}, num green {0-255}, num blue {0-255} [, num opacity {0-1}, num textureindex])
Draw a 3D disk
Description
Draws a flat planar disk with its origin (center of radius) positioned at x, y, z. The disk's dimensions are defined by an inner radius, an outer radius, a start angle, and a sweep angle. A sweep angle of 360 makes a complete circle. An innerradius greater than 0 will create a disk with a hole in the middle of it. The disk can be rotated in degrees about the x, y, and z axis by rx, ry, and rz. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 255.
An optional opacity parameter will change the disk from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be used as texturing across the face of the disk.
The location, size and rotation of the disk are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
An optional opacity parameter will change the disk from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be used as texturing across the face of the disk.
The location, size and rotation of the disk are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
Example
drawdisk(0,0,0, .5,2, 90,270, 0,0,0, 175,175,175, 1,3);
drawflattext
(str text)
Description
This command can only be used in a 3D view. It draws a texture-mapped text string. This uses the same functionality that draws
the names and stats below objects. If scaled correctly, it draws a very crisp, readable text. Use this in conjunction with setdrawnamefunction()
to customize the data that is shown in the box below objects. Unlike drawtext(), this command's parameter set is much more stripped down, so you
should use gl commands (i.e. fglTranslate(), fglScale(), fglColor(), etc.) to set up the location, size, and render settings before drawing
the text.
Example
Add the following code to an object's Custom Draw Code trigger:
if(!param(2)) {
setdrawnamefunction(80, 15, c, param(1), 1);
} else {
fglTranslate(-40, -15, 0);
drawflattext("Hello World");
}
drawfont
(num font)
Specifies the font to be used with drawtext()
Description
Call before drawtext, to define font to be drawn. After drawtext is called, the font will be reset to default. There are currently 12 font types (numbers 0 through 11).
Example
drawfont(2)
drawimage
(obj view, str imagepath, num x, num y, num width, num height, num scaling)
Draws an image
Description
Draws the image at imagepath in the view. The scaling value specifies
how the image will be positioned and scaled.
NO_SCALE (or 0): Draws the image at location x,y with the width and height being based on the size of the image.
SCALE_DOWN: Draws the image centered in the rectangle created by x,y,width,height and scales the image proportionally down to fit if necessary.
SCALE_UP_DOWN: Draws the image centered in the rectangle created by x,y,width, height and scales the image proportionally up or down to fit.
SCALE_INDEPENDENT: Draws the image at x,y with the size of width and height.
NO_SCALE (or 0): Draws the image at location x,y with the width and height being based on the size of the image.
SCALE_DOWN: Draws the image centered in the rectangle created by x,y,width,height and scales the image proportionally down to fit if necessary.
SCALE_UP_DOWN: Draws the image centered in the rectangle created by x,y,width, height and scales the image proportionally up or down to fit.
SCALE_INDEPENDENT: Draws the image at x,y with the size of width and height.
Example
drawimage(c, "buttons\\visible_eye.png", 0, 10, 0, 0, 0);
drawline
(obj view, num x1, num y1, num z1, num x2, num y2, num z2, num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1})
Draws a planar line
Description
This command draws a planar line with a starting point of xloc1, yloc1, zloc1, and an ending point of xloc2, yloc2, zloc2. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 1.
Example
fglDisable(GL_LIGHTING);
drawline(view, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 1, 0, 0);
fglEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
This example draws a line from point (0,0,0) to point (2,2,2). The line will be red in color.
drawline(view, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 1, 0, 0);
fglEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
This example draws a line from point (0,0,0) to point (2,2,2). The line will be red in color.
drawobject
(obj view, num shapeindex, num textureindex[, num animation, treenode shapedata])
Draws a 3D shape
Description
Draws a 3d object with the specified shape and texture indices.
Example
drawtomodelscale(current);
drawobject(view,getshapeindex("fs3d//texturebox.wrl"),gettextureindex("flexsim.bmp"));
Set the drawing scale to that of the model, then draw the texturebox.wrl shape using flexsim.bmp as a texture.
drawobject(view,getshapeindex("fs3d//texturebox.wrl"),gettextureindex("flexsim.bmp"));
Set the drawing scale to that of the model, then draw the texturebox.wrl shape using flexsim.bmp as a texture.
drawpie
(obj view, num x, num y, num z, num x2, num y2, num z2, num startangle, num endangle, num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1})
Draws a flat pie shape
Description
Draws a flat pie shape with its origin (center of radius) positioned at the midpoint between [x1,y1,z1] and [x2,y2,z2]. The angles are measured in degrees counterclockwise from the positive x axis. Negative angles are measured clockwise. The pie is filled from the start angle to the endangle counterclockwise. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 1.
Example
drawpie(view,3,3,0,0,0,0,45,90,0.5,0,0);
drawquad
(obj view, num x1, num y1, num z1, num x2, num y2, num z2, num x3, num y3, num z3, num x4, num y4, num z4, num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1})
Draws a planar quadrilateral
Description
This command draws a planar quadrilateral with vertices defined by x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, x3, y3, z3, x4, y4, and z4. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 1. The resultant shape and lighting is dependent on the order or sequence in which the vertices are defined. If vertices are all in one plane, consider using drawrectangle() command.
Example
drawquad(view, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 4, 5, 6, 1, 0, 0);
This example draws a quadrilateral with vertices defined by the following four points: (0,0,0), (1,0,0), (2,2,2), and (4,5,6). The quadrilateral will be red in color.
This example draws a quadrilateral with vertices defined by the following four points: (0,0,0), (1,0,0), (2,2,2), and (4,5,6). The quadrilateral will be red in color.
drawrect
(obj view, num x1, num y1, num z1, num x2, num y2, num z2, num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1})
Draws a planar rectangle
Description
This command draws a planar rectangle with opposite corners defined by x1, y1, z1, and x2, y2, and z2. Both points must lie in a plane parallel to the xy plane.
The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 1.
This command can be called in a planar, 3D, graph, or panel view. See also drawquad()
Example
drawrect(view, 0,0,.5, 1, 1, .5, 1, 0, 0);
Draws a red rectangle with opposite corners (0,0,.5) and (1,1,.5).
Draws a red rectangle with opposite corners (0,0,.5) and (1,1,.5).
drawrectangle
(num x, num y, num z, num length, num width, num rx, num ry, num rz, num red {0-255}, num green {0-255}, num blue {0-255} [, num opacity {0-1}, num textureindex, num textureXrepeat, num textureYrepeat])
Draw a 3D rectangle
Description
Draws a flat planar rectangle with a user-defined location, length, width, rotation, and color. The drawquad() command must be used to draw a rectangle that is not parallel with the x, y or z plane.
An optional opacity parameter will change the rectangle from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be repeated textureXrepeat and textureYrepeat times across the face of the rectangular plane as texturing.
The location, size and rotation of the rectangle are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
An optional opacity parameter will change the rectangle from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be repeated textureXrepeat and textureYrepeat times across the face of the rectangular plane as texturing.
The location, size and rotation of the rectangle are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
Example
drawrectangle(0,0,0, 2,3, 0,0,0, 175,175,175, .6, 1, 2,3);
drawshadow
(num phase (1,2,3))
In OnDraw: draw shadow volume
Description
In OnDraw: draw shadow volume
Example
drawshadow(1);
drawsphere
(num x, num y, num z, num radius, num red {0-255}, num green {0-255}, num blue {0-255} [, num opacity {0-1}, num textureindex])
Draw a 3D sphere
Description
Draws a hollow sphere with its origin (center of sphere) positioned at x, y, z. The sphere's dimensions are defined by a single radius. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 255.
An optional opacity parameter will change the sphere from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be wrapped over the surface of the sphere as a texture.
The location, size and rotation of the sphere are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
An optional opacity parameter will change the sphere from clear (0) to opaque (1). If a valid textureindex number is entered, then the associated image will be wrapped over the surface of the sphere as a texture.
The location, size and rotation of the sphere are by default relative to the object it is drawn on. The optional parameters shown in brackets [ ] must ALL be used or ALL not used. The textureindex is a numeric value that can be learned using the gettextureindex() command or through the Tools | Media Files menu.
Example
drawsphere(0,0,0,5,175,175,175,1,3);
drawtext
(obj view, str text, num x, num y, num z [, num width, num height, num thickness, num rx, num ry, num rz, num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1} , num opacity {0-1}, num flags])
Draws text
Description
This command draws text at a location defined by x, y, and z.
The width parameter is not used. The text width and height is determined by the height parameter.
The rotation is defined by rx, ry, and rz. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 1. You can
define the flags parameter as follows: 0x1 = bold, 0x2 = italic, 0x4 = underline. The flags parameter only applies to non-3d views
The opacity if used should be a number ranging between 0 (full transparency) to 1 (opaque).
Call drawfont() command to change font type before calling drawtext() if desired.
This command can be used in a planar, 3D, graph or panel view.
Example
drawtext(view, "Hello", 0,0,0, 0,.3,.1, 90,0,0, 1,0,0, .8);
This example draws "Hello" at location (0,0,0) with size 0.3, thickness 0.1, rotation (90,0,0), an rgb color (1,0,0), and opacity of 0.8.
This example draws "Hello" at location (0,0,0) with size 0.3, thickness 0.1, rotation (90,0,0), an rgb color (1,0,0), and opacity of 0.8.
drawtomodelscale
(obj object)
Gets the current drawing scale of the model
Description
Returns the current drawing scale to that of the model after a previous call of drawtoobjectscale(). This is equivalent to the following OpenGL function:
glScalef(1/object.location.x,1/object.location.y,1/object.location.z);
glScalef(1/object.location.x,1/object.location.y,1/object.location.z);
Example
drawtomodelscale(current);
drawtoobjectscale
(obj object)
Scale subsequent draw commands to the size of the object
Description
This command causes all subsequent draw commands to be scaled according to the size of the object. This is equivalent to the following OpenGL function:
glScalef(object.location.x,object.location.y,object.location.z);
By default, the scale is originally set to that of the object.
glScalef(object.location.x,object.location.y,object.location.z);
By default, the scale is originally set to that of the object.
Example
drawtoobjectscale(current);
drawtriangle
(obj view, num x1, num y1, num z1, num x2, num y2, num z2, num x3, num y3, num z3, num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1})
Draws a planar triangle
Description
This command draws a planar triangle with vertices defined by xloc1, yloc1, zloc1, xloc2, yloc2, zloc2, xloc3, yloc3, and zloc3. The color is defined by the red, green, blue color components ranging from 0 to 1.
Example
drawtriangle(view, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0);
This example draws a triangle with vertices defined by the following three points: (0,0,0), (1,0,0), and (0,1,0). The triangle will be red in color.
This example draws a triangle with vertices defined by the following three points: (0,0,0), (1,0,0), and (0,1,0). The triangle will be red in color.
fglColor
(num red {0-1}, num green {0-1}, num blue {0-1}[, num alpha {0-1}])
Sets the color for drawing a mesh in OpenGL
Description
Sets the color for drawing a mesh in OpenGL. The rgb color components are between 0 and 1. The optional alpha component is between 0 (transparent) and 1 (opaque).
Example
fglDisable
(num setting)
Disables an OpenGL draw setting
Description
Disables an OpenGL draw setting. See glEnable() for list of draw settings.
You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
fglDisable(GL_LIGHTING);
fglEnable
(num setting)
Enables an OpenGL draw setting
Description
Enables an OpenGL draw setting.
Note that for optimization purposes, FlexSim's drawing engine does not automatically restore the
enabled/disabled state of a given setting, so it is up to you, if you use this command, to restore
the setting to its default after you have executed your drawing functionality. Failing to restore
a setting to its default will result in weird rendering of other objects in the model.
Common OpenGL draw settings:
GL_LIGHTING
Turns lighting on and off.
Turn it on if polygons do not change color when they turn away from the viewer.
Default: enabled.
GL_CULL_FACE
Turns back-face culling on and off
Turn it off if you want both sides (front and back) of all polygons drawn.
Default: disabled.
GL_TEXTURE_2D
Turns texturing on and off.
Turn it off if a texture is being displayed and you don't want it there.
Default: enabled.
You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation on glEnable() for more information if needed.
Common OpenGL draw settings:
GL_LIGHTING
Turns lighting on and off.
Turn it on if polygons do not change color when they turn away from the viewer.
Default: enabled.
GL_CULL_FACE
Turns back-face culling on and off
Turn it off if you want both sides (front and back) of all polygons drawn.
Default: disabled.
GL_TEXTURE_2D
Turns texturing on and off.
Turn it off if a texture is being displayed and you don't want it there.
Default: enabled.
You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation on glEnable() for more information if needed.
Example
fglEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
fglinfo
(num operation, obj view)
Gets information about a 3D view's draw state
Description
This command gives you access to various information about the draw state of a 3d view.
Logic/data that is performed/returned is based on the operation parameter, as follows:
FGL_INFO_SHADERTYPE - returns what part of the draw pass is happening, such as rendering the shadow map (SHADERTYPE_RENDER_SHADOWS), blurring the shadow map (SHADERTYPE_BLUR), or rendering the objects to the screen (SHADERTYPE_DEFAULT).
FGL_INFO_SHADERTYPE - returns what part of the draw pass is happening, such as rendering the shadow map (SHADERTYPE_RENDER_SHADOWS), blurring the shadow map (SHADERTYPE_BLUR), or rendering the objects to the screen (SHADERTYPE_DEFAULT).
Example
/*do not draw this object when rendering the shadow map*/
if (fglinfo(FGL_INFO_SHADERTYPE, view) == SHADERTYPE_RENDER_SHADOWS)
return 0;
if (fglinfo(FGL_INFO_SHADERTYPE, view) == SHADERTYPE_RENDER_SHADOWS)
return 0;
fglLoadIdentity
()
Description
Loads the identity matrix into the current OpenGL drawing context, or in other words, replaces the current matrix with the
identity matrix. A matrix is just a way to specify a whole bunch of n-dimensional transformations in one convenient package. Loading
the identity matrix is simply a way of resetting things to the origin, so there's no rotation, translation or scaling. The default
position is (0,0,0) and the default orientation is looking down the negative z-axis. You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation for
more information if needed.
Example
fglLoadIdentity()
fglMatrixMode
(num mode)
Specifies which matrix stack is the target for subsequent matrix operations
Description
Specifies which matrix stack is the target for subsequent matrix operations. A matrix is just a way to specify a whole bunch of n-dimensional transformations in one convenient package. Three values are accepted: GL_MODELVIEW, GL_PROJECTION, and GL_TEXTURE. The initial value is GL_MODELVIEW which is used when moving objects around the scene. You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
fglMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
fglNormal
(num x, num y, num z)
Sets the normal vector for shading subsequent vertices in OpenGL
Description
Sets the normal vector for shading subsequent vertices in OpenGL drawing.
Polygons will be flat shaded unless normals are applied to them.
A normal is a vector that is perpendicular to the polygon and points in the direction the
polygon is facing. Remember polygons with vertices defined in a counter-clockwise winding
points forward per the "right-hand rule". Polygon shading is based on the angle between
the normals and the light source. Normals are applied to each vertex in the same way
colors are, but is usually just defined at the start of each polygon definition. When a
polygon's normals point directly at the light source, they are brightly shaded; and are
darker shaded when the angles are skewed. You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation
for more information if needed.
Example
fglNormal(1,0,0);
fglPopMatrix
()
Pops the current OpenGL drawing context from the matrix stack
Description
Pops the current OpenGL drawing context from the matrix stack, or in other words returns to the space on the top of the stack. The OpenGL stack stores the space matrix in a LIFO fashion. You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
fglPopMatrix();
fglPushMatrix
()
Pushes the current OpenGL drawing context onto the matrix stack
Description
Pushes the current OpenGL drawing context onto the matrix stack which can later be retrieved with glPopMatrix(). If you are drawing more than one object and you don't want the glTranslated, glRotated or glScaled to affect the next objects, you should use glPushMatrix and glPopMatrix. The OpenGL stack stores the space matrices in a LIFO fashion. You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
fglPushMatrix();
fglRotate
(num degrees, num x, num y, num z)
Rotates the current OpenGL drawing context by degrees around axis x,y,z
Description
Rotates the current OpenGL drawing context by degrees around an axis defined by the vertex (x,y,z). Anything drawn after
a rotation is based on the new rotation of the axes. See glVertex3d for definition of the OpenGL xyz coordinate system. You can refer
to standard OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
fglRotate(90,1,0,0);
fglScale
(num x, num y, num z)
Scales the current OpenGL drawing context by x,y,z
Description
Scales the current OpenGL drawing context by the given scale parameters. See glVertex3d for definition of the OpenGL xyz
coordinate system. Anything drawn after this command is based on the change in scale of the axes. You can refer to standard OpenGL
documentation for more information if needed.
Example
fglScale(2,4,1);
fglTranslate
(num x, num y, num z)
Translates the current OpenGL drawing context by x,y,z
Description
Translates the current OpenGL drawing context by the given translation parameters. See glVertex3d for definition of the
OpenGL xyz coordinate system. Anything drawn after a translation is based on the new location of the axes. You can refer to standard
OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
fglTranslate(15, 4, 0);
getdrawtextmetric
(str text, num fontsize, num metric[, num a])
Description
Returns information about the text. If metric is 1, it will return the width of the text. If metric is 2, it will return the height of the text. If metric is 3, it will return the max fitting length of the text using 'a' as the max extent.
Example
getdrawtextmetric("Hello",12,1,0);
glIsEnabled
(num setting)
Returns 1 if the OpenGL setting is enabled, 0 otherwise
Description
Returns 1 if the OpenGL setting is enabled, 0 otherwise. See fglEnable() for list of draw settings.
Note that this is an extremely slow operation and is discouraged.
You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
glIsEnabled(GL_LIGHTING)
glLineWidth
(num linewidth)
Specifies the line width for subsequent lines draw in OpenGL
Description
Specifies the line width for subsequent lines drawn in OpenGL. You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
glLineWidth(3);
glPointSize
(num pointsize)
Specifies the point size in pixels for subsequent vertices drawn in OpenGL
Description
Specifies the point size in pixels for subsequent vertices drawn in OpenGL. You can refer to standard OpenGL documentation for more information if needed.
Example
glPointSize(5);
mesh
(node meshnode, int pervertexattribs, int flags)
Creates an empty mesh and assigns it to meshnode
Description
Creates an empty mesh and assigns it to meshnode. The pervertexattribs takes a bit-wise ORed combination of the following attributes:
MESH_POSITION (Added by default)
MESH_TEX_COORD2
MESH_NORMAL
MESH_DIFFUSE
MESH_DIFFUSE4
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE4
Flags can be any of the following:
MESH_STATIC_DRAW
MESH_DYNAMIC_DRAW
MESH_INDEXED
MESH_POSITION (Added by default)
MESH_TEX_COORD2
MESH_NORMAL
MESH_DIFFUSE
MESH_DIFFUSE4
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE4
Flags can be any of the following:
MESH_STATIC_DRAW
MESH_DYNAMIC_DRAW
MESH_INDEXED
Example
mesh(Model.find("mesh"), MESH_NORMAL | MESH_DIFFUSE, MESH_STATIC_DRAW)
meshaddindex
(node meshnode, int index)
Adds an indexed vertex to a mesh
Description
Adds an indexed vertex to the mesh associated with meshnode.
This command is ignored if the mesh does not have a MESH_INDEXED flag.
Example
int newindex = meshaddindex(node("/mesh",model()), 4)
meshaddvertex
(node meshnode)
Adds a vertex to a mesh
Description
Adds a vertex to the mesh associated with meshnode.
Returns the index of the added vertex.
Returns the index of the added vertex.
Example
meshaddvertex(Model.find("mesh"))
meshdraw
(node meshnode, int drawmode, int offset, int count [, int stride])
Draws a mesh
Description
Draws the mesh associated with meshnode. The value for drawmode can be any of the following:
GL_POINTS
GL_LINES
GL_LINE_LOOP
GL_TRIANGLES
GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP
GL_TRIANGLE_FAN
Offset specifies which vertex index to begin at. Count specifies how many vertexes to set the drawmode. Stride specifies how many vertex indexes to skip between.
For an indexed meshed, stride is ignored.
GL_POINTS
GL_LINES
GL_LINE_LOOP
GL_TRIANGLES
GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP
GL_TRIANGLE_FAN
Offset specifies which vertex index to begin at. Count specifies how many vertexes to set the drawmode. Stride specifies how many vertex indexes to skip between.
For an indexed meshed, stride is ignored.
Example
meshdraw(node("/mesh",model()), GLTRIANGLES, 0, 3, 0)
meshinfo
(node meshnode, int type[,int index, int param])
Gets the specified information from a mesh
Description
Gets the specified information from the mesh associated with meshnode. Index is the index of the requested vertex (base 0). Type is specified as one of the following for the mesh (index and param ignored):
MESH_PER_VERTEX_ATTRIBS
MESH_PER_MESH_ATTRIBS
MESH_FLAGS
MESH_NR_VERTS
MESH_GET_INDEX - Returns the vertex index for the given index (only valid with MESH_INDEXED flag)
The following are vertex specific types:
MESH_POSITION
MESH_TEX_COORD2
MESH_NORMAL
MESH_DIFFUSE
MESH_DIFFUSE4
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE4
If specifying a vertex, the following are valid for param:
MESH_COLOR_RED
MESH_COLOR_GREEN
MESH_COLOR_BLUE
MESH_COLOR_ALPHA
MESH_POS_X
MESH_POS_Y
MESH_POS_Z
MESH_TEX_S
MESH_TEX_T
MESH_PER_VERTEX_ATTRIBS
MESH_PER_MESH_ATTRIBS
MESH_FLAGS
MESH_NR_VERTS
MESH_GET_INDEX - Returns the vertex index for the given index (only valid with MESH_INDEXED flag)
The following are vertex specific types:
MESH_POSITION
MESH_TEX_COORD2
MESH_NORMAL
MESH_DIFFUSE
MESH_DIFFUSE4
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE4
If specifying a vertex, the following are valid for param:
MESH_COLOR_RED
MESH_COLOR_GREEN
MESH_COLOR_BLUE
MESH_COLOR_ALPHA
MESH_POS_X
MESH_POS_Y
MESH_POS_Z
MESH_TEX_S
MESH_TEX_T
Example
double xposition = meshinfo(Model.find("mesh"), MESH_POSITION, 6, MESH_POS_X)
meshsetattrib
(node meshnode, int attribid, double param1 [, double param2, double param3, double param4])
Adds/sets the value of attribid to the vertindex of a mesh
Description
Sets the value of attribid to be applied to the entire mesh associated with meshnode. The following attributes can be used as the attribid:
MESH_NORMAL
MESH_AMBIENT
MESH_DIFFUSE
MESH_DIFFUSE4
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE4
MESH_SPECULAR
MESH_SHININESS
MESH_EMISSIVE
MESH_NORMAL
MESH_AMBIENT
MESH_DIFFUSE
MESH_DIFFUSE4
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE4
MESH_SPECULAR
MESH_SHININESS
MESH_EMISSIVE
Example
meshsetattrib(Model.find("mesh"), 1, MESH_DIFFUSE4, 1, 0, 0, 1)
meshsetvertexattrib
(node meshnode, int vertindex, int attribid, double param1 [, double param2, double param3, double param4])
Sets the value of attribid at the vertindex of a mesh
Description
Sets the value of attribid at the vertindex of the mesh associated with meshnode. The following attributes can be used as the attribid:
MESH_POSITION
MESH_TEX_COORD2
MESH_NORMAL
MESH_DIFFUSE
MESH_DIFFUSE4
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE4
Note: The attribid must be defined previously when creating the mesh.
MESH_POSITION
MESH_TEX_COORD2
MESH_NORMAL
MESH_DIFFUSE
MESH_DIFFUSE4
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE
MESH_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE4
Note: The attribid must be defined previously when creating the mesh.
Example
mesh(Model.find("mesh"), MESH_NORMAL | MESH_DIFFUSE4, MESH_STATIC_DRAW)
meshsetvertexattrib(Model.find("mesh"), 1, MESH_DIFFUSE4, 1, 0, 0, 1)
meshsetvertexattrib(Model.find("mesh"), 1, MESH_DIFFUSE4, 1, 0, 0, 1)
setdrawnamefunction
(num boxwidth, num boxheight, node nodefunction[, num pval1, num pval2, num pval3])
Description
This command gives direct access to the functionality that displays information in boxes below objects in the model.
FlexSim's 3D display mechanism works by performing multiple drawing passes over the objects in the model. First, it gathers and caches
data for what needs to be drawn. Then it goes through and draws the object shapes and calls the objects' custom draw functionality. Finally it
draws any overlays such as connectors, information boxes, etc. The setdrawnamefunction() command, if called as part of an object's custom draw
functionality, i.e. its OnDraw event or its Custom Draw Code trigger, will cause a callback to be fired when the drawing sequence gets to the
information box step for that object. To do this, call the command and specify the size that you want the box to be drawn, and pass as the nodefunction
parameter a reference to a node holding the code you want to fire to draw the box information, as well as up to 3 parameters that will be passed
as param(1), param(2), and param(3) into that nodefunction. Then implement the nodefunction code to draw any information you want, using the
drawflattext() command, or any other OpenGL drawing commands. Note that when the nodefunction is call, the OpenGL model view matrix will be set so
that the (0,0,0) point is at the top-center of the display box, and one length unit represents one pixel on the screen.
Example
Add the following code to an object's Custom Draw Code trigger:
if(!param(2)) {
setdrawnamefunction(80, 15, c, param(1), 1);
} else {
fglTranslate(-40, -15, 0);
drawflattext("Hello World");
}
spacebase
([num view/object])
Description
Set the OpenGL matrix to the scaled space of the current object/view. If the parameter is 0, then the object's base space matrix will be loaded. If the parameter is 1, then the view's space will be loaded, meaning any subsequent draw commands will face the viewer directly and not change scale. This command can only be used in OnDraw event and Custom Draw Code trigger. See drawtoobjectscale() when scaling the OpenGL space by the object's size.
Example
spacebase(0);
spacerotate
(num x, num y, num z)
Description
Apply rotation to the OpenGL space. This corresponds to the following OpenGL code (keep in mind that OpenGL coordinate systems have y pointing in the direction of FlexSim's z axis, and have z pointing in the direction of FlexSim's -y axis):
glRotatef( z, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
glRotatef(-y, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
glRotatef( x, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
glRotatef( z, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
glRotatef(-y, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
glRotatef( x, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
Example
spacerotate(90, 0, 0)
This rotates the current coordinate space by 90 degrees around the FlexSim x-axis. Subsequent draw commands will be performed from this new rotation.
This rotates the current coordinate space by 90 degrees around the FlexSim x-axis. Subsequent draw commands will be performed from this new rotation.
spacescale
(num x, num y, num z)
Description
Apply scale transform to the OpenGL space. This corresponds to the following OpenGL code (keep in mind that OpenGL coordinate systems have y pointing in the direction of FlexSim's z axis, and have z pointing in the direction of FlexSim's -y axis):
glScalef(x,z,y);
glScalef(x,z,y);
Example
spacescale(2, 1, 1)
This scales the current coordinate space by 2 times in the FlexSim x direction. Subsequent draw commands will be performed from this new scaling.
This scales the current coordinate space by 2 times in the FlexSim x direction. Subsequent draw commands will be performed from this new scaling.
spacetranslate
(num x, num y, num z)
Description
Apply translation to the OpenGL space. This corresponds to the following OpenGL code (keep in mind that OpenGL coordinate systems have y pointing in the direction of FlexSim's z axis, and have z pointing in the direction of FlexSim's -y axis):
glTranslatef(x,z,-y);
glTranslatef(x,z,-y);
Example
spacetranslate(current.size.x, -current.size.y, 0)
This translates to the bottom left corner of the object assuming no translation has previously been applied. Subsequent draw commands will be performed from this new location.
This translates to the bottom left corner of the object assuming no translation has previously been applied. Subsequent draw commands will be performed from this new location.
textureaxis_s
(num x, num y, num z, num a)
Description
Once we have a texture bound in an OpenGL call sequence, we can specify the texture coordinates. OpenGL uses the concept of texture coordinates for mapping. This function is used to set the texture S axis. Once set, the texture axes will be used to render any polygons drawn subsequently.
Example
textureaxis_s(1,0,0,0)
textureaxis_t
(num x, num y, num z, num a)
Description
Once we have a texture bound in an OpenGL call sequence, we can specify the texture coordinates. OpenGL uses the concept of texture coordinates for mapping. This function is used to set the texture T axis. Once set, the texture axes will be used to render any polygons drawn subsequently.
Example
textureaxis_t(0,0,1,0)
Events
Commands for creating, searching and manipulating events.
addtoeventtypelegend
(str name, num parameter, num value, str legendname)
Description
The eventtype legend allows you to associate a string with a given value for a given parameter in that eventtype.
Passing a negative number for 'parameter' allows you to add a preceeding string to explain the parameter.
If the 'parameter' is negative and the 'value' is -1, then it assumes the number is a pointer to a node and will display the node's path as a string.
Example
addtoeventtypelegend(index,-1,-1,"resource: "); // for p1, display the text "resource: " and display the path for the object
addtoeventtypelegend(index,-2,0,"covermode: "); // for p2, display the text "covermode: "
addtoeventtypelegend(index,2,1,"YellowToGreen"); // for p2, a value of 1 should display "YellowToGreen" instead of the number 1
addtoeventtypelegend(index,2,2,"RedToGreen"); // for p2, a value of 2 should display "RedToGreen" instead of the number 2
addtoeventtypelegend(index,3,0,""); // for p3, this makes zeroes blank
addtoeventtypelegend(index,4,0,""); // for p4, this makes zeroes blank
addtoeventtypelegend(index,-2,0,"covermode: "); // for p2, display the text "covermode: "
addtoeventtypelegend(index,2,1,"YellowToGreen"); // for p2, a value of 1 should display "YellowToGreen" instead of the number 1
addtoeventtypelegend(index,2,2,"RedToGreen"); // for p2, a value of 2 should display "RedToGreen" instead of the number 2
addtoeventtypelegend(index,3,0,""); // for p3, this makes zeroes blank
addtoeventtypelegend(index,4,0,""); // for p4, this makes zeroes blank
createevent
(obj object, num time, num code[, str data, node involved])
Description
For developer use. This command creates an event that will occur sometime in the future in the model's run. The event will be created for the object specified by object. It will occur time seconds from the time that this command is called. If an event needs to occur that the same simulation time that it was created at, time should be 0. When the event occurs, the OnTimerEvent event function of the class of object will be called. This function will be passed code, data, and involved. These values can be accessed in OnTimerEvent as eventcode, eventdata, and i. Generally, eventcode is used to determine what type of event is being created or executed. Eventdata is used as a description of the event for the user's benefit. It is generally not important to the execution of OnTimerEvent. Any objects that are involved in the event, such as a flowitem that is entering or exiting, are passed as involved and are referenced in OnTimerEvent as i. There are predefined values for code that the user should use listed below:
1 - EVENT_OPENINPUTS
2 - EVENT_OPENOUTPUTS
3 - EVENT_PROCESSFINISH
4 - EVENT_CREATEPART
5 - EVENT_DESTROYPRODUCT
6 - EVENT_CONVEYEND
7 - EVENT_BEGINLOADTIME
8 - EVENT_BEGINUNLOADTIME
9 - EVENT_ENDLOADTIME
10 - EVENT_ENDUNLOADTIME
11 - EVENT_ENDDELAYTIME
12 - EVENT_BEGINDOWNTIME
13 - EVENT_ENDDOWNTIME
14 - EVENT_ENDWAITTIME
15 - EVENT_MEETBATCHQTY
16 - EVENT_ENDTRAVELTIME
17 - EVENT_ENDSETUP
If a user wishes to create their own types of events, they should use values for code that are greater than 100. See also eventcode and eventdata.
1 - EVENT_OPENINPUTS
2 - EVENT_OPENOUTPUTS
3 - EVENT_PROCESSFINISH
4 - EVENT_CREATEPART
5 - EVENT_DESTROYPRODUCT
6 - EVENT_CONVEYEND
7 - EVENT_BEGINLOADTIME
8 - EVENT_BEGINUNLOADTIME
9 - EVENT_ENDLOADTIME
10 - EVENT_ENDUNLOADTIME
11 - EVENT_ENDDELAYTIME
12 - EVENT_BEGINDOWNTIME
13 - EVENT_ENDDOWNTIME
14 - EVENT_ENDWAITTIME
15 - EVENT_MEETBATCHQTY
16 - EVENT_ENDTRAVELTIME
17 - EVENT_ENDSETUP
If a user wishes to create their own types of events, they should use values for code that are greater than 100. See also eventcode and eventdata.
Example
if (current.subnodes.length >= current.mincontent)
{
createevent(current,5,EVENT_OPENOUTPUTS,"openoutputs",involved);
}
This creates an event that will occur in 5 simulation seconds that will open the output ports of the object specified as current, for the flowitem specified by involved, if the content of current is less than the label called mincontent of the object referenced by current.
{
createevent(current,5,EVENT_OPENOUTPUTS,"openoutputs",involved);
}
This creates an event that will occur in 5 simulation seconds that will open the output ports of the object specified as current, for the flowitem specified by involved, if the content of current is less than the label called mincontent of the object referenced by current.
createtickevent
(obj fluidobject)
Creates a tick event for fluidobject and all objects assigned to that Ticker
Description
Creates a Tick event for the Fluid Object that is passed in and all of the other Fluid Objects that are controlled by the same Ticker. This allows the user to cause fluid material to move at times that are not the Ticker's normal tick times. The user can also pass a specific Ticker as the parameter to this command.
Example
createtickevent(current);
delayevents
(num value)
Description
For developer use. Delay all events in the eventlist. The times of all events in the eventlist will be incremented by value.
Example
delayevents(20)
delayeventsofobject
(obj object, num value)
Description
For developer use. Delay events of object. The timed events of object are incremented by value, and the eventlist re-sorted. Value may be positive or negative.
Example
delayeventsofobject(model().subnodes[2],20)
destroyevent
(node event)
Description
For developer use. Destroys a particular event from the event list.
Example
destroyevent(node("MAIN:/1/exec/events").last)
destroyeventsofobject
(obj object [, num simtime, num code, str data, node involved])
Destroys events associated with object
Description
Destroys events associated with the given object. The first parameter, object, is the only required parameter. Other parameters are optional and provide a filter for choosing which events to destroy, as follows:
time: If greater than or equal to the time that that the command is called, this parameter will filter events by their time. If the event's time is not equal to the time passed in, then the event will not be destroyed. Pass -1 if you don't want this as a filter.
code: If greater than 0, this parameter filters events by their event code. If the event's code is not equal to the code passed in, the event will not be destroyed.
data: If not NULL, this parameter filters events by the data string associated with the event. If the event's data string is not equal to the string passed in, the event will not be destroyed.
involved: If not NULL, this parameter filters events by their involved node or object. If the event's involved node is not equal to the node passed in, the event will not be destroyed.
time: If greater than or equal to the time that that the command is called, this parameter will filter events by their time. If the event's time is not equal to the time passed in, then the event will not be destroyed. Pass -1 if you don't want this as a filter.
code: If greater than 0, this parameter filters events by their event code. If the event's code is not equal to the code passed in, the event will not be destroyed.
data: If not NULL, this parameter filters events by the data string associated with the event. If the event's data string is not equal to the string passed in, the event will not be destroyed.
involved: If not NULL, this parameter filters events by their involved node or object. If the event's involved node is not equal to the node passed in, the event will not be destroyed.
Example
destroyeventsofobject(model().subnodes[2])
destroymessageevents
(obj object, num time, obj fromobj[, num param1, num param2, num param3])
Destroys message events associated with object
Description
Destroys message events associated with the given object.
If no message parameters are included, all message events will be destroyed.
If no message parameters are included, all message events will be destroyed.
Example
destroymessageevents(current, time(), NULL, 8)
eventcode
<no parentheses>
Description
For developer use. This command returns the number value that was passed to the createevent() command as code. It is only used in the OnTimerEvent function of the library objects. It is generally used to identify the type of event that is occurring. This command should not have parentheses when it is called. See also createevent() and eventdata.
Example
if (eventcode == EVENT_OPENINPUTS)
thisobjectdata->openinputs();
This calls a method called openinputs() on the object referenced by thisobjectdata if the value EVENT_OPENINPUTS was passed to the createevent() function.
thisobjectdata->openinputs();
This calls a method called openinputs() on the object referenced by thisobjectdata if the value EVENT_OPENINPUTS was passed to the createevent() function.
eventdata
<no parentheses>
Description
For developer use. This command returns the string value that was passed to the createevent() command as data. It is only used in the OnTimerEvent function of the library objects. Generally, it is used as a description to the user of the type of event that is occurring. It is not generally used in the execution of the OnTimerEvent function, for speed reasons. This command should not have parentheses when it is called. See also createevent() and eventcode.
Example
if (comparetext(eventdata,"openinputs"))
{
thisobjectdata->openinputs();
}
This calls a method called openinputs on the object referenced by thisobjectdata if the string value passed to createevent() is equal to "openinputs".
{
thisobjectdata->openinputs();
}
This calls a method called openinputs on the object referenced by thisobjectdata if the string value passed to createevent() is equal to "openinputs".
eventget
(num index, num thing)
An event attribute for the event at index
Description
Returns an event attribute at the specified index in MAIN:/project/exec/events.
thing can be:
1 = client
2 = time
3 = code
4 = data
5 = involved
6 = event node
thing can be:
1 = client
2 = time
3 = code
4 = data
5 = involved
6 = event node
Example
eventget(2,3)
eventloginfo
(num operation, num n1)
Description
For developer use. Returns a string value describing something related to the Event Log.
Operations:
ELI_GET_OBJECTPATH 1 - returns the path of the object at index n1 from the objectpaths array.
ELI_GET_INVOLVEDPATH 2 - returns the path of the object at index n1 from the involvedpaths array.
ELI_GET_OTHERPATH 3 - returns the path of the object at index n1 from the otherpaths array.
ELI_EVENTTYPE_NAME 4 - returns the name of the eventtype at index n1 from the eventtypes array.
ELI_LOGGEDEVENTTYPE_NAME 5 - returns the name of the logged eventtype at index n1 from the loggedeventtypes array.
Other operations relating to the Event Log that return number values can be accessed using the applicationcommand() function:
"seteventlogging" - enables or disables logging for eventtype n1.
"geteventlogging" - returns whether logging is enabled for eventtype n1.
"getobjectpathslistsize" - returns the size of the objectpaths array.
"getinvolvedpathslistsize" - returns the size of the involvedpaths array.
"getotherpathslistsize" - returns the size of the otherpaths array.
"geteventtypeslistsize" - returns the size of the eventtypes array.
"getloggedeventtypeslistsize" - returns the size of the loggedeventtypes array.
"geteventtypecode" - returns the index of the eventtype by name passed as n1.
Operations:
ELI_GET_OBJECTPATH 1 - returns the path of the object at index n1 from the objectpaths array.
ELI_GET_INVOLVEDPATH 2 - returns the path of the object at index n1 from the involvedpaths array.
ELI_GET_OTHERPATH 3 - returns the path of the object at index n1 from the otherpaths array.
ELI_EVENTTYPE_NAME 4 - returns the name of the eventtype at index n1 from the eventtypes array.
ELI_LOGGEDEVENTTYPE_NAME 5 - returns the name of the logged eventtype at index n1 from the loggedeventtypes array.
Other operations relating to the Event Log that return number values can be accessed using the applicationcommand() function:
"seteventlogging" - enables or disables logging for eventtype n1.
"geteventlogging" - returns whether logging is enabled for eventtype n1.
"getobjectpathslistsize" - returns the size of the objectpaths array.
"getinvolvedpathslistsize" - returns the size of the involvedpaths array.
"getotherpathslistsize" - returns the size of the otherpaths array.
"geteventtypeslistsize" - returns the size of the eventtypes array.
"getloggedeventtypeslistsize" - returns the size of the loggedeventtypes array.
"geteventtypecode" - returns the index of the eventtype by name passed as n1.
Example
string objectpath = eventloginfo(ELI_GET_OBJECTPATH,1);
eventqty
()
Gets the number of events currently pending
Description
Returns the number of events currently pending.
Example
eventqty()
listenerinfo
(int info)
Description
For developer use. This command returns information for use within the OnListen and OnPreListen event functions.
The information returned is information that was passed to the event you are listening to.
Info 1 will return the engine event code. Engine event codes have macros such as SM_MESSAGE and SM_DRAW.
Info 2 and 3 return pointers to associated treenodes.
To set up listening, you add a "listeners" attribute to the object you want to listen to (Object A). The listeners attribute should have subnodes that are couplings to the object(s) that you want to listen from (Object B). Before an event fires on Object A, Object B's OnPreListen event function will fire. After an event first on Object A, Object B's OnListen event function will fire. You can also filter events by additing a subnode with number data below Object B's coupling node. The number data should be a bitwise sum of the bitshifted event codes you want to listen for. If the coupling has no subnode, the object will default to listening to every event.
The information returned is information that was passed to the event you are listening to.
Info 1 will return the engine event code. Engine event codes have macros such as SM_MESSAGE and SM_DRAW.
Info 2 and 3 return pointers to associated treenodes.
To set up listening, you add a "listeners" attribute to the object you want to listen to (Object A). The listeners attribute should have subnodes that are couplings to the object(s) that you want to listen from (Object B). Before an event fires on Object A, Object B's OnPreListen event function will fire. After an event first on Object A, Object B's OnListen event function will fire. You can also filter events by additing a subnode with number data below Object B's coupling node. The number data should be a bitwise sum of the bitshifted event codes you want to listen for. If the coupling has no subnode, the object will default to listening to every event.
Example
treenode current = c;
treenode involved = i;
int code = listenerinfo(1);
treenode associated = tonode(listenerinfo(2));
treenode coupling = tonode(listenerinfo(3));
print("OnListen");
print("current: ", current);
print("involved: ", involved);
print("code: ", code);
print("associated: ", associated);
print("coupling: ", coupling);
logevent
(num/str index/name[, obj object, obj involved, num p1, num p2, num p3, num p4])
Description
Logs an event as an entry in the Event Log. Use the name passed into registereventtype() or the index returned by registereventtype().
Example
logevent("MyEventType",current,item,port);
registereventtype
(str name)
Description
Registers a custom event type for use with the Event Log. Returns the index of the eventtype to be used later by other commands such as logevent().
Example
int index = registereventtype("MyEventType");
startlisten
(obj listener)
Description
For developer use. Tell the executive that an object is a listener. Not persistent across sessions. This command will add a node in the executive listener list pointing to listener. When a session is reloaded, or after a compile, listeners need to be reset. The listening mechanism can add a significant load to the executive, so use minimally. Listeners will receive OnListen messages when an event (OnTimerEvent) is dispatched to any object in the model. The listener must filter the message to decide whether to respond to the OnListen message. Refer to the Online Reference Guide for the parameters passed into an OnListen message.
Example
startlisten(so())
stoplisten
(obj listener)
Description
For developer use. Tell the executive that this object is not a listener anymore. This command will remove the pointer to listener from the listeners list if previously added with the startlisten() command. Listeners will receive OnListen messages when an event (OnTimerEvent) is dispatched to any object in the model.
Example
stoplisten(so())
FixedResources
Commands associated with FixedResource objects. Most of these commands are used when developing custom behavior for the BasicConveyor or BasicFR object.
evaluatepullcriteria
(obj fixedresource, obj item, num portnr[, num bypassflags])
Causes the FixedResource object to re-fire its pull requirement
Description
Tells the FixedResource to evaluate its pull requirement for the passed item that is in the object through the input port portnr. This command returns the value returned by the pull requirement field if the item can be pulled. If the item cannot be pulled for any of various reasons (such as closed ports or the item not being released), then this command returns 0. The bypassflags parameter is a bitwise combination of macros that start with BYPASS_ to specify certain criteria to ignore in determining item availability.
Example
evaluatepullcriteria(current, item, 1); // See also Pull Best Item picklist option
getiteminvolved
(obj item)
Gets the object reference stored in the FixedResource involved variable for the item
Description
This returns the object reference stored in the FixedResource involved variable for the item.
The FixedResource class allows sub-classes to store 1 involved variable on each flowitem. What these variables mean is dependent on the type of class.
For example, a Processor uses the involved variable to store a reference to the dispatcher called for a flowitem if the Processor is set to use operators for the process or setup time.
If you are using the explicit FixedResource class as an object in your model, you can use this command, along with the setitemvar, getitemvar, and setiteminvolved commands, to store variables on the items the object receives.
The FixedResource class allows sub-classes to store 1 involved variable on each flowitem. What these variables mean is dependent on the type of class.
For example, a Processor uses the involved variable to store a reference to the dispatcher called for a flowitem if the Processor is set to use operators for the process or setup time.
If you are using the explicit FixedResource class as an object in your model, you can use this command, along with the setitemvar, getitemvar, and setiteminvolved commands, to store variables on the items the object receives.
Example
getiteminvolved(current.first)
getitemsendto
(obj item)
Gets the value of the evaluated sendto for the item
Description
This returns the value of the evaluated sendto for the item if it is in a FixedResource and has been released.
Example
getitemsendto(item)
getitemstate
(obj item)
Gets the FixedResource state of the flowitem
Description
Returns the FixedResource state of the flowitem. This will be one of 3 values:
FRSTATE_INQUEUE: The flowitem is in-process; it has not been released yet.
FRSTATE_READY: The flowitem has been release, but has not found a downstream object that is ready to receive it.
FRSTATE_MOVEREQUESTED: The flowitem has been released, and a downstream object is ready to receive it, but the item is waiting to get picked up by a transport.
For more information, refer to the FixedResource documentation.
FRSTATE_INQUEUE: The flowitem is in-process; it has not been released yet.
FRSTATE_READY: The flowitem has been release, but has not found a downstream object that is ready to receive it.
FRSTATE_MOVEREQUESTED: The flowitem has been released, and a downstream object is ready to receive it, but the item is waiting to get picked up by a transport.
For more information, refer to the FixedResource documentation.
Example
getitemstate(so())
getitemvar
(obj item, num var)
Gets the value of a FixedResource variable for the item
Description
This returns the value of a FixedResource variable for the item. The var parameter should be either 1, 2, or 3. The FixedResource class allows sub-classes to keep up to 3 number variables on each flowitem. What these variables mean is dependent on the type of class.
For example, a Processor uses variable 1 to store the time the item started its processing time, and variable 2 to store the item's processing time.
If you are using the explicit FixedResource class as an object in your model, you can use this command, along with the setitemvar, getiteminvolved, and setiteminvolved commands, to store variables on the items the object receives.
For example, a Processor uses variable 1 to store the time the item started its processing time, and variable 2 to store the item's processing time.
If you are using the explicit FixedResource class as an object in your model, you can use this command, along with the setitemvar, getiteminvolved, and setiteminvolved commands, to store variables on the items the object receives.
Example
getitemvar(current.first, 3)
holditem
(obj item)
Holds the item if it has already been released
Description
Holds the specified item if it has already been released. This in effect "unreleases" the item so that it will not leave. This only applies if the item is in a FixedResource and it has already been released and has not been "allocated" to a downstream object (it is not waiting for a transport).
Example
holditem(item)
inititem
(obj item)
Initializes the FixedResource variables of a flowitem
Description
Initializes the FixedResource variables of a flowitem, usually done when the flowitem first enters the fixed resource. This is usually already done for you, but may be used in some exceptional cases when developing your own BasicFR object behavior.
Example
inititem(item)
pullitem
(obj fixedresource, obj item, num portnr[, num bypassflags])
Description
Tells the fixedresource to evaluate its pull requirement for the passed item that is in the object through the input port portnr. If the pull evaluation is true, this command pulls the item immediately. This command returns 1 if the item was successfully pulled and 0 if not. If the item cannot be pulled for any of various reasons (such as closed ports or the item not being released), then this command returns 0. The bypassflags parameter is a bitwise combination of macros that start with BYPASS_ to specify certain criteria to ignore in determining item availability. You can specify BYPASS_ALL to immediately pull the item regardless of availability.
Example
pullitem(current, item, 1); // See also Pull Best Item picklist option
receiveitem
(obj station [, num port ] )
Tells the FixedResource to open inputs and receive a flowitem
Description
Tells the FixedResource station to open its inputs and receive a flowitem.
The port parameter is optional, and should only be used if you know exactly which port you want to receive from. If the port parameter is specified, this object will try to receive any item from the upstream object if its corresponding output port is open, ignoring any items' previous send-to return values (similarly to how pull logic works). This function should be executed only once to receive an item, and it should only executed again once you have received (or have confirmed reception of) that item.
See also releaseitem() command. This function should generally only be used from within a BasicFR's code fields, as other objects implement receiveitem() on their own. If the object receives an item immediately, then it will return 1, otherwise 0.
The port parameter is optional, and should only be used if you know exactly which port you want to receive from. If the port parameter is specified, this object will try to receive any item from the upstream object if its corresponding output port is open, ignoring any items' previous send-to return values (similarly to how pull logic works). This function should be executed only once to receive an item, and it should only executed again once you have received (or have confirmed reception of) that item.
See also releaseitem() command. This function should generally only be used from within a BasicFR's code fields, as other objects implement receiveitem() on their own. If the object receives an item immediately, then it will return 1, otherwise 0.
Example
receiveitem(current)
recycleitem
(obj item , num binrank )
Recycles the flowitem to the flowitem bin
Description
Recycles the specified flowitem to the flowitem bin. Binrank should be the rank in the flowitem bin to recycle to (texturedcoloredbox = 5, etc.)
Example
recycleitem(item, 5);
releaseitem
(obj flowitem [, num port ])
Releases the flowitem from its current object
Description
Releases the specified flowitem. A flowitem is released when it is free to exit the object currently containing it, at which time the Send to Port is evaluated. This command should only be used if the flowitem is in a BasicFR object and the flowitem has not been released already, or if it is any FixedResource and has been held with holditem().
The second paramter, port, is optional. If passed, the sendto will not be evaluated, but the item will instead be released out the specified port. If the flowitem exits, releaseitem will return 1. Otherwise it will return 0.
See also receiveitem() command.
The second paramter, port, is optional. If passed, the sendto will not be evaluated, but the item will instead be released out the specified port. If the flowitem exits, releaseitem will return 1. Otherwise it will return 0.
See also receiveitem() command.
Example
releaseitem(item)
resetuniqueid
(obj flowitem)
Resets the uniqueid attributes on a flowitem to a value that has not been assigned to another flowitem
Description
This command resets the uniqueid attribute on a flowitem to a value that has not been assigned to another flowitem already. This attribute is required to collect Full History information for the Full Report. This command should be used if a flowitem has not been destroyed but needs to be considered as a new item for data collection purposes. For example, if a flowitem is being recycled by a modeler (not with the built-in recycling functionality), they should call this when the flowitem is returned to circulation. Flowitems typically only have the uniqueid attribute when Full History collection is enabled.
Example
resetuniqueid(item);
resumetransportsin
(obj fixedresource [, num saverank])
Description
This should only be executed from triggers of a BasicFR object, and usually will only be executed from the resume object field. This command looks up references to taskexecuters that have been saved using the savestoppedtransportin command, and notifies those taskexecuters that they can resume their unload operation. The saverank parameter refers to a rank in the tree of a specific saved reference. If the saverank parameter is not specified, all saved references will be resumed. If this parameter is specified, only the taskexecuter associated with the specific rank will be allowed to resume. Saved references are stored as sub-nodes in the BasicFR's nroftransportsin variable. References to specific saved taskexecuters can be referenced by: nroftransportsinnode.subnodes[saverank].value
Example
resumetransportsin(current);
resumetransportsout
(obj fixedresource [, num saverank])
Description
This should only be executed from triggers of a BasicFR object, and usually will only be executed from the resume object field. This command looks up references to taskexecuters that have been saved using the savestoppedtransportout command, and notifies those taskexecuters that they can resume their load operation.The saverank parameter refers to a rank in the tree of a specific saved reference. If the saverank parameter is not specified, all saved references will be resumed. If this parameter is specified, only the taskexecuter associated with the specific rank will be allowed to resume. Saved references are stored as sub-nodes in the BasicFR's nroftransportsout variable. References to specific saved taskexecuters can be referenced by: nroftransportsoutnode.subnodes[saverank].value
Example
resumetransportsout(current);
savestoppedtransportin
(obj fixedresource, obj taskexecuter)
Description
This should only be executed from the transport in complete trigger of a BasicFR object.
If the BasicFR is not ready to receive an item that a taskexecuter is about to unload, it must save off a reference to the taskexecuter, then return the value -1.
The taskexecuter will then go into a blocked state and wait until the BasicFR is ready to receive it. When the BasicFR becomes ready to receive the item(s), it should call the resumetransportsin() command.
This will look up saved references and notify their corresponding taskexecuters that they can immediately resume their unload operation.
If the BasicFR is not ready to receive an item that a taskexecuter is about to unload, it must save off a reference to the taskexecuter, then return the value -1.
The taskexecuter will then go into a blocked state and wait until the BasicFR is ready to receive it. When the BasicFR becomes ready to receive the item(s), it should call the resumetransportsin() command.
This will look up saved references and notify their corresponding taskexecuters that they can immediately resume their unload operation.
Example
if(getvarnum(current, "nrofstops") > 0)
{
savestoppedtransportin(current, transporter);
return -1;
}
{
savestoppedtransportin(current, transporter);
return -1;
}
savestoppedtransportout
(obj fixedresource, obj taskexecuter)
Description
This should only be executed from the transport out complete trigger of a BasicFR object.
If the BasicFR is not ready to send an item that a taskexecuter is about to load, it must save off a reference to the taskexecuter, then return the value -1.
The taskexecuter will then go into a blocked state and wait until the BasicFR is ready to send the item. When the BasicFR becomes ready to send the item, it should call the resumetransportsout command.
This will look up saved references and notify their corresponding taskexecuters that they can immediately resume their load operation.
If the BasicFR is not ready to send an item that a taskexecuter is about to load, it must save off a reference to the taskexecuter, then return the value -1.
The taskexecuter will then go into a blocked state and wait until the BasicFR is ready to send the item. When the BasicFR becomes ready to send the item, it should call the resumetransportsout command.
This will look up saved references and notify their corresponding taskexecuters that they can immediately resume their load operation.
Example
if(getvarnum(current, "nrofstops") > 0)
{
savestoppedtransportout(current, transporter);
return -1;
}
{
savestoppedtransportout(current, transporter);
return -1;
}
setiteminvolved
(obj item, obj involved)
Description
This sets the object reference stored in the FixedResource involved variable for the item. The FixedResource class allows sub-classes to store 1 involved variable on each flowitem. What these variables mean is dependent on the type of class. For example, a Processor uses the involved variable to store a reference to the dispatcher called for a flowitem if the Processor is set to use operators for the process or setup time. Only use this command if you are using the explicit FixedResource class as and object in your model. You can use this command, along with the setitemvar, getitemvar, and getiteminvolved commands, to store variables on the items the object receives.
Example
setiteminvolved(current.first, current.centerObjects[1])
setitemsendto
(obj item, num value)
Description
This sets the value of the sendto for the item if it is in a FixedResource. Only use this command if you are using an explicit FixedResource class object and want to store a sendto value on the item before releasing it, and then later use the releaseitem() command, passing the port in. If you want to change the evaluated sendto of an item that has already been released, execute holditem(), and then releaseitem() again, instead of this command.
Example
setitemsendto(item, current.currentsendto)
setitemvar
(obj item, num var, num value)
Description
This sets the value of a FixedResource variable for the item. The var parameter should be either 1, 2, or 3, and the value parameter should be whatever value you want to set it to. The FixedResource class allows sub-classes to keep up to 3 number variables on each flowitem. What these variables mean is dependent on the type of class.
For example, a Processor uses variable 1 to store the time the item started its processing time, and variable 2 to store the item's processing time. If you are using the explicit FixedResource class as an object in your model, you can use this command, along with the getitemvar, getiteminvolved, and setiteminvolved commands, to store variables on the items the object receives.
For example, a Processor uses variable 1 to store the time the item started its processing time, and variable 2 to store the item's processing time. If you are using the explicit FixedResource class as an object in your model, you can use this command, along with the getitemvar, getiteminvolved, and setiteminvolved commands, to store variables on the items the object receives.
Example
setitemvar(current.first, 3, time())
transportincomplete
(obj object, obj item [, num inport, obj transporter])
Notifies the FixedResource object that item will now be moved into it
Description
This command notifies a downstream FixedResource object that the specified item will now be moved into it from an upstream object. This should only be used if the upstream object's Use Transport field is checked, but you are moving the item explicitly, instead of using an FRLOAD task. This allows the downstream FixedResource to manage data on how many items are slated to enter the object, but haven't arrived yet. Execute this command just before you move the item out with the moveobject command. For more information, refer to the FixedResource documentation. If this command returns 0, then the object has been stopped using the stopobject command, and you must wait until it has been resumed before moving the item into it.
Example
transportincomplete(current.outObjects[port], item, opipno(current, port));
This example should be executed from the Request Transport From field before a moveobject command if you decide that you don't want to use a transport, but rather want to immediately move the flowitem
This example should be executed from the Request Transport From field before a moveobject command if you decide that you don't want to use a transport, but rather want to immediately move the flowitem
transportoutcomplete
(obj object, obj item [, num outport, obj transporter])
Notifies the FixedResource object that item will now be moved out of it
Description
This command notifies the FixedResource object that the specified item will now be moved out of it. This should only be used if the object's Use Transport field is checked, but you are moving the item explicitly, instead of using an FRLOAD task. This allows the FixedResource to manage data on how many items are still in the object but are ready to leave. Execute this command just before you move the item out with the moveobject command. For more information, refer to the FixedResource documentation. If this command returns 0, then the object has been stopped using the stopobject command, and you must wait until it has been resumed before moving the item into it.
Example
transportoutcomplete(current, item, port);
This example should be executed from the Request Transport From field before a moveobject command if you decide that you don't want to use a transport, but rather want to immediately move the flowitem
This example should be executed from the Request Transport From field before a moveobject command if you decide that you don't want to use a transport, but rather want to immediately move the flowitem
Kinematics and Splines
Commands associated with kinematics and spline math.
addkinematic
(node infonode, num x, num y, num z, num targetspeed, num acc, num dec, num startspeed, num endspeed, num starttime, num type )
Adds one kinematic operation to a set of kinematics
Description
Adds one kinematic operation to a set of kinematics. For more information, refer to the user manual documentation on kinematics.
Example
addkinematic(current.labels["kinematics"], 1, 0, 0, 5,0,0, 0,0, time(), KINEMATIC_TRAVEL);
deactivatekinematics
(node kinematicsnode)
Causes kinematics to do nothing when updatekinematics() is called
Description
Causes kinematics to do nothing when updatekinematics() is subsequently called instead of updating the object. Call this in the reset trigger of an object to free the object to move it around in the ortho view.
Example
deactivatekinematics(current.labels["kinLabel"]);
dynamicsplineall
(node starttree)
Description
For developer use. Un-cache all splines for objects under starttree. Any splines in the model become editable or "unlocked". Spline rendering becomes slower in editable mode. In editable mode, splines can be edited dynamically.
Example
dynamicsplineall(model())
fastspline
(obj spline, num perc [0-1])
Description
For developer use. Get a spline mapping from a cached spline. This command will set the values to be returned by subsequent calls to the splinex(), spliney(), splinez(), splinerx(), splinery(), splinerz(), splinelength(), splineposobject() commands. It will use the precalculated values for the spline object given in spline. The parameter perc is the position along the spline of interest. The precalculated values are evaluated when the fastsplineall() or fastsplineupdate() commands are used.
Example
fastspline(splinestartnode,1)
This activates the spline pointed to splinestartnode at its furthest point (100 percent along the spline).
This activates the spline pointed to splinestartnode at its furthest point (100 percent along the spline).
fastsplineall
(obj starttree {model}, num res)
Description
For developer use. Cache all splines at once. The geometry for all splines in the model are evaluated and "locked" in order to accelerate the rendering and evaluation of spline geometry. This command will set the values to be returned by subsequent calls to the splinex(), spliney(), splinez(), splinery(), splinery(), splinery(), splinelength(), splineposobject() commands whenever calling fastspline().
Example
fastsplineall(model(),20)
fastsplineupdate
(obj spline, num res)
Description
For developer use. Cache a spline's shape to increase it's speed. The geometry for all splines in the model are re-evaluated and "locked" in order to accelerate the rendering and evaluation of spline geometry. This command will set the values to be returned by subsequent calls to the splinex(), spliney(), splinez(), splinerx(), splinery(), splinerz(), splinelength(), splineposobject() commands whenever calling fastspline().
Example
fastsplineupdate(so(),20)
getkinematics
(node infonode, num querytype[, num kinematicindex, num updatetime/traveldist])
Gets information from the specified kinematics operation
Description
Gets information from the specified kinematics operation. For more information, refer to the help documentation on kinematics.
Example
getkinematics(current.labels["kinematics"], KINEMATIC_ARRIVALTIME, 1, current.size.x);
initkinematics
(node infonode, obj/num object/x[, num flags/y, num z, num rx, num ry, num rz, num flags, num unused])
Initializes a kinematic operation
Description
Initialize a kinematic operation.
Infonode is a blank node that can hold kinematic information.
Object is the object that you want kinematics to be performed on.
flags defines various flags for how you want it to behave.
The unused parameter deprecated, i.e. you can define this through the flags parameter.
Refer to kinematics documentation in the user manual for more information.
Infonode is a blank node that can hold kinematic information.
Object is the object that you want kinematics to be performed on.
flags defines various flags for how you want it to behave.
The unused parameter deprecated, i.e. you can define this through the flags parameter.
Refer to kinematics documentation in the user manual for more information.
Example
initkinematics(current.labels["kinematics"], current)
profilekinematics
(node infonode, num kinematicindex)
Prints information about the specified kinematics operation to the output console
Description
Prints information about the specified kinematics operation to the output console. For more information, refer to the help documentation on kinematics.
Example
printkinematics(current.labels["kinematics"], 0);
scalekinematicstotime
(node kinematics, int kinematicnr, double scaletotime)
Scales the kinematics to a defined time
Description
Scales the kinematic(s) to a defined time. This can be used to preserve the characteristics of the kinematics, i.e. accelerate->peak speed->decelerate, but have the total time it takes to perform the kinematics be defined by some other mechanism such as a distribution. If kinematicnr is 0, then the entire set of kinematics will be scaled to the given time. If kinematicnr is greater than 0, then only that kinematic will be scaled. The return value is the new end time of the kinematic(s).
Example
scalekinematicstotime(kinematics, 0, exponential(0, 10));
setkinematicsrotoffset
(node infonode, num rx, num ry, num rz)
Description
Sets the initial kinematics rotational offset for a kinematics operation. For more information, refer to the help documentation on kinematics.
Example
setkinematicsrotoffset(current.labels["kinematics"], 0, 0, 180);
spline
(obj spline, num perc)
Description
For developer use. Calculate spline mapping and set the current spline parameters using the spline object spline. This command will set the values to be returned by subsequent calls to the splinex(), spliney(), splinez(), splinerx(), splinery(), splinerz(), splinelength(), splineposobject() commands. It will not set the precalculated values for the spline object given in spline, as in fastspline().The parameter perc is the position along the spline of interest. This command does not lock precalculated values as when the fastsplineall() or fastsplineupdate() commands are used. A spline can be defined as any chain of objects that are connected from output ports to input ports. Pass the first object in the output port to input port chain as parameter 1.
Example
spline(splinestartobject,0.6)
splinedraw
(obj object)
Description
For developer use. Draw a line along a spline based on the current spline geometry as calculate by the spline().
Example
splinedraw()
splinedrawextrusion
(obj object, num step, num wide, num high, num top, num side)
Description
For developer use. Draw a spline based on the current spline geometry as calculate by the spline() with a rectangular extrusion. Using parameters of spline object.
Example
splinedrawextrusion(current,20,1,2,1,1)
splinelength
()
Description
For developer use. Current spline parameter. This will return the length of the current spline.
Example
splinelength()
splineposobject
(obj object)
Description
For developer use. Position object according to current spline parameters.
Example
splineposobject(current)
splinerx
()
Description
For developer use. Current spline parameter. This will give the orientation of an object as if placed on the spline at the parameter p given in the last call to spline().
Example
splinerx()
splinery
()
Description
For developer use. Current spline parameter. This will give the orientation of an object as if placed on the spline at the parameter p given in the last call to spline().
Example
splinery()
splinerz
()
Description
For developer use. Current spline parameter. This will give the orientation of an object as if placed on the spline at the parameter p given in the last call to spline().
Example
splinerz()
splinex
()
Description
For developer use. Current spline parameter. This will give the position on the spline at the parameter p given in the last call to spline().
Example
splinex()
spliney
()
Description
For developer use. Current spline parameter. This will give the position on the spline at the parameter p given in the last call to spline().
Example
spliney()
splinez
()
Description
For developer use. Current spline parameter. This will give the position on the spline at the parameter p given in the last call to spline().
Example
splinez()
updatekinematics
(node infonode, obj object [, num updatetime])
Updates the location of the object based on its kinematics
Description
Updates the location of the object based on the kinematics operation and the current time. For more information, refer to the help documentation on kinematics.
Example
updatekinematics(current.labels["kinematics"], current, time());
Language
Flexscript or C++ keywords and constructs.
a
<no parentheses>
Description
This command is used to reference objects during iterations of certain flexscript commands such as forobjectlayerunder() and forobjecttreeunder(). This command does not require parentheses, and can only be used in C++.
Example
See forobjecttreeunder().
break
Description
Break out of a loop or the case of a switch statement {}
Example
break;
case
value:
Description
One case in a switch statement {}
Example
case 5: { msg("case statement",""); }
continue
Description
Continues immediately to the next iteration of a for or while loop without executing any of the remaining code in the current loop.
Example
if(thisloopnotneeded) continue;
default
:
Description
The default case in a switch statement {}
Example
default: { msg("case statement",""); }
else
{ }
Description
Used in conjunction with the "if" statement to declare what (if any) code should be executed when the condition for the "if" is false.
Example
if( item.Weight < 100 )
{
msg("TRUE","");
}
else
{
msg("FALSE","");
}
This example will display the TRUE message when the value of the item's Weight label is less than 100, and the FALSE message when it is not.
{
msg("TRUE","");
}
else
{
msg("FALSE","");
}
This example will display the TRUE message when the value of the item's Weight label is less than 100, and the FALSE message when it is not.
for
(initalstatement; whiletrueexpression ; countstatement)
Description
Perform a number of loops. The initialstatement will be executed once before starting the loop. The whiletrueexpression will be evaluated before executing each loop and the loop will stop as soon as this expression is true. The countstatement is executed at the end of each loop and usually increments a counter. Refer to the help manual under Writing Logic in FlexSim for more information.
Example
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
msg("for loop","");
}
{
msg("for loop","");
}
forobjecttreeunder
(node container) { }
Description
Execute a block of code for each node that is in the tree under the node specified as container, including all sub-trees. To access the node that is currently active in the loop, the "a" command is used. The forobjecttreeunder() command can only be used in flexscript, not C++.
Example
forobjecttreeunder(model())
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of every object in the model, including those inside other objects.
{
pt(a.name); pr();
}
This prints to the outputconsole the name of every object in the model, including those inside other objects.
if
(num condition) { }
Description
If the condition is true (i.e. the conditional expression returns a 1), then the statement immediately following the closing parenthesis will be executed. If braces { } are what immediately follows the closing parenthesis, then the block of code within the braces will be executed when the condition is true. Nothing is executed if the condition is false (returns a 0), unless an "else" has been defined. Refer to the Users Manual for more information.
Example
if (item.Weight < 100)
msg("TRUE", "");
This example will display a popup message saying "TRUE" when the item's Weight label has a value less than 100
msg("TRUE", "");
This example will display a popup message saying "TRUE" when the item's Weight label has a value less than 100
return
(num value)
Description
This command causes a function to stop executing and return value to the function that called it.
Example
double res = item.rank * 5;
return res;
This sets the value of res to 5 times the rank of the item referenced by item. The value stored in res is then returned to the function that called this one.
return res;
This sets the value of res to 5 times the rank of the item referenced by item. The value stored in res is then returned to the function that called this one.
stringcompare
(str text1, str text2)
Compare strings for alphabetical order
Description
Compare strings for alphabetical order. The return value is zero if the strings are the same. If text1 is alphabetically before text2, a negative number is returned. If text1 is alphabetically after text2, a positive number is returned. Same as the strcmp() C++ function.
Example
stringcompare("zenith","beta") returns 1
comparetext("aqua","yellow") returns -1
comparetext("aqua","yellow") returns -1
switch
(num value)
Description
Execute one of several possible cases, based on value
Example
int msgcase = msgparam(1);
switch(msgcase)
{
case 1:msg("","case 1");break;
case 2:msg("","case 2");break;
default:msg("","case 2");break;
}
switch(msgcase)
{
case 1:msg("","case 1");break;
case 2:msg("","case 2");break;
default:msg("","case 2");break;
}
while
(num expression) {}
Description
Repeatedly execute the following block {} while the expression returns a non-zero value. Be careful with this function because it can cause FlexSim to freeze if the value never becomes false.
Example
while(current.subnodes.length > 4)
{
current.last.destroy();
}
{
current.last.destroy();
}
Media
Commands associated with presentation and media such as images, sounds, 3D shapes, video and flypaths.
applyshapefactors
(obj object)
Applies all of the shape factors to object
Description
This command applies all of the shape factors to the object if it has any.
Example
applyshapefactors(item);
autoloadallmedia
([node thenode])
Description
For developer use. This command loads all of the media (images and shapes) required by the current views, library, and model. Images are either .bmp or .jpg graphics files. Shapes are either .3ds or .wrl files. This command may take some time to complete, if there are many images or shapes that need to be loaded. This command is not available in C++.
Example
autoloadallmedia();
This reloads all of the media needed for the current model.
This reloads all of the media needed for the current model.
autoloadimages
()
Description
For developer use. This command loads all of the images required by the current views, library, and model. Images are either .bmp or .jpg graphics files. This command may take some time to complete, if there are many images that need to be loaded. This command is not available in C++.
Example
autoloadimages();
This reloads all of the images needed for the current model.
This reloads all of the images needed for the current model.
autoloadshapes
()
Description
For developer use. This command loads all 3D shapes required by the current views, library, and model. Shapes are either .3ds or .wrl files. This command may take some time to complete, if there are many shapes that need to be loaded. This command is not available in C++.
Example
autoloadshapes();
This reloads all of the shapes needed for the current model.
This reloads all of the shapes needed for the current model.
autoloadsounds
()
Description
For developer use. This command loads all sounds required by the current views, library, and model as declared by "sound" attributes on the objects. This command may take some time to complete, if there are many sounds that need to be loaded. This command is not available in C++.
Example
autoloadsounds();
This reloads all of the sounds needed for the current model.
This reloads all of the sounds needed for the current model.
flyactive
()
Returns 1 if there is an fly path running, 0 otherwise
Description
Returns 1 if there is a fly path currently being run, 0 otherwise.
Example
flyactive()
flyendnode
(node x)
Gets a reference to the node that represents the stopping point for the current fly path
Description
Returns a reference to the node in the tree that represents the stopping point for the current fly path.
Example
Used in the presentation builder GUI.
flypath
(obj view, num pathno [, num singlerun])
Description
For developer use. This command begins the predefined flypath numbered pathno in the view designated specified as view. Any view window can be passed as view.
Example
flypath(ownerview(c),1);
This will run flypath number 1 in the view window containing an event's code.
This will run flypath number 1 in the view window containing an event's code.
flypathadd
(obj view, num pathno)
Description
For developer use. This command adds a flypath to the flypath numbered pathno in the view designated specified as view. Any view window can be passed as view.
Example
flypathadd(ownerview(c),1);
This will add a flypath to flypath number 1 in the view window containing an event's code.
This will add a flypath to flypath number 1 in the view window containing an event's code.
flypathreset
(obj view, num pathno)
Description
For developer use. This command clears the points from the flypath numbered pathno in the view specified as view. Once the points have been cleared, a new set of flypath points can be generated.
Example
flypathreset(ownerview(c),1);
This clears the flypath points out of flypath 1 in the view containing an event's code.
This clears the flypath points out of flypath 1 in the view containing an event's code.
flystart
(obj view)
Description
For developer use. Start fly mode.
Example
flystart(ownerview(c))
flystop
()
Description
For developer use. This command stops any active flypaths.
Example
flystop();
This causes all flypaths that are currently active to stop moving.
This causes all flypaths that are currently active to stop moving.
flyto
(obj view, num endtime, num x, num y, num z, num rx, num ry, num rz)
Description
For developer use. Fly to the specified viewpoint over time.
Example
flyto(sv(),10000,0,0,20,-50,0,-30);
flyupdate
()
Updates the currently active fly path
Description
Updates the currently active fly path if there is one
Example
getshapeindex
(str name)
Gets the index of a loaded 3D shape
Description
Get the index of a loaded shape by its file path name. The file path name used in this command must use double backslashes as shown in the example. Use View -> Media Files to see a complete list of currently loaded shapes with their associated file path names and indexes.
Example
getshapeindex("fs3d\\Operator\\BasicOperator\\Chest.3ds");
getsoundindex
(str name)
Gets the index of a loaded sound
Description
Returns the index of a loaded sound by the name associated with it in the project/media/sounds folder.
Example
getsoundindex("C:/My Sounds/APPLAUSE.WAV");
gettextureindex
(str name)
Gets the index of a loaded image
Description
Get the index of a loaded image by name. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded textures (images). Each texture has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to a texture's name.
Example
gettextureindex("myimage")
loadimage
(str file, str name)
Description
For developer use. Load an image directly. An image file on disk will be loaded into FlexSim and recorded in the Media List. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded images. Each image has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the loaded image.
Example
loadimage("c:/myimage.bmp","myimage")
loadthreedobject
(str file, str name)
Description
For developer use. Load a 3D model directly. A shape file on disk will be loaded into FlexSim and recorded in the Media List. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded shapes. Each shape has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the loaded shape.
Example
loadthreedobject("c:/myshape.wrl","myshape")
mediareset
()
Description
For developer use. Unload all media. This will unload all currently loaded media from FlexSim: images; shapes; and sounds.
Example
mediareset()
objectsoundcode
(obj object)
Gets the index of object's default sound
Description
Get the index of the object's default sound. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded sounds. Each sound has a corresponding name and an index. This function will return the index corresponding to the objects default sound assuming the object has a sound and soundindex attribute (default objects do not at this time)
Example
objectsoundcode(current)
shapeinfo
(num info[, p1, p2, p3])
Gets or sets information about loaded 3D shapes.
Description
Gets or sets information about loaded 3D shapes.
Example
shapeinfo(SHAPEINFO_GET_ANIMATION_COUNT, shapeIndex);
soundchange
(obj view, num sound, num volume, num tempo, num repeat, num balance)
Change a currently playing sond
Description
Change a currently playing sound. Sounds are attached to a window by the operating system, so the view parameter is important. To get the soundindex use getsoundindex(). The volume, tempo and balance are numbers between 0 and 1. To continuosly repeat the sound, use a repeat of 1 else 0. Interesting affects are achieved when the volume and balance are changed based on the viewpoint relative to an object making the object appear to be emitting the sound.
Example
soundchange(sv(),1,1,1,1,.5)
soundload
(str path+filename)
Load a sound into FlexSim
Description
A sound file on disk will be loaded into FlexSim and recorded in the Media List. The media list of FlexSim will keep a list of all loaded sounds. Each sound has a corresponding name and an index. This command will return the index corresponding to the loaded sound. Microsoft Wave Format files (.wav) can be loaded and played. Sounds can have their volume, balance and frequency adjusted dynamically. Multiple channels are managed through the Microsoft DirectSound Interface.
Example
int applauseindex = soundload("c:/My Music/APPLAUSE.WAV");
soundplay
(obj view, num soundindex, num volume [, num tempo, num repeat y/n, num balance])
Play a loaded sound
Description
Play a loaded sound. Sounds are attached to a window by the operating system, so the view parameter is important. To get the soundindex use getsoundindex(). The volume, tempo and balance are numbers between 0 and 1. To continuosly repeat the sound, use a repeat of 1 else 0.
Example
soundplay(sv(),3,.75,.25,1,.5)
Continuously play sound index 3 in the selected view with 3/4 volume, and 1/4 tempo and balanced evenly across both speakers.
Continuously play sound index 3 in the selected view with 3/4 volume, and 1/4 tempo and balanced evenly across both speakers.
soundplayfile
(obj view, str path+filename, num volume [, num tempo, num repeat, num balance])
Play a sound directly from a file
Description
Play a sound directly from a file. Sounds are attached to a window by the operating system, so the view parameter is important. The volume, tempo and balance are numbers between 0 and 1. To continuosly repeat the sound, use a repeat of 1 else 0.
Example
soundplayfile(sv(),"C:/My Sounds/APPLAUSE.WAV",1,1,0,.5);
soundstop
(obj view, num sound)
Stop a sound playing
Description
Stop a sound playing. Sounds are attached to a window by the operating system, so the view parameter is important.
Example
soundstop(sv(),1)
unloadimage
(int textureid)
Description
For developer use. Unload an image from the Media List by index.
Example
treenode view = node("VIEW:/1>Documents/Dashboard/1+/~/GraphPanel/1/1");
repaintview(view);
viewtofile(view, modeldir() + "test.png");
unloadimage(gettextureindex(modeldir() + "test.png"));
int newindex = loadimage(modeldir() + "test.png", modeldir() + "test.png");
setobjecttextureindex(Model.find("Plane1"), newindex);
This example renders a dashboard chart to an image file, unloads that image from the media list, reloads the image back into the media list, and sets the texture index of a plane to that image.
repaintview(view);
viewtofile(view, modeldir() + "test.png");
unloadimage(gettextureindex(modeldir() + "test.png"));
int newindex = loadimage(modeldir() + "test.png", modeldir() + "test.png");
setobjecttextureindex(Model.find("Plane1"), newindex);
This example renders a dashboard chart to an image file, unloads that image from the media list, reloads the image back into the media list, and sets the texture index of a plane to that image.
viewtofile
(obj view, str path[, num width, num height])
Saves the specified view as a bitmap image
Description
Saves the specified view as a bitmap image to the specified file.
Example
viewtofile(node("VIEW:/active/ortho"), modeldir() + "screenshot.bmp"));
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous commands that have not been categorized.
addsystemcontrolleritem
(obj systemcontroller, num productid, num linenum, num target, num starttime [, num newcolumn1, num newcolumn2, num newcolumn3, num newcolumn4])
For Dynamo use
Description
For Dynamo use. Adds a new line item to a SystemController's schedule during a model run. Does not actually add a new row to the table. The parameters are the same data that the SystemController's schedule requires. The newcolumn parameters are numbers that could have been added to each row of the SystemController's schedule table.
Example
addsystemcontrolleritem(current.centerObjects[1],0,1,1,0);
commandlineparam
(str param)
Description
Returns the specified commandline parameter that was passed in if FlexSim is being run from the commandline.
Example
commandlineparam("nrofops");
This example will return the "nrofops" commandline parameter.
If a batch opens FlexSim with the line:
flexsim.exe myfile.fsm -nrofops 8
Then within FlexSim, commandlineparam("nrofops") will return "8". You can use either the unix-style hyphen (-) or the windows-style forward slash (/) to define a command-line parameter
This example will return the "nrofops" commandline parameter.
If a batch opens FlexSim with the line:
flexsim.exe myfile.fsm -nrofops 8
Then within FlexSim, commandlineparam("nrofops") will return "8". You can use either the unix-style hyphen (-) or the windows-style forward slash (/) to define a command-line parameter
contextdragconnection
(obj fromobject, obj toobject, str/num characterpressed)
Creates an A or S connection between objects
Description
This command mimicks holding the specified letter down on the keyboard, clicking on the fromobject and then dragging to the toobject with the mouse.
Whatever context sensitive action takes place when using the actual keyboard and mouse combinations, will occur when this command is executed.
This command can be used in both Flexscript and C++.
Whatever context sensitive action takes place when using the actual keyboard and mouse combinations, will occur when this command is executed.
This command can be used in both Flexscript and C++.
Example
contextdragconnection(model().subnodes[5], model().subnodes3], "A");
createuserlibrary
()
Description
For developer use. This command creates a new user library
Example
createuserlibrary();
deleteselected
()
Description
For developer use. Deletes all selected objects in the model.
Example
deleteselected()
dropuserlibraryobject
(obj object [, obj ontoobject, num x, num y, num z, obj ontoview, num viewalreadyset])
Description
For developer use. Drops the specified object as if it were dragged from a user library into the model.
Example
dropuserlibraryobject(node("MAIN:/project/userlibrary/1/1"));
duplicateselected
()
Description
For developer use. Duplicates all selected objects in the model.
Example
duplicateselected()
executefsfile
(str filename, num direct)
Description
For developer use. Executes Flexscript code in a file. The specified file is loaded and its content is executed. The contents of the file are assumed to be valid Flexscript code. If direct is 0, then FlexSim's program directory will be concatenated onto the front of filename, otherwise filename will remain as it is.
Example
executefsfile("c:/myscript.fs",1)
filebrowse
(str extension, str description, str startpath)
Opens a file selection dialog
Description
Opens a file selection dialog that allows the user to select the specified file type(s). Different types should be separated by semicolons(;). The dialog's default directory is the path specified. The commands pdir() and cdir() can only be passed as the path parameter in C++.
Example
string filename = filebrowse("*.fsm; *.fsp; *.fsv; *.fss","FlexSim Files",pdir());
firecreateevent
(obj object, num x, num y, num z, num iscopy [, num libraryfunctiononly])
Description
For developer use. Fires the creation event of the specified object. x, y, and z are the rz the object was dropped at.
Example
firevalue of 0 islast(model()),0,0,0, 1);
flipselected
(num firstX, num firstY, num secondX, num secondY[, node roottree])
Flip selected objects across an axis
Description
Flip selected objects across the axis defined by the two passed xy points
Example
flipselected(1, 5, 2, 7)
This example flips the selected objects across the axis defined by the points point (1, 5) and (2, 7)
This example flips the selected objects across the axis defined by the points point (1, 5) and (2, 7)
geteventtime
(str EventName, num mode[1/2/3])
Gets a UserEvent's event time
Description
Returns a UserEvent's event time. Mode: 1 - Repeat time intervals, 2 - Exact event time, 3 - Time until event fires
Example
double remainingtime = geteventtime("myevent",3);
getlastfiletype
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the type of the last file saved. 1 = Model file 2 = Project file 3 = View file 4 = Session file 0 = Other file
Example
if (getlastfiletype()) {pt("Known file type"); pr(); }
getlinecontrollerdata
(obj linecontroller, num datatype, num column)
For Dynamo use
Description
For Dynamo use. Returns data about the LineController's current job, 1 = ProdID, 2 = LineNum, 3 = Target, 4 = StartTime. 5 = Extra Column
Example
getlinecontrollerdata(current,1,0);
getmodelunit
(num querytype)
Description
Returns information about the model's unit settings.
FlexSim's typical units are: time - 1 second, length - 1 meter, volume - 1 liter, mass - 1 kilogram. Also may return a name or abbreviation of the current model's units
querytype can be one of the following values:
TIME_MULTIPLE returns the number of seconds represented by each time unit in the current model
LENGTH_MULTIPLE returns the number of meters represented by each length unit in the current model
FLUID_MULTIPLE returns the number of liters represented by each fluid unit in the current model
FLUID_TYPE returns 0 if the fluid units represent volume, or returns 1 if the fluid units represent mass
DATE_TIME_NODE returns a reference to the date/time node in the model units tree
START_TIME returns the start time in seconds (since Jan 1, 1601)
START_TIME_NODE returns a reference to the start time node in the model units tree
CURRENT_TIME returns the current time in seconds (since Jan 1, 1601)
CURRENT_TIME_NODE returns a reference to the current time node in the model units tree
STOP_TIME returns the next stop time in seconds (since Jan 1, 1601)
STOP_TIME_NODE returns a reference to the stop times node in the model units tree
START_YEAR returns the year associated with the start time as a number
START_MONTH returns the month associated with the start time as a number betweeen 1 (Jan) and 12 (Dec)
START_DAY returns the day associated with the start time as a number, where 1 indicates the first day of the month
START_DAYOFWEEK returns the day associated with the start time as a number, where 0 indicates Sunday
START_HOUR returns the hour associated with the start time as a number between 0 and 23
START_MINUTE returns the minute associated with the start time as a number between 0 and 59
START_SECOND returns the second associated with the start time as a number between 0 and 59
START_MILLISECOND returns the millisecond associated with the start time as a number between 0 and 999
CURRENT_YEAR returns the number of years since the model start time
CURRENT_DAY returns the number of days since the model start time
CURRENT_HOUR returns the number of hours since the model start time
CURRENT_MINUTE returns the number of minutes since the model start time
CURRENT_SECOND returns the number of seconds since the model start time
CURRENT_MILLISECOND returns the number of milliseconds since the model start time
CURRENT_YEAR_OF_TIME returns the year associated with the current time as a number
CURRENT_MONTH_OF_YEAR returns the month associated with the current time as a number between 1 (Jan) and 12 (Dec)
CURRENT_DAY_OF_MONTH returns the day associated with the current time as a number, where 1 indicates the first day of the month
CURRENT_DAY_OF_WEEK returns the day associated with the current time as a number, where 0 indicates Sunday
CURRENT_HOUR_OF_DAY returns the hour associated with the current time as a number between 0 and 23
CURRENT_MINUTE_OF_HOUR returns the minute associated with the current time as a number between 0 and 59
CURRENT_SECOND_OF_MINUTE returns the second associated with the current time as a number between 0 and 59
CURRENT_MILLISECOND_OF_SECOND returns the millisecond associated with the current time as a number between 0 and 999
TIME_NAME returns the name of the model time units
TIME_PLURAL_NAME returns the plural name of the model time units
TIME_ABBREVIATION returns the abbreviation of the model time units
LENGTH_NAME returns the name of the model length units
LENGTH_PLURAL_NAME returns the plural name of the model length units
LENGTH_ABBREVIATION returns the abbreviation of the name of the model length units
FLUID_NAME returns the name of the model fluid units
FLUID_PLURAL_NAME returns the plural name of the model fluid units
FLUID_ABBREVIATION returns the abbreviation of the name of the model fluid units
START_TIME_STR returns the start time as a string, formatted by the date and time formats
CURRENT_TIME_STR returns the current time as a string, formmatted by the date and time formats
STOP_TIME_STR returns the next stop time as a string, formatted by the date and time formats
TIME_FORMAT returns the time format used to format date/time strings
DATE_FORMAT returns the date format used to format date/time strings
FlexSim's typical units are: time - 1 second, length - 1 meter, volume - 1 liter, mass - 1 kilogram. Also may return a name or abbreviation of the current model's units
querytype can be one of the following values:
TIME_MULTIPLE returns the number of seconds represented by each time unit in the current model
LENGTH_MULTIPLE returns the number of meters represented by each length unit in the current model
FLUID_MULTIPLE returns the number of liters represented by each fluid unit in the current model
FLUID_TYPE returns 0 if the fluid units represent volume, or returns 1 if the fluid units represent mass
DATE_TIME_NODE returns a reference to the date/time node in the model units tree
START_TIME returns the start time in seconds (since Jan 1, 1601)
START_TIME_NODE returns a reference to the start time node in the model units tree
CURRENT_TIME returns the current time in seconds (since Jan 1, 1601)
CURRENT_TIME_NODE returns a reference to the current time node in the model units tree
STOP_TIME returns the next stop time in seconds (since Jan 1, 1601)
STOP_TIME_NODE returns a reference to the stop times node in the model units tree
START_YEAR returns the year associated with the start time as a number
START_MONTH returns the month associated with the start time as a number betweeen 1 (Jan) and 12 (Dec)
START_DAY returns the day associated with the start time as a number, where 1 indicates the first day of the month
START_DAYOFWEEK returns the day associated with the start time as a number, where 0 indicates Sunday
START_HOUR returns the hour associated with the start time as a number between 0 and 23
START_MINUTE returns the minute associated with the start time as a number between 0 and 59
START_SECOND returns the second associated with the start time as a number between 0 and 59
START_MILLISECOND returns the millisecond associated with the start time as a number between 0 and 999
CURRENT_YEAR returns the number of years since the model start time
CURRENT_DAY returns the number of days since the model start time
CURRENT_HOUR returns the number of hours since the model start time
CURRENT_MINUTE returns the number of minutes since the model start time
CURRENT_SECOND returns the number of seconds since the model start time
CURRENT_MILLISECOND returns the number of milliseconds since the model start time
CURRENT_YEAR_OF_TIME returns the year associated with the current time as a number
CURRENT_MONTH_OF_YEAR returns the month associated with the current time as a number between 1 (Jan) and 12 (Dec)
CURRENT_DAY_OF_MONTH returns the day associated with the current time as a number, where 1 indicates the first day of the month
CURRENT_DAY_OF_WEEK returns the day associated with the current time as a number, where 0 indicates Sunday
CURRENT_HOUR_OF_DAY returns the hour associated with the current time as a number between 0 and 23
CURRENT_MINUTE_OF_HOUR returns the minute associated with the current time as a number between 0 and 59
CURRENT_SECOND_OF_MINUTE returns the second associated with the current time as a number between 0 and 59
CURRENT_MILLISECOND_OF_SECOND returns the millisecond associated with the current time as a number between 0 and 999
TIME_NAME returns the name of the model time units
TIME_PLURAL_NAME returns the plural name of the model time units
TIME_ABBREVIATION returns the abbreviation of the model time units
LENGTH_NAME returns the name of the model length units
LENGTH_PLURAL_NAME returns the plural name of the model length units
LENGTH_ABBREVIATION returns the abbreviation of the name of the model length units
FLUID_NAME returns the name of the model fluid units
FLUID_PLURAL_NAME returns the plural name of the model fluid units
FLUID_ABBREVIATION returns the abbreviation of the name of the model fluid units
START_TIME_STR returns the start time as a string, formatted by the date and time formats
CURRENT_TIME_STR returns the current time as a string, formmatted by the date and time formats
STOP_TIME_STR returns the next stop time as a string, formatted by the date and time formats
TIME_FORMAT returns the time format used to format date/time strings
DATE_FORMAT returns the date format used to format date/time strings
Example
getmodelunit(LENGTH_MULTIPLE)
getreportnum
(node report, int column, int rowsback)
For Dynamo use
Description
For Dynamo use. Returns the value from a Report object that is in the specified column. The row is determined by subtracting the rowsback parameter from the number of rows in the table.
Example
double myval = getreportnum(current,3,0);
groupsetnames
(node namenode, num startnum, num append)
Description
For developer use. Sets the names of all of the selected objects in the model to the string data on namenode. If append is 1, then a number is appended to the end of each name, starting at startnum and increasing by 1 for each object.
Example
groupsetnames("WeldStation",1,1);
hideprogressbar
()
Description
For developer use. Hides the progress bar
Example
hideprogressbar();
highestconnection
()
Gets the highest numbered server connection index
Description
Returns the highest numbered server connection index.
Example
int highconn = highestconnection();
insertcopy
(obj originalobject, obj containerobject)
Creates a copy of the flowitem and moves it into the container object
Description
Creates a copy of the flowitem and moves it into the container object, causing the OnReceive event of the container to execute.
Example
insertcopy(item, current);
Creates a duplicate of the flowitem and moves it into the current object.
Creates a duplicate of the flowitem and moves it into the current object.
integrityscan
(obj class, obj start)
Description
For developer use. Checks that attributes have not been deleted from model objects, based on their class object. A search is done starting at the given starting node.
Example
integrityscan(rank(library(1)),model())
isprojectcompiled
()
Description
For developer use. Returns 1 if the project has been compiled.
Example
isprojectcompiled()
loadselectedfromfile
(obj highlightedobj)
Description
For developer use. Loads previously saved tree file into the highlighted object.
Example
loadselectedfromfile(selectedobject(ownerview(c)))
loadstate
()
Description
For developer use. Loads the state of the project. If savestate() has been executed, then this command must be executed before you can run the model again.
Example
loadstate();
loaduserlibrary
(str libfile [, obj libraryview, num reloadmedia, num changeitemcurrent, num autoinstall])
Description
For developer use. Loads a library from the path specified in libfile. If reloadmedia is true, autoloadallmedia() will be called
after loading the library. If autoinstall is true, the library's load and new model autoinstall objects will be added to the model. The
libraryview and changeitemcurrent parameters are no longer used.
Example
loaduserlibrary(cdir() + "libraries/mylib.fsl");
memberadd
(obj childobject, str parentname, num type)
Description
If type = 1, then the childobject is added as a member to a Time Table named "parentname".
If type = 2, then the childobject is added as a member to a MTBFMTTR object named "parentname".
This is useful for dynamically assigning operators to different shifts for instance.
If type = 2, then the childobject is added as a member to a MTBFMTTR object named "parentname".
This is useful for dynamically assigning operators to different shifts for instance.
Example
memberadd(model().subnodes[2],"TimeTable1",1)
memberremove
(obj childobject, str parentname, num type)
Description
If type = 1, then the childobject is removed as a member from a Time Table named "parentname".
If type = 2, then the childobject is removed as a member from a MTBFMTTR object named "parentname".
see memberadd()
If type = 2, then the childobject is removed as a member from a MTBFMTTR object named "parentname".
see memberadd()
Example
memberremove(model().subnodes[2],"TimeTable1",1)
memberremoveall
(str parentname, num type)
Description
If type = 1, then all members are removed from a Time Table named "parentname".
If type = 2, then all members are removed from a MTBFMTTR object named "parentname".
see memberremove()
If type = 2, then all members are removed from a MTBFMTTR object named "parentname".
see memberremove()
Example
memberremoveall("TimeTable1",1)
moveobject
(obj object, obj location[, num outport])
Moves object to the specified location
Description
This command moves the object to the specified location through the specified port. The specified port does not have to actually exist, this value is used by the receiving location to be able to reference the port the object came in through. When an object moves into location, the OnReceive event function of location is executed. This includes the OnEntry trigger function. Explicitly calling this on a flowitem with events queued up for it may cause problems. Only use when you know that no events are pending for the object being moved.
Example
moveobject(current.first,current.centerObjects[1]);
This moves the first object that is inside the object referenced by current to the object connected to current's first center port.
This moves the first object that is inside the object referenced by current to the object connected to current's first center port.
moveselectedintohighlighted
(obj highlightedobj [, node selectedcontainer])
Description
For developer use. Moves all selected objects in the model into the highlighted object.
Example
moveselectedintohighlighted(selectedobject(ownerview(c)))
nametomodelpath
(obj node, obj object)
notifylinecontroller
(node object, int controllernum, num output, num sendinglast [0/1])
For Dynamo use
Description
For Dynamo use. Informs a LineController connected to the object that material has left the line so the Controller can decide if the run is complete. The number of the LineController to be notified is the contollernum parameter. The object should report how much material (of any kind) has left it since the model began running and whether or not the material leaving is the last material in the object.
Example
notifylinecontroller(current,1,current.stats.output + 1,(current.subnodes.length == 1));
pickoptiononselect
(obj view)
Description
For developer use. This command is used by pick list gui controls to modify the combobox text when an option is selected.
Example
pickoptiononselect(c);
rotateselected
(double angle, double x, double y[, obj roottree])
Description
Rotates all selected objects in the model around the designated origin x/y location
Example
rotateselected(90, 5, 0)
This example rotates selected objects 90 degrees around the location (5,0)
This example rotates selected objects 90 degrees around the location (5,0)
savebyname
(obj tree, str filename)
Description
For developer use. Saves the specified tree node to a file with the given name.
Example
savebyname(Model.find("MyProcessor"), "C:\\MyProcessor.t");
savemodelprepare
()
Description
For developer use. Prepares the model to be saved, including reseting, etc.
Example
savemodelprepare();
saveselectedtofile
()
Description
For developer use. Saves all selected objects in the model to a tree file.
Example
saveselectedtofile()
savestate
()
Description
For developer use. Saves the state of the project. Once this command is executed, you can save your project (.fsp), then open in later, compile, execute loadstate(), and run from the previous spot you started from.
Example
savestate();
savetree
(node tree, str extension, str description, str startingpath)
Description
For developer use. Opens a save file dialog prompting the user for a file name to save. The tree passed in will be saved with the specified name, unless a session is selected. Then the first parameter is ignored. cdir() and pdir() may not be directly used as the path in FlexScript.
Example
savetree(model(),"fsm","FlexSim Model",documentsdir());
searchfornode
(str/node searchstr, node startnode, num findnr[, num searchobjects])
Description
For developer use. Recursively searches the startnode for a node with a name containing the searchstr.
The findnr parameter is useful when the search finds multiple nodes containing the given name, specifying a number i here will give you
the ith node found. Set searchobjects to 1 to search the object's data nodes.
Example
seteventtime
(str EventName, num time, num timemode[1/2], num createevent[1/0])
Sets the "Repeat Event Time" for the global UserEvent
Description
Sets the "Repeat Event Time" for the specified global UserEvent. If timemode = 1, then timeval will be used directly; otherwise, the timeval - time() will be used. If createevent = 1, then in addition to updating the "Repeat Event Time", a single event will be created at the previous time specified.
Example
seteventtime("UserEvent1",20,1,0);
The global userevent named "UserEvent1" will have its "Repeat Event Time" to 20.
The global userevent named "UserEvent1" will have its "Repeat Event Time" to 20.
setprogressbar
(num progress)
Description
For developer use. Sets the progress bar to the specified value. Should be a value between 0 and 100.
Example
setprogressbar((numread / numtotal) * 100);
showprogressbar
(str caption)
Description
For developer use. Opens the progress bar with the specified caption. The bar's progress will be initialized to 0. Use setprogressbar to update the progess value.
Example
showprogressbar("Loading data, please wait");
so
()
Gets a reference to the last node designated as so()
Description
This command returns a reference to the last node that was designated the selected object. This command is only used in the scripting window. To designate a node as so, right-click on the node in the tree and select Edit|Designate This Node (so). Any node in the tree can be designated the selected object.
Example
getnodename(so())
This returns the name of the object that is currently designated the selected object. This command would generally only be used in the scripting window. The final semicolon (;) is not needed in the scripting window.
This returns the name of the object that is currently designated the selected object. This command would generally only be used in the scripting window. The final semicolon (;) is not needed in the scripting window.
startuploadlibraries
([num viewalreadyset])
Description
For developer use. Loads libraries on startup.
Example
startuploadlibraries()
transfernodeobj
(node movenode, node container)
Moves movenode into the container node's object data
Description
This command moves movenode into the container node's object data. This is like the moveobject command, except no events (ie. OnSend, OnReceive) are executed.
Example
transfernodeobj(current.attrs.find("body"), current.next);
updatereport
(num/str/node report)
For Dynamo use
Description
For Dynamo use. Causes the specified Report to add a new row to its table and populate it correctly. This is used to add entries that are not time-based.
Example
updatereport("ResultsReport");
userinput
(obj targetnode, str text [, int stop])
Prompts the user for a value in a dialog box
Description
Prompts the user for a value in a dialog box. The value is placed in the specified node. The model does not stop running while the dialog is open unless the stop parameter is specified. If the stop parameter is specified, then the model stops until the dialog is closed and it returns the value.
Example
userinput(model().subnodes[3].labels["myLabel"],"Please enter a value");
validatename
(obj node, num isviewtext [, obj object])
Description
For developer use. Makes sure the name of node is a valid FlexSim name, replacing invalid characters with underscores and bringing up a message if changes were made. If isviewtext is 1, it assumes the node passed is an edit field, and it changes the viewtext of the field, instead of the name of the node. If the object parameter is specified, it checks that object's name against all the other names of objects in its container. If there are names that are the same, it will pop up an error message. This command is called when you press the Apply or OK buttons in an object's Properties window.
Example
validatename(current, 0);
Model Execution
Commands for stopping, starting, and managing simulation runs.
endreplication
(num onlyifexperimenting)
Ends the current experimenter replication
Description
Will end the current experimenter replication. Use this if your experiment's end time is dependent on a certain condition becoming true instead of a set end time. Specify 1 for onlyifexperimenting to make sure that you only stop if you are running the experiment.
Example
if(current.stats.output >= 5000) endreplication(1);
fastforward
()
Description
For developer use. Saves off the current runspeed, sets the run speed to max, suspends draw, and then runs to the next stop time. Once the next stop time is reached drawing is resumed and the runspeed is restored.
Example
fastforward()
getrunstate
([int checkProcessingEvent])
Returns 1 if the model is currently running, 0 if not
Description
Returns 1 if the model is currently running, 0 if not. If you pass a true value, returns whether an event is currently executing.
Example
if(!getrunstate()){msg("Model Stopped", "The model is not running right now.",1);}
If executed from the script window, this message will only appear if the model is stopped.
If executed from the script window, this message will only appear if the model is stopped.
go
([num fast])
Starts the simulation run
Description
This command starts the simulation run. If there are any events in the event queue, they will occur when the clock reaches them. If there are no events in the queue, the clock will stop. This command will not reset the simulation. If fast is 1, then it will not bind objects before starting. This improves speed if you are stopping and starting the simulation often. See also runfunction().
Example
stop();
if (msg("Model Stopped","Continue?")==1)
{
go();
}
This stops the model then prompts the user if it should start again. If the user presses "OK", the model continues from where it was stopped.
if (msg("Model Stopped","Continue?")==1)
{
go();
}
This stops the model then prompts the user if it should start again. If the user presses "OK", the model continues from where it was stopped.
realtime
([num timecode = 0])
Gets the real clock time
Description
Returns the real clock time in a variety of formats based on the timecode:
0 = the number of seconds and milliseconds since midnight, Jan 1, 1970
1 = the number of seconds since midnight, Jan 1, 1970
2 = the number of milliseconds since the last second change
10 = a time string with format hh:mm:ss
11 = a date string with format mm/dd/yy
12 = a date/time string with format Mon Nov 15 15:49:12 2004
0 = the number of seconds and milliseconds since midnight, Jan 1, 1970
1 = the number of seconds since midnight, Jan 1, 1970
2 = the number of milliseconds since the last second change
10 = a time string with format hh:mm:ss
11 = a date string with format mm/dd/yy
12 = a date/time string with format Mon Nov 15 15:49:12 2004
Example
string curdatetime = realtime(12);
resetexperiment
()
Description
For developer use. Reset the experiment without performing a full model reset. It is typically used internally by the experiment manager.
Example
resetexperiment()
resetlayer
(obj layer)
Description
For developer use. Resets the layer passed. Use resetmodel instead.
Example
resetmodel
([num buildflexscript])
Resets the model
Description
Resets the model. Use this command instead of reset(). The parameter specifies whether the engine should build all flexscript functions as well.
Example
resetmodel()
resetstats
()
Description
For developer use. Reset all object statistics without performing a full model reset. It is typically used internally by the experiment manager.
Example
resetstats()
runfunction
(num noreset)
Description
For developer use. Block user input/output, perform a model run at maximum speed possible by cpu, and return control when stoptime is met. If stoptime = 0, the stoptime is assumed to be 1000. See go().
Example
runfunction(1)
runspeed
(num speed[, num precisionMode])
Sets the simulation speed
Description
This command sets the speed at which the simulation will run. It is the same as clicking and dragging the
slider bar on the Run Control window, but more precise. The speed that the model will attempt to run at is defined as
the number of simulation time units per real second. The model may not actually achieve this speed if the computer cpu
can not keep up. precisionMode defines the precision to use. If 0, the precision mode will remain what it was before the
call. If you pass RUN_SPEED_LOW_PRECISION, it will set to a low precision run speed. If you pass RUN_SPEED_HIGH_PRECISION,
it will run in high precision mode. This is used for emulation purposes. The precision mode will be reset to low precision
on every reset, so you need to have something in your model set it back on reset or when the model starts to enable high
precision mode.
Example
runspeed(10);
go();
This sets the speed to 10 simulation seconds per real second, then runs the model.
go();
This sets the speed to 10 simulation seconds per real second, then runs the model.
skip
()
Description
For developer use. Advance the model run by one step (process exactly one event) and then process any and all events at that same exact model time.
Example
skip()
step
()
Description
For developer use. Advance the model run by one step. One step means to process exactly one event.
Example
step()
stop
([num fast])
Stops the simulation run
Description
This command stops the simulation clock from running. The model stops with all of its pending events still in the queue. If the user starts the model again before resetting, the model will continue from the exact time that it stopped at. If fast is 1, then FlexSim will not rebind objects. This will improve speed if you are stopping and starting often.
Example
stop()
stoptime
(num time [, num stopNum=1])
Sets the time when the simulation should stop
Description
This command sets the time at which the simulation should stop running. The model will not necessarily stop at the exact time specified, but will stop at the first system check on or after the specified stop time. The model may stop early if there are no more events to execute. If stopNum is specified, the stop time at that rank will be set. If time is -1, the command returns the stoptime of stopNum. If time is 0 and stopNum is -1, all stop times will be reset such that there is only one disabled stop time at time 0.
Example
if (stoptime(-1) < 500)
stoptime(500);
This sets the stoptime to 500 if it was less than 500 to begin with.
stoptime(500);
This sets the stoptime to 500 if it was less than 500 to begin with.
updatestates
()
Updates the states of all objects in the model
Description
Updates the states of all objects in the model. Additionally, this command also updates the content stats of all the objects. The 'Stop' button and menu option both call this function before executing a stop() so that objects' stats are updated. Otherwise, reports will not reflect the time the object was in its last state.
Example
updatestates();
NetworkNodes
Commands associated with NetworkNode objects and network paths.
closenodeedge
(obj object, num edgenum)
Closes entry to the networknode's edge
Description
Closes entry to the networknode's specified edge number.
The edge's color will turn orange indicating it is closed.
Open or close status of an edge will only be checked by a traveler
when traveling from one node to the next (not when entering a node from an offset)
The edge's color will turn orange indicating it is closed.
Open or close status of an edge will only be checked by a traveler
when traveling from one node to the next (not when entering a node from an offset)
Example
closenodeedge(current.centerObjects[1], 3);
getedgedist
(obj netnode, num edgenum)
Gets the distance of the edge of a network node
Description
Returns the distance of the specified edge of the network node.
Example
getedgedist(current, 1)
getedgespeedlimit
(obj netnode, num edgenum)
Gets the speed limit of the edge of a network node
Description
Returns the speed limit of the specified edge of the network node.
Example
getedgespeedlimit(current, 1)
getnetnode
(obj object, num nodenr)
Gets the nth network node connected to object with an A connection line
Description
Returns the nth network node connected to the object with a "blue" or "station" connection line
Example
getnetnode(current, 1)
getnetnodespline
(obj netnode, num edgenr)
Gets a reference to the spline head of netnode's edge edgenr
Description
Returns a reference to the spline head for the specified edge of the network node. You can
use spline() commands to then access location data for that spline. Note that the spline head may not be
inside the network node you're passing, but rather may be in the network node on the other side of the edge.
You can use the isedgeforward() command to query whether the spline is inside the network node. If not, then
spline percentages disances passed to the spline() command will be backwards.
Example
treenode splinehead = getnetnodespline(netnode, 2);
getnetworkdistance
(num fromnetnoderank, num tonetnoderank)
Gets the network distance between two network nodes
Description
Returns the network distance between the network nodes. Note that the
network nodes are referenced by their member ranks, not by the pointer to the network node.
Use rankfromnetnode() to get a network node's member rank.
Example
getnetworkdistance(rankfromnetnode(current), rankfromnetnode(current.outObjects[1]));
getnextnetnode
(num fromnn, num tonn)
Gets the rank of the next network node from fromnn in order to get to tonn
Description
Returns the rank of the next network node to go to from one network node in getting to
the destination network node. The return value and parameters will all be network node member
ranks. Use rankfromnetnode() to get the member rank of a network node, and netnodefromrank()
to get the network node from the member rank.
Example
treenode nextnode = netnodefromrank(getnextnetnode(rankfromnetnode(current), rankfromnetnode(Model.find("NN5"))));
getnextnetnodeoutport
(num fromnn, num tonn)
Gets the output port of the network node fromnn in order to get to tonn
Description
Returns the output port, or edge number, to go to in getting from a source network node
to a destination network node.
Example
int outport = getnextnetnodeoutport(rankfromnetnode(current), rankfromnetnode(Model.find("NN5")));
gettenetnode
(obj taskexecuter)
Gets the current network node that a taskexecuter is attached to with an A Connection
Description
Returns the current network node that a taskexecuter (TE) is attached to with a red line.
Example
treenode netnode = gettenetnode(current);
gettenetworkinfo
(obj taskexecuter, obj destobj, num info)
Gets information regarding the current state of a taskexecuter on a node network
Description
Returns information regarding the current state of a taskexecuter on a node network. Valid queries are as follows:
NETWORK_INFO_DEST_NET_NODE_RANK - returns the destination column/rank of the network node that the TE would travel to were he to be given a travel task to destobj. Usually this will simply be the network node attached to destobj, but if multiple network nodes are attached to destobj, the command will find the closest one.
NETWORK_INFO_ORIGIN_NET_NODE_RANK - returns the origin column/rank of the network node that the TE would start from were he to be given a travel task to destobj. Usually this will simply be the current network node where the TE is located, but if that network node has virtual exits, the command will find the virtual exit that renders the shortest travel distance.
NETWORK_INFO_DISTANCE - returns the shortest travel distance to the destination object through the network.
NETWORK_INFO_CUR_DIST_ALONG_EDGE - Only valid when the TE is actively doing a travel task. This returns the current distance that the TE has traveled along its current network edge. For this query, destobj should be NULL.
NETWORK_INFO_CUR_TRAVEL_ORIGIN_RANK - Only valid when the TE is actively doing a travel task. This returns the rank of the origin node at which the TE starts its current travel operation. For this query, destobj should be NULL.
NETWORK_INFO_CUR_TRAVEL_DEST_RANK - Only valid when the TE is actively doing a travel task. This returns the rank of the destination node to which the TE is traveling for its current travel operation. For this query, destobj should be NULL.
NETWORK_INFO_DEST_NET_NODE_RANK - returns the destination column/rank of the network node that the TE would travel to were he to be given a travel task to destobj. Usually this will simply be the network node attached to destobj, but if multiple network nodes are attached to destobj, the command will find the closest one.
NETWORK_INFO_ORIGIN_NET_NODE_RANK - returns the origin column/rank of the network node that the TE would start from were he to be given a travel task to destobj. Usually this will simply be the current network node where the TE is located, but if that network node has virtual exits, the command will find the virtual exit that renders the shortest travel distance.
NETWORK_INFO_DISTANCE - returns the shortest travel distance to the destination object through the network.
NETWORK_INFO_CUR_DIST_ALONG_EDGE - Only valid when the TE is actively doing a travel task. This returns the current distance that the TE has traveled along its current network edge. For this query, destobj should be NULL.
NETWORK_INFO_CUR_TRAVEL_ORIGIN_RANK - Only valid when the TE is actively doing a travel task. This returns the rank of the origin node at which the TE starts its current travel operation. For this query, destobj should be NULL.
NETWORK_INFO_CUR_TRAVEL_DEST_RANK - Only valid when the TE is actively doing a travel task. This returns the rank of the destination node to which the TE is traveling for its current travel operation. For this query, destobj should be NULL.
Example
int destrank = gettenetworkinfo(current, NULL, NETWORK_INFO_CUR_TRAVEL_DEST_RANK);
isedgeforward
(obj netnode, num edgenr)
Returns 1 if the network node's edge is forward, 0 otherwise
Description
Returns 1 if the network node's edge is "forward" meaning when created, the connection was
dragged FROM this network node to the other network node. If the edge is forward, then the spline head is
contained by this network node, and the spline distance values go forward from this network node.
Example
isedgeforward(current, 2)
netnodefromrank
(num rank)
Returns the network node member at rank rank
Description
Takes a network node member rank and returns the actual reference to the network node.
Example
treenode netnode = netnodefromrank(5);
opennodeedge
(obj networknode, num edgenum)
Opens entry to the networknode's edge
Description
Opens entry to the networknode's specified edge number. Closing a node's edge with closenodeedge() blocks travelers from entry onto the edge. This command opens the edge up again.
Example
opennodeedge(current.centerObjects[1], 3);
Opens node edge 3 of a NetworkNode connected to center port 1 of the current object.
Opens node edge 3 of a NetworkNode connected to center port 1 of the current object.
optimizenetwork
()
Causes the model's network navigator to regenerate its distance table
Description
Causes the model's network navigator to regenerate its distance table.
Use this command if you are dynamically connecting edges in your network during the simulation run.
This may take several seconds to do for large networks.
Use this command if you are dynamically connecting edges in your network during the simulation run.
This may take several seconds to do for large networks.
Example
optimizenetwork()
rankfromnetnode
(obj netnode)
Returns the member rank of network node netnode
Description
Takes a network node reference and returns the member rank of that network node. Each network node has a specific "member rank", which is used as a
row/column reference in the network's distance and next node tables. The first network node that is added to a model gets member rank 1, the second gets member rank
2, and so on.
Example
int memberrank = rankfromnetnode(current);
reassignnetnode
(obj taskexecuter, obj networknode)
Description
TaskExecuters using a NetworkNode system are always associated with a specific NetworkNode in the system (red line graphic) which continually changes as they travel around. This command reassigns the specified taskexecuter to networknode.
Warning!!! Do not execute this command unless the TaskExecuter is on a network, and unless you know the TaskExecuter is not currently executing a travel task.
Warning!!! Do not execute this command unless the TaskExecuter is on a network, and unless you know the TaskExecuter is not currently executing a travel task.
Example
reassignnetnode(current, current.centrObjects[5]);
Reassign the current TaskExecuter to the NetworkNode connected to its fifth center port.
Reassign the current TaskExecuter to the NetworkNode connected to its fifth center port.
redirectnetworktraveler
(obj traveler, obj newdest)
Description
Attempts to change the end destination of the traveler to that of the newdest object. Only works if the traveler is currently on a TASKTYPE_TRAVEL task and is on a travel network. Returns 1 if successful.
Example
redirectnetworktraveler(traveler, Model.find("Processor5"));
Redirects the traveler to an object in the model named Processor5 assuming traveler is a pointer to a taskexecuter currently traveling on a network node system and Processor5 is connected to the network.
Redirects the traveler to an object in the model named Processor5 assuming traveler is a pointer to a taskexecuter currently traveling on a network node system and Processor5 is connected to the network.
trafficcontrolinfo
(obj trafficcontrol, num info [, num a, num b])
Gets information on a traffic controller
Description
This command gives you access to various information on a traffic control, as well as lets you direct the traffic control
to perform logic. Logic/data that is performed/returned is based on the info parameter, as follows:
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_NR_ACTIVE_TRAVELERS) - returns the total number of active travelers in the traffic control.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER, num travelnr) - returns a reference to the nth active traveler in the traffic control.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER_COUPLING, num travelernr) - returns a reference to a coupling node, stored in the Traffic Control's variables tree, that is associated with the nth active traveler. This coupling can be used to stored custom user information regarding that active traveler. To do this, add sub-nodes to the coupling node with nodeinsertinto(), add data, etc. Note that once the active traveler leaves the traffic control area, the coupling, and its sub-nodes, will automatically be destroyed.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER_RANK_FROM_TRAVELER, obj traveler) - This command takes a reference to a traveler object and returns which index in the traffic control's active travelers is associated with that traveler. If zero is returned then the object is not an active traveler in the traffic control.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_NR_MEMBERS) - Returns the total number of network nodes that are members of the traffic control area
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_MEMBER, num membernr) - Returns a reference the nth network node member of the traffic control
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_MEMBER_COUPLING, num membernr) - Returns a reference to a coupling node, stored in the traffic control's variables, that is associated with the nth network node member of the traffic control. Like TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER_COUPLING, this node may be used to store data associated with that network node.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_MEMBER_RANK_FROM_NETWORK_NODE, obj netnode) - Takes a network node reference and returns the member index of that network node in the traffic control. If zero is returned then the network node is not a member of the traffic control.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_NR_ENTRY_REQUESTS) - Returns the number of entry requests currently in queue waiting to enter the traffic control area.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ENTRY_REQUEST_TRAVELER, num requestnr) - Returns a reference to the traveler associated with the nth entry request, who is waiting get into the traffic control area.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ENTRY_REQUEST_NETWORK_NODE, num requestnr) - Returns a reference to the network node where the traveler is waiting, associated with the nth entry request
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ENTRY_REQUEST_NODE, num requestnr) - Returns a reference to a node associated with the nth entry request. Like TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER_COUPLING, you may add sub-nodes to store data associated with the request. Do not, however, change the data on this node, as this is used by the traffic control logic.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ALLOW_ENTRY, num requestnr) - Calling this command will instruct the traffic control to allow the traveler associated with the nth entry request to enter the traffic control area.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_SET_ENTRY_REQUEST_RANK, num requestnr, num settorank) - Calling this command will cause the traffic control to rerank its nth entry request to the specified rank.
Also, a note regarding using the traffic control triggers to override the traffic control's default logic. The traffic control's OnEntryRequest trigger, which fires when a traveler first requests entry into the traffic control area, can take 3 different return values:
TC_ON_ENTRY_REQUEST_DEFAULT - If this value is returned from the trigger, the traffic control will perform its normal filtering logic.
TC_ON_ENTRY_REQUEST_ALLOW - If this value is returned, the traffic control will ignore its default logic and simply allow the traveler into the area. Note that if this is used, the traffic control will ignore its maximum capacity variable, so depending on the logic you define, the number of travelers in the area may exceed the maximum capacity variable you specify on the traffic control.
TC_ON_ENTRY_REQUEST_QUEUE - If this value is returned, the traffic control will ignore its default logic and add the request to its request queue, disallowing the traveler from entering the area at that time.
The traffic control's OnExit trigger may take one of two return values:
0 - If this value is returned, the traffic control will perform its default logic, allow other travelers to enter, etc.
1 - If this value is returned, the traffic control will do nothing. In this case the user should use the trigger to explicitly tell the traffic control which traveler(s) to receive using TCI_ALLOW_ENTRY.
If you plan on implementing your own custom logic for allowing travelers into the area, then it is recommended that you use the traffic control's default "Mutual Exclusion" mode.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_NR_ACTIVE_TRAVELERS) - returns the total number of active travelers in the traffic control.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER, num travelnr) - returns a reference to the nth active traveler in the traffic control.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER_COUPLING, num travelernr) - returns a reference to a coupling node, stored in the Traffic Control's variables tree, that is associated with the nth active traveler. This coupling can be used to stored custom user information regarding that active traveler. To do this, add sub-nodes to the coupling node with nodeinsertinto(), add data, etc. Note that once the active traveler leaves the traffic control area, the coupling, and its sub-nodes, will automatically be destroyed.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER_RANK_FROM_TRAVELER, obj traveler) - This command takes a reference to a traveler object and returns which index in the traffic control's active travelers is associated with that traveler. If zero is returned then the object is not an active traveler in the traffic control.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_NR_MEMBERS) - Returns the total number of network nodes that are members of the traffic control area
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_MEMBER, num membernr) - Returns a reference the nth network node member of the traffic control
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_MEMBER_COUPLING, num membernr) - Returns a reference to a coupling node, stored in the traffic control's variables, that is associated with the nth network node member of the traffic control. Like TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER_COUPLING, this node may be used to store data associated with that network node.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_MEMBER_RANK_FROM_NETWORK_NODE, obj netnode) - Takes a network node reference and returns the member index of that network node in the traffic control. If zero is returned then the network node is not a member of the traffic control.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_NR_ENTRY_REQUESTS) - Returns the number of entry requests currently in queue waiting to enter the traffic control area.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ENTRY_REQUEST_TRAVELER, num requestnr) - Returns a reference to the traveler associated with the nth entry request, who is waiting get into the traffic control area.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ENTRY_REQUEST_NETWORK_NODE, num requestnr) - Returns a reference to the network node where the traveler is waiting, associated with the nth entry request
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ENTRY_REQUEST_NODE, num requestnr) - Returns a reference to a node associated with the nth entry request. Like TCI_ACTIVE_TRAVELER_COUPLING, you may add sub-nodes to store data associated with the request. Do not, however, change the data on this node, as this is used by the traffic control logic.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_ALLOW_ENTRY, num requestnr) - Calling this command will instruct the traffic control to allow the traveler associated with the nth entry request to enter the traffic control area.
trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_SET_ENTRY_REQUEST_RANK, num requestnr, num settorank) - Calling this command will cause the traffic control to rerank its nth entry request to the specified rank.
Also, a note regarding using the traffic control triggers to override the traffic control's default logic. The traffic control's OnEntryRequest trigger, which fires when a traveler first requests entry into the traffic control area, can take 3 different return values:
TC_ON_ENTRY_REQUEST_DEFAULT - If this value is returned from the trigger, the traffic control will perform its normal filtering logic.
TC_ON_ENTRY_REQUEST_ALLOW - If this value is returned, the traffic control will ignore its default logic and simply allow the traveler into the area. Note that if this is used, the traffic control will ignore its maximum capacity variable, so depending on the logic you define, the number of travelers in the area may exceed the maximum capacity variable you specify on the traffic control.
TC_ON_ENTRY_REQUEST_QUEUE - If this value is returned, the traffic control will ignore its default logic and add the request to its request queue, disallowing the traveler from entering the area at that time.
The traffic control's OnExit trigger may take one of two return values:
0 - If this value is returned, the traffic control will perform its default logic, allow other travelers to enter, etc.
1 - If this value is returned, the traffic control will do nothing. In this case the user should use the trigger to explicitly tell the traffic control which traveler(s) to receive using TCI_ALLOW_ENTRY.
If you plan on implementing your own custom logic for allowing travelers into the area, then it is recommended that you use the traffic control's default "Mutual Exclusion" mode.
Example
treenode netnode = trafficcontrolinfo(tc, TCI_MEMBER, 2);
Object Data
Commands for accessing and assigning data on objects.
assertvariable
(obj object, str variablename, num datatype)
Gets a reference to variable variablename of object, creates the variable if it does not exist
Description
This command returns a reference to a variable with the given name. If the variable does not exist, one is created with the defined data type.
Example
treenode newvar = assertvariable(Model.find("/Processor1"),"MyVariable", DATATYPE_NUMBER);
classobject
(obj object)
Returns the class object of an instance
Description
Returns the class object of an instance.
Example
if(classobject(current) == library().find("?Processor"))
{
pt("Processor1 is an instance of the Processor class.");pr();
}
This prints a message to the output console if current is a Processor.
{
pt("Processor1 is an instance of the Processor class.");pr();
}
This prints a message to the output console if current is a Processor.
contentunder
(node thenode [, num objectsonly)
Description
This command returns the number of nodes in the tree that are inside the node specified as thenode plus the number of nodes that may be contained in any sub-trees that begin at that layer. If thenode does not contain any other nodes, this command returns 0. If objectsonly is not specified or 0, any node in the FlexSim tree can be passed as thenode. If objectsonly is not 0, any node passed in as thenode that isn't an object will return 0.
Example
if (contentunder(current) >= getvarnum(current,"maxcontent"))
{
current.input.close;
}
This closes the inputs of current if the number of objects contained under current is greater than or equal to the variable called maxcontent of the object referenced by thisobjectdata.
{
current.input.close;
}
This closes the inputs of current if the number of objects contained under current is greater than or equal to the variable called maxcontent of the object referenced by thisobjectdata.
emptyfluidobject
(obj object)
Sets the contents of the fluid object to 0
Description
Sets the contents of the fluid object to 0.
Example
emptyfluidobject(current);
fluidcontent
(obj fluidobject)
Gets the current fluid content of fluidobject
Description
Returns the current fluid content of the specified Fluid Object. It is the same as reading the "curcontent" variable on the object. This does not have any meaning if a Discrete object is passed in.
Example
double objcontent = fluidcontent(current.outObjects[1]);
fluidmaxcontent
(obj fluidobject)
Gets the max fluid content of fluidobject
Description
Returns the defined maximum fluid content of the specified Fluid Object. It is the same as reading the "maxcontent" variable on the object. This does not have any meaning if a Discrete object is passed in.
Example
double objmaxcontent = fluidmaxcontent(current.outObjects[1]);
getanimationvar
(obj object, num/str animation, str varName)
Gets the current value of an animation variable
Description
Gets the current value of an animation variable. See setanimationvar() for more information on animation
variables.
Example
treenode curItem = getanimationvar(current, "Animation1", "Item1");
getcreationtime
(obj object)
Gets the time that a flow item was created
Description
Returns the time that a flowitem was first created.
Example
time() - getcreationtime(item)
getentrytime
(obj object)
Gets the time that a flow item entered the current object it is in
Description
Returns the last entry time of the item (the time the flowitem last entered another object).
Example
time() - getentrytime(item)
getframe
(obj object)
Gets the current Shape Frame being drawn for object
Description
Returns the current 3D shape frame that is being drawn for the object. If the 3D shape assigned to the object was named myshape.3ds, and if two additional 3D shapes with file names myshapeFRAME1.3ds and myshapeFRAME2.3ds resided in the same directory as myshape.3ds, then the two additional files would be loaded into FlexSim automatically at the same time myshape.3ds was loaded, and setting the object's frame from 0 to 1 to 2 would change the object's shape to each of the shapes defined by the three files in order.
Example
if(getframe(current) == 3)) setframe(current, 5);
getobjectshapeindex
(obj object)
Gets the index number of the 3D shape assigned to object
Description
Returns the index number of the 3D shape currently assigned to the object.
Example
getobjectshapeindex(item);
getobjecttextureindex
(obj object)
Gets the index number of the image assigned as the texture for the object's 3D shape
Description
Returns the index number of the bmp or jpeg image currently assigned as the default texture for the object's 3D shape.
Example
getobjecttextureindex(item);
getoutput
(obj involved)
getvarnode
(obj object, str/num var)
Gets a node reference to an object's variable
Description
Returns a reference to the specified variable's node in the specified object.
Example
treenode schedule = getvarnode(current,"schedule");
getvarnum
(obj object, str/num var)
Gets the value of an object's numeric variable
Description
Returns the numeric value stored in the specified variable of the specified object.
Example
double speed = getvarnum(current,"speed");
getvarstr
(obj object, str/num var)
Gets the value of an object's string variable
Description
Returns the string data stored on the specified variable of the specified object.
Example
pt(getvarstr(model().subnodes[2],"creationtrigger"));
isclasstype
(obj object, num/str classtype)
Compares the object to classtype, returns 1 for yes, 0 for no
Description
Returns whether or not the object is of the given classtype. 1 means yes, 0 means no. Possible classtype parameters are:
CLASSTYPE_FLEXSIMOBJECT
CLASSTYPE_FIXEDRESOURCE
CLASSTYPE_TASKEXECUTER
CLASSTYPE_NETWORKNODE
etc.
CLASSTYPE_FLEXSIMOBJECT
CLASSTYPE_FIXEDRESOURCE
CLASSTYPE_TASKEXECUTER
CLASSTYPE_NETWORKNODE
etc.
Example
isclasstype(current, CLASSTYPE_DISPATCHER);
reassignticker
(obj fluidobject, obj ticker[, int resortticker])
Reassigns the Fluid Object's ticker
Description
Changes the Fluid Object passed in as the first parameter from the control of its current Ticker, to the Ticker that is passed in as the second parameter. The object will then have its fluid movement calculated whenever the new Ticker's tick-time elapses. It is recommended that Fluid Objects that are connected to each other always be controlled by the same Ticker. If resortticker is 1, then the new Ticker will immediately resort its list of controlled objects. This may change the order that some fluid objects are evaluated and may have side-effects in the model behavior.
Example
reassignticker(current,Model.find("Ticker2",1);
resumeanimation
(obj object, num/str animation[, num resumeAtType, num resumeAtVal])
Deprecated, use Animation class
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Animation class instead.
Resumes an animation from some point in the middle of the animation.
Resumes an animation from some point in the middle of the animation.
Example
resumeanimation(current, "Stand");
setanimationvar
(obj object, num/str animation, str varName, num/obj toValue)
Sets the value of an animation variable on an object
Description
Sets the value of an animation variable on an object. Animation variables are attributes of an animation
that may need to dynamically change for different runs of the animation, such as surrogates, time between keyframes,
or position/rotation/size values of a given keyframe. For example, you may use surrogates in building your animation.
You do this by choosing a default visual from the flowitem bin to use as you create the animation. Then when the
simulation runs, you substitute real flowitems in for those surrogates when you run the simulation. You do this
substitution by setting the value of an animation variable that you've associated with that surrogate to the actual
reference to the flowitem. Another example is you may use an animation variable to dynamically define the z position
of a keyframe at run-time.
Example
setanimationvar(current, "Animation1", "Item1", current.first);
setframe
(obj object, num/str toframe)
Sets the shape frame of an object
Description
Sets the frame attribute of the object to the framenumber. The frame defines which 3D image to display.
This is a nice way of changing the 3D shape of an object on the fly. There are two ways to define frames on an object.
First, you can do it through the naming of various 3D files. For example, if the object was assigned Operator.3ds as
its default shape, and there are additional files in the same directory as
Operator.3ds named OperatorFRAME1.3ds, OperatorFRAME2.3ds and OperatorFRAME3.3ds, then the frame attribute could be
set to 0,1,2, or 3 which would change the displayed shape to each of the 3ds files respectively. Secondly, you can
add sub-nodes to an obejct's shape attribute, each with a path to the 3D file associated with that frame. Subsequently,
frame 1 would be associated with the shape attribute's first sub-node, etc. This is the method used within FlexSim's
environment to define shape frames. If toframe is a string, then the latter method is assumed, and it will find the
shape attribute sub-node with the corresponding name. One use of this command
would be to change the 3d shape in the OnDown trigger to show a "broken" shape.
Example
if(getframe(current) == 3)) setframe(current, 5);
setobjectbillboard
(obj object, num mode)
Sets the billboard attribute of the visual tool object
Description
This command sets the billboard attribute of the visual tool object. The following modes are available:
0: No Billboard, the visual tool will display based on its set rotation.
1: Vertical Billboard (plane only), this will cause the plane to stand vertically in the model and always face toward the camera along the same viewing plane.
2: All Around Billboard (plane only), this will cause the plane always present its face to you no matter what the viewing angle is.
3: Screen Locked Billboard, locks the Visual Tool in front of the view.
0: No Billboard, the visual tool will display based on its set rotation.
1: Vertical Billboard (plane only), this will cause the plane to stand vertically in the model and always face toward the camera along the same viewing plane.
2: All Around Billboard (plane only), this will cause the plane always present its face to you no matter what the viewing angle is.
3: Screen Locked Billboard, locks the Visual Tool in front of the view.
Example
setobjectbillboard(current, 1);
setobjectshapeindex
(obj object, num index)
Sets the index number for the 3D shape of an object
Description
Sets the index number for the 3D shape of an object. For the new index to take effect, the shape node of the object must be removed or renamed, so this command renames the shape node to "_shape" for you. The index number must be a valid index number of a currently imported 3D shape. To view currently imported 3D shapes and to import more shapes, use View -> Media Files. See setframe() as another solution to changing the 3D shape of an object on the fly.
Example
setobjectshapeindex(item,getshapeindex("fs3d\\Processor.3ds"));
setobjecttextureindex
(obj object, num index)
Sets the index number of the image assigned as a texture for the object's 3D shape
Description
Sets the index number of the bmp or jpeg image to be assigned as the texture for the object's 3D shape. The index number must be a valid index number of a currently imported bmp or jpeg image. To view currently imported images, or to import another bmp or jpeg image, use the Import Media option in the ToolBox. Note that this command does not change the object's imageobject attribute so the original texture will return when the model is reset.
Example
setobjecttextureindex(item,gettextureindex("bitmaps\\flowitempicture.bmp"));
setresetposition
(obj object)
Sets the reset position of the object
Description
Sets the reset position of the object to its current position.
Example
setresetposition(current);
setvarnum
(obj object, str/num var, num value)
Sets the value of an object's numeric variable
Description
Set the specified variable on the object to the number passed in as value.
Example
setvarnum(current.centerObjects[1],"speed",1.5);
setvarstr
(obj object, str/num var, str value)
Sets the value of an object's string variable
Description
Set the string value of the specified variable on the object.
Example
setvarstr(current,"cycletime","return exponential(10,1);");
switch_enablestats
(obj object[, num off/on])
Get or set the "stats" flag of the object
Description
Get or set an object's "stats" flag. A value of 1 is enable, a value of 0 is disable, and a value of -1 gets the current value.
Example
switch_enablestats(so(),1)
switch_hideconnectors
(obj object[, num off/on])
Get or set the "Hide Connectors" flag of the object
Description
Get or set the "Hide Connectors" flag of the object. A value of 1 is hide, a value of 0 is show, a value of -1 gets the current value. Hiding the connectors will turn off the display of ports and their connections both to and from the object. Note that view windows have an attribute named hideallconnectors that controls the display of connectors for ALL objects in their view.
Example
switch_hideconnectors(so(),1)
switch_hidecontents
(obj object[, num off/on])
Get or set the "Show Contents" flag of the object
Description
Get or set the "Show Contents" flag of the object. A value of 1 is hide, a value of 0 is show, a value of -1 gets the current value. Hiding the contents of an objects will stop the display of objects (e.g. flowitems) contained within it.
Example
switch_hidecontents(so(),1)
switch_hidelabel
(obj object[, num off/on])
Get or set the "Show Name" flag of the object
Description
Get or set the "Show Name" flag of the object. A value of 1 will hide the object's name and stats from being displayed on the screen, a value of 0 will show the object's name and possibly stats depending on the viewhidealllabels attribute of the view window. A value of -1 gets the current value for the switch. The viewhidealllabels attribute of the view window has the following possible values which will apply to the label display of all objects in the window: 0=show name and stats, 1=hide name and stats, 2=show just names.
Example
switch_hidelabel(so(),1)
switch_hideshape
(obj object[, num off/on])
Get or set the "Show 3D Shape" flag of the object
Description
Get or set the "Show 3D Shape" flag of the object. A value of 1 is hide, a value of 0 is show, and a value of -1 gets the current value. Note that view windows also have an attribute called hidealldrawcontent that controls the display of 3D shapes for ALL objects in their view.
Example
switch_hideshape(so(),1)
switch_showobject
(obj object[, num off/on])
Expand/collaps the object data of an object node
Description
Expand or collapse the object data of an object node in a tree view. This is analogous to clicking the > next to the object node in a tree view. A value of 1 is expand, a value of 0 is collapse, a value of -1 gets the current value.
Example
switch_showobject(so(),1)
updatelocations
(obj object)
Updates the location of the object and the objects inside of it
Description
This command causes the object to update the location of itself and possibly the objects inside of it. Use this command to refresh locations before querying or executing functionality that would query the location of an object.
Example
updatelocations(current);
updatestate
(obj object [, num profilenr])
Updates the state of the object
Description
Updates the state of the specified object. Could be used in the OnDraw function of an object to make its states display smoothly while the model is running.
Example
updatestate(current);
Object Functions
Commands associated with calling functions on objects and nodes; including nodefunctions, events, messages and their related access variables.
c
<no parentheses>
Description
This command is used to reference the active node during a function's execution. If the function was called using nodefunction(), c returns a reference to the node on which the function is written. If the function is an event function, c returns a reference to the object that contains the event.
Example
treenode current = ownerobject(c);
debug
([num operation, num/obj p2, num/obj p3])
Acts like a breakpoint in Flexscript to start debugging
Description
For developer use. This command is used to control the Flexscript step debugger. Calling this command without any parameters will behave as if there is a breakpoint at that line of code.
Operations:
DEBUG_STOP 0
DEBUG_STEP 1
DEBUG_CONTINUE 2
DEBUG_IS_STOPPED 3
DEBUG_GET_LINE_NR 4
DEBUG_DUMP_VARIABLES 5
DEBUG_STOP_SIMULATION 6
DEBUG_REFRESH_BREAK_POINTS 7
DEBUG_ADD_BREAK_POINT 8
DEBUG_DELETE_BREAK_POINT 9
DEBUG_GET_WATCH_VARIABLE 10
DEBUG_ENABLE_CODE_PROFILING 11
DEBUG_PRINT_CODE_PROFILING_INFO 12
DEBUG_RESET_CODE_PROFILING 13
Operations:
DEBUG_STOP 0
DEBUG_STEP 1
DEBUG_CONTINUE 2
DEBUG_IS_STOPPED 3
DEBUG_GET_LINE_NR 4
DEBUG_DUMP_VARIABLES 5
DEBUG_STOP_SIMULATION 6
DEBUG_REFRESH_BREAK_POINTS 7
DEBUG_ADD_BREAK_POINT 8
DEBUG_DELETE_BREAK_POINT 9
DEBUG_GET_WATCH_VARIABLE 10
DEBUG_ENABLE_CODE_PROFILING 11
DEBUG_PRINT_CODE_PROFILING_INFO 12
DEBUG_RESET_CODE_PROFILING 13
Example
debug();
delayednodefunction
(node thenode, double timeDelay[, par1, par2, ... par10])
Description
For developer use. This command executes a function that is defined on thenode after a defined delay time. It works the same as the nodefunction() command, except it delays firing the node for the given delay time.
Example
delayednodefunction(current.myFunc, tonum(item));
eventlisten
(obj object, str eventName, node relayNode[, num flags, par1, par2, ... par10])
Description
This command will create a listening mechanism where whenever the defined event is called on object, relayNode will also be executed.
flags is a bitwise mask of one of the following values:
To get a list of the events that can be listened to on an object, call function_s(object, "enumerateEvents", destNode). The object will dump a table onto destNode that contains information on all the events that can be listened to on the object.
Some events may have "requirements". This means that in order to properly bind to the event, you have to pass additional parameters in. The enumeration table will give information on the number of requirements and their names. When requirements are needed they displace and shift par1, par2, etc. For example, if an event has 2 requirements, these requirements will take up par1 and par2 of the eventlisten() call, and par3 will then become param(1) in relayNode's code.
EVENT_PRE_LISTEN: The listening function will be called before theNode is called.
EVENT_LISTEN: (default) The listening function will be called after theNode is called.
EVENT_PERSIST: The listener will persist across model resets.
EVENT_PASS_THROUGH_PARAMS: When theNode is called, the parameters passed into the event will also be "passed through"
into the listening node. In this case, par1, par2, etc. are not used.
EVENT_LISTEN_ONCE: The listening mechanism will automatically be removed after the first event firing.
When the listening node is called, if it returns EVENT_STOP_LISTENING, the listener mechanism will be removed and the listening node will no longer be called.
The return value is a reference to a node associated with the listening. If this node is later deleted, the listening mechanism will stop.To get a list of the events that can be listened to on an object, call function_s(object, "enumerateEvents", destNode). The object will dump a table onto destNode that contains information on all the events that can be listened to on the object.
Some events may have "requirements". This means that in order to properly bind to the event, you have to pass additional parameters in. The enumeration table will give information on the number of requirements and their names. When requirements are needed they displace and shift par1, par2, etc. For example, if an event has 2 requirements, these requirements will take up par1 and par2 of the eventlisten() call, and par3 will then become param(1) in relayNode's code.
Example
eventlisten(current, "OnEntry", current.entrylistener);
executefsnode
(node thenode, node c[, node i, node/num/str eventdata, int nobuild])
Execute a node as Flexscript
Description
Dynamically execute a node as Flexscript. If the node is not already Flexscript, the nobuild parameter should be 0. Used to parse string data into Flexscript to execute, such as from a global table or label. The c and i parameters can be accessed in the function as c and i. The eventdata parameter can be accessed as eventdata if it is a string or as eventcode (an integer) if it is a number. If eventdata is a node, it can be accessed using tonode(eventdata) in the function.
Example
executefsnode(current.labels["myFunc"],NULL,NULL,NULL,0)
This executes the script on current's myFunc label, passing NULL into the function for c,i,and eventdata.
This executes the script on current's myFunc label, passing NULL into the function for c,i,and eventdata.
i
<no parentheses>
Description
For developer use. This command is used only in event functions. It is used to reference the object that was passed to the value of 0 is) command as the involved object.
Example
string involvedname = i.name;
This sets involvedname to the name of the object that was passed to value of 0 is) as the involved object.
This sets involvedname to the name of the object that was passed to value of 0 is) as the involved object.
inheritcode
()
Description
For developer use. This command is used for subclass function inheritance. Call this in an event function to call that same event function on the object's classobject. In C++ or DLL code, call _inheritcode(callpoint);
Example
Flexscript: inheritcode();
C++ or DLL: _inheritcode(callpoint);
C++ or DLL: _inheritcode(callpoint);
ip
<no parentheses>
Description
For developer use. Node pointer meaning 'involved port'. Alias for 'eventdata'.
Example
msgparam
(num param)
Within an OnMessage trigger, get the value of a message parameter
Description
Example
int msgtype = msgparam(1);
treenode item = msgparam(2);
Array data = msgparam(3);
treenode item = msgparam(2);
Array data = msgparam(3);
msgsendingobject
()
Within an OnMessage trigger, get a reference to the object sending the message
Description
Example
treenode sender = msgsendingobject;
nodefunction
(node thenode [, par1, par2, ... par10])
Description
For developer use. This command executes a function that is defined on thenode. Thenode must be toggled as either a C++ node or a Flexscript node. If the node is C++, the model must be compiled before calling this command. Any parameters that need to be passed to the function are passed as par1, par2, etc. Up to 10 parameters may be passed. The values that are passed using this command must all be numbers, but can then be accessed and recast from within the function called using the command param(x) where x is the number of the parameter.
Example
nodefunction(node_v_entrytrigger,tonum(item),portnum);
nodefunctionlisten
(node theNode, node relayNode[, num flags, par1, par2, ... par10])
Description
For developer use. This command will create a listening mechanism where whenever nodefunction() is called on theNode, relayNode will also be executed.
flags is a bitwise mask of one of the following values:
NFL_PRE_LISTEN: The listening function will be called before theNode is called.
NFL_LISTEN: (default) The listening function will be called after theNode is called.
NFL_PERSIST: The listener will persist across model resets.
NFL_PASS_THROUGH_PARAMS: When theNode is called, the parameters passed into that function will also be "passed through"
into the listening node. In this case, par1, par2, etc. are not used.
When the listening node is called, if it returns NFL_STOP_LISTENING, the listener mechanism will be removed and the listening node will no longer be called.
The return value is a reference to a node associated with the listening. If this node is later deleted, the listening mechanism will stop.
Example
nodefunctionlisten(getvarnode(current, "entrytrigger"), current.entrylistener);
param
(num index)
Gets a parameter passed into a function
Description
This command is used inside a function that is called by the nodefunction() command. It returns the parameter
passed to nodefunction specified by index as a node (or treenode), string, int, double, stringarray, intarray, doublearray or treenodearray.
The first additional parameter passed to nodefunction() is parameter 1, the second is parameter 2, etc.
Example
If a trigger/field is called with:
nodefunction(thefuncnode, item)
then within the trigger/field, getting access to the item passed as the first additional parameter would be done with:
treenode item = param(1);
Other examples include:
double quantity = param(2);
var value = param(1); //In this example value could be used as any type
nodefunction(thefuncnode, item)
then within the trigger/field, getting access to the item passed as the first additional parameter would be done with:
treenode item = param(1);
Other examples include:
double quantity = param(2);
var value = param(1); //In this example value could be used as any type
parqty
()
Description
For developer use. Get the number of parameters passed into the nodefunction. This is used together with the nodefunction command. The value returned only applies when using Flexscript, not C++.
Example
parqty()
selectall
()
Description
For developer use. Selects all objects in the model.
Example
selectall()
thisclass
<no parentheses>
Description
For developer use. This keyword is used in an eventfunction to get the class of the object receiving the call.
Example
thisclass
Object Ports
Commands associated with the port connections of an objects.
closeallip
(obj object)
Close all input ports of object
Description
Close all input ports of object. Closing all input ports of an object will block entry to the object. Modelers should only use this command when working with fluid objects because the internal behavior of discrete objects controls the opening and closing of their ports, and therefore this command may be overridden. For discrete objects the modeler is referred to closeinput() and stopinput().
Example
closeallip(current)
closeallop
(obj object)
Close all output ports of object
Description
Close all output ports of object. Closing all output ports of an object will block the exit of that object. Modelers should only use this command when working with fluid objects because the internal behavior of discrete objects controls the opening and closing of their ports, and therefore this command may be overridden. For discrete objects the modeler is referred to closeoutput() and stopoutput().
Example
closeallop(current)
closeip
(obj object, num inputportnum)
Close one input port of object
Description
Close just inputportnum of object. Closing an input port of an object will block entry to the object through that port. Modelers should only use this command when working with fluid objects because the internal behavior of discrete objects controls the opening and closing of their ports, and therefore this command may be overridden. For discrete objects the modeler is referred to closeinput() and stopinput().
Example
closeip(current,1)
closeop
(obj object, num outputportnum)
Close one output port of object
Description
Close just outputportnum of object. Closing an output port of an object will block the exit from the object through that port. Modelers should only use this command when working with fluid objects because the internal behavior of discrete objects controls the opening and closing of their ports, and therefore this command may be overridden. For discrete objects the modeler is referred to closeoutput() and stopoutput().
Example
closeop(current,1)
cpcpno
(obj object, num port)
Description
This command returns the center port number that is connected to the specified center port number of object.
Example
int otherport = cpcpno(current,1);
This sets otherport to the number of the port that current's first center port is connected to.
This sets otherport to the number of the port that current's first center port is connected to.
inputopen
(obj object)
Returns 1 if the object's input is open, 0 otherwise
Description
Returns 1 if the object's input is open, 0 otherwise. The closeinput(), stopinput(), openinput(), and resumeinput() commands affect the return value of this command. The commands like closeip() and closeallip() do NOT affect the return value.
Example
if(inputopen(current)) current.input.close;
ipavailable
(obj object, num inputportnum)
Description
Returns a 1 if the upstream object through the specified object's input port is available. Particularly, it checks if the upstream object exists, if it is stopped, if its output is open, and if the connected output port is open. This function returns 0 if the upstream object isn't available.
Example
ipavailable(current,1)
ipopen
(object object, num inputportnum)
Description
Returns a 1 if the inputportnum on object is open. Otherwise returns zero.
Example
ipopen(current,1)
ipopno
(obj object, num inputportnum)
Output port number that is connected to inputportnum of object
Description
This command returns the output port number that is connected to inputportnum of object.
Example
int otherport = ipopno(current,1);
This sets otherport to the port number of the output port that the current object's first input port is connected to.
This sets otherport to the port number of the output port that the current object's first input port is connected to.
ipready
(obj object, num inputportnum)
Description
Returns a 1 if the inputportnum of object is open and the connecting output port of the other object is also open. Otherwise a 0 is returned. This command does not take into consideration whether or not the input of this object or the output of the connecting object are currently open.
Example
ipready(current,1)
numconnections
()
Gets the number of server connections that are currently active
Description
Returns the number of server connections that are currently active.
Example
int numconns = numconnections();
Sets the numconns variable to the number of server connections that are currently active.
Sets the numconns variable to the number of server connections that are currently active.
opavailable
(obj object, num outputportnum)
Description
Returns a 1 if the downstream object through the specified object's output port is available. Particularly, it checks if the downstream object exists, if it is stopped, if its input is open, and if the connected input port is open. This function returns 0 if the downstream object isn't available.
Example
opavailable(current,1)
openallip
(obj object)
Open all input ports of object
Description
Open all input ports of object. If an input port has a pass-through state as a result (both connected ports are open), both objects will be sent a notification message that the port has become "ready". The object with the input port will receive an OnInOpen message and the object with an output port will receive an OnOutOpen message. During traversal of the ports, any given port will only allow pass-through evaluation once. Modelers should only use this command when working with fluid objects because the internal behavior of discrete objects controls the opening and closing of their ports, and therefore this command may be overridden. For discrete objects the modeler is referred to openinput() and resumeinput().
Example
openallip(current)
openallop
(obj object)
Open all output ports of object
Description
Open all output ports of object. If an output port has a pass-through state as a result (both connected ports are open), both objects will be sent a notification message that the port has become "ready". The object with the input port will receive an OnInOpen message and the object with an output port will receive an OnOutOpen message. During traversal of the ports, any given port will only allow pass-through evaluation once. Modelers should only use this command when working with fluid objects because the internal behavior of discrete objects controls the opening and closing of their ports, and therefore this command may be overridden. For discrete objects the modeler is referred to openoutput() and resumeoutput().
Example
openallop(current)
openip
(obj object, num inputportnum)
Open one input port of object
Description
Open just inputportnum of object. Opening an input port of an object will allow entry to the object through that port. Modelers should only use this command when working with fluid objects because the internal behavior of discrete objects controls the opening and closing of their ports, and therefore this command may be overridden. For discrete objects the modeler is referred to openinput() and resumeinput().
Example
openip(so(),1)
openop
(obj object, num outputportnum)
Open one output port of object
Description
Open just outputportnum of object. Opening an output port of an object will allow exiting from the object through that port. Modelers should only use this command when working with fluid objects because the internal behavior of discrete objects controls the opening and closing of their ports, and therefore this command may be overridden. For discrete objects the modeler is referred to openoutput() and resumeoutput().
Example
openop(so(),1)
opipno
(obj object, num outputportnum)
Input port number that is connect to outputportnum of object
Description
This command returns the input port number that is connected to outputportnum of object.
Example
int otherport = opipno(current,1);
This sets otherport to the number of the input port that current's first output port is connected to.
This sets otherport to the number of the input port that current's first output port is connected to.
opopen
(obj object, num outputportnum)
Description
Returns a 1 if the outputportnum on object is open. Otherwise returns zero.
Example
opopen(current,1)
opready
(obj object, num outputportnum)
Description
Returns a 1 if the outputportnum of object is open and the connecting input port of the other object is also open. Otherwise a 0 is returned. This command does not take into consideration whether or not the output of this object or the input of the connecting object are currently open.
Example
opready(current,1)
outputopen
(obj object)
Returns 1 if the object's output is open, 0 otherwise
Description
Returns 1 if the object's output is open, 0 otherwise. The closeoutput(), stopoutput(), openoutput(), and resumeoutput() commands affect the return value of this command. The commands like closeop() and closeallop() do NOT affect the return value.
Example
if(outputopen(current)) current.output.close;
If the output is open for the current object, then close the output.
If the output is open for the current object, then close the output.
transitionport
()
Description
Get the most recently traversed port number by an object in the model. It refers to the last moveobject() call which occurred in the model run.
Example
transitionport()
Output
Commands for giving feedback to the modeler for debugging or reporting purposes.
endoffile
()
Returns 1 if the end of the currently open file has been reached
Description
Returns 1 if the end of the currently open file has been reached. Used with fileopen()
Example
while(!endoffile()){string nextline = filereadline();}
fileclose
()
Closes the FlexSim file interface
Description
Closes the FlexSim file interface and saves any data written to the file while it was open.
Example
fileclose()
fileexists
(str filepath)
Returns 1 if the file exists, 0 otherwise
Description
Returns 1 if the file exists, otherwise 0.
Example
if(fileexists("C:/myfile.txt"))
{
fileopen("C:/myfile.txt");
fpt("Hello World");
fileclose();
}
{
fileopen("C:/myfile.txt");
fpt("Hello World");
fileclose();
}
fileopen
(str filename [, str opentype])
Opens the FlexSim file interface
Description
Opens the FlexSim file interface. Returns 1 if successful. Returns 0 if an error is encountered.
Parameter 2 can be "w" for writing, "r" for reading, or "a" for appending. Default is "w". Use the commands fpt(), fpr(), fpf(), etc. to write to the opened text file. Use filereadline() to read a line from the file. Using this command, you can only have one file open at a time. To write to multiple files simultaneously, use the C standard fopen/fclose commands or C++ standard fstream classes in C++ or through a dll.
If in write mode, the contents of the file will be cleared, and the file pointer will be set to the top of the file. The file must be closed to save any data written to the file.
Parameter 2 can be "w" for writing, "r" for reading, or "a" for appending. Default is "w". Use the commands fpt(), fpr(), fpf(), etc. to write to the opened text file. Use filereadline() to read a line from the file. Using this command, you can only have one file open at a time. To write to multiple files simultaneously, use the C standard fopen/fclose commands or C++ standard fstream classes in C++ or through a dll.
If in write mode, the contents of the file will be cleared, and the file pointer will be set to the top of the file. The file must be closed to save any data written to the file.
Example
fileopen("C:/myfile.txt", "w");
filereadline
()
Reads a line from the currently open file
Description
Reads a line from the currently open file. Used with fileopen()
Example
string nextline = filereadline();
fpc
(num value)
Prints an ASCII character to the open file
Description
Prints an ASCII character to the open file. Common values: TAB = 9, LF = 10, CR = 13
Example
fpc(9)
fpd
(num value)
Prints an integer value to the open file
Description
Prints an integer value to the open file. Floating point values will be truncated.
Example
fpd(3) prints 3
fpd(3.23) prints 3
fpd(3.954) prints 3
fpd(4) prints 4
fpd(3.23) prints 3
fpd(3.954) prints 3
fpd(4) prints 4
fpf
(num value)
Prints a floating point value to the open file
Description
Prints a floating point value to the open file.
Example
fpf(1.234)
fpr
()
Prints a return (new line) to the open file
Description
Prints a return (new line) to the open file.
Example
fpr()
fpt
(str text)
Prints a string to the open file
Description
Prints a string to the open file.
Example
fpt("Hello")
mpd
(num value)
Print an integer to the system console
Description
Prints the integer value to the system console
Example
mpd(6);
mpf
(num value)
Print a floating point value to the system console
Description
Prints the floating point value to the system console.
Example
mpf(7.69);
mpr
()
Print a new line to the system console
Description
Prints a new line to the system console
Example
mpr();
mpt
(str printvalue)
Print text to the system console
Description
Prints the text printvalue to the system console.
Example
mpt("System console printout");
outputtreecontent
(node containernode, str path+filename)
Writes the data of all nodes in the tree under containernode to a text file
Description
Writes the data of all nodes in the tree under containernode to a text file on disk. If file does not exist, it will be created. For more functionality, use menu option: Stats | Model Documentation.
Example
outputtreecontent(model(),"C:/MyModelDocumentation.txt")
print
([var value, var value2, ...])
Print the contents of the given parameters and a new line to the console
Description
This command takes 0 to 20 variants as parameters. Each parameter is printed to the console and separated by a space.
After all the parameters are printed a new line character is printed to the console. The output console must be open to write to it.
To open the console, use Debug > Output Console in the menu.
Example
print("Number:", 1); print([1, 2]);
This prints "Number: 1" and "Array[2]: {1,2}" on different lines of the output console.
This prints "Number: 1" and "Array[2]: {1,2}" on different lines of the output console.
profileevents
()
Prints descriptions of all events currently in the event queue to the output console
Description
Prints to the output console descriptions of all of the events currently waiting in the event queue. The output console must be open to write to it. To open console, use menus View | Output Console.
Example
profileevents()
report
(obj containerobj, str path+filename, num append [0/1])
Description
For developer use. Generate a standard report file in "comma separated value" (csv) format for all objects under containerobj which are currently selected. If append is 1, then the report will be appended to the end of the file specified. If append is 0, then either the file will be created or the existing file will be cleared before the report is written to it.
Example
report(model());
reportmode
(int mode [0=general, 1=state])
Description
For developer use. Set the report mode. (General or state.)
Example
reportmode(0);
People
getactiverole
(treenode person)
Description
Return the person's active role
Example
getactiverole(token.Person)
getcensus
([obj model/group/location])
Description
Get the number of people in the model, a Location group, or an individual location
Example
int census = getcensus(Group("PodA"));
getnumpeopleresources
(obj group [, num availability{0=available/1=acquired}, num priority])
Description
Get the number of available/acquired objects in a people resource group.
If a priority value is passed resources will also be considered available
if a request of that priority would preempt the resource.
Example
int numAvailable = getnumpeopleresources(Group("PodA"));
getpeopleresourceutilization
(obj object/group[, num mode{0=ByState/1=ByAcquires}])
Description
Returns the utilization percentage of a people object or
the average of all members of a people group.
Example
double utilization = getpeopleresourceutilization(Group("PodA"));
reacquirepreemptedresource
(node token, node instance, node preemptedObject, node info, node activeProcess, num sameAsLast [, num newPriority])
Description
Example
reacquirepreemptedresource(token, current, preemptedObject, info, activeProcess);
shiftscheduledownfunction
(node downBehavior, node table, node downObject, double duration)
Description
Example
shiftscheduledownfunction(lunch, shiftSchedule1, doctor, 400);
Process Flow
createtoken
(obj instanceObject, obj/str activity, int start)
executesubflow
(obj/str processFlow [, obj instanceObject, str startActivity, str finishActivity])
Description
Creates a token in a Process Flow Sub Flow which starts that sub flow. Once the created token hits a Finish activity it will return the value evaluted from the Return Value field.
instanceObject: If the instanceObject is specified then current may be used by the activities in the Sub Flow to get access to the instanceObject. This can be useful when multiple objects execute the same Sub Flow but require object specific data.
If no Start activity is specified, the activities in the Sub Flow will be searched and the first Start activity will be used.
If multiple Finish activities are contained in the Sub Flow, the return value will be evaluated from whichever Finish activity the token enters. However, if internal sub flows cause other tokens to enter a Finish activity, it may be necessary to specify the Finish activity name so the correct return value is evaluated.
NOTE: It is important that the activities used in the Sub Flow do not create delays or wait. If the token is interrupted by a delay or wait, the token will not arrive at the Finish activity when the executesubflow function finishes.
instanceObject: If the instanceObject is specified then current may be used by the activities in the Sub Flow to get access to the instanceObject. This can be useful when multiple objects execute the same Sub Flow but require object specific data.
If no Start activity is specified, the activities in the Sub Flow will be searched and the first Start activity will be used.
If multiple Finish activities are contained in the Sub Flow, the return value will be evaluated from whichever Finish activity the token enters. However, if internal sub flows cause other tokens to enter a Finish activity, it may be necessary to specify the Finish activity name so the correct return value is evaluated.
NOTE: It is important that the activities used in the Sub Flow do not create delays or wait. If the token is interrupted by a delay or wait, the token will not arrive at the Finish activity when the executesubflow function finishes.
Example
return executesubflow("SubFlow1", processor);
getactivity
(node/obj/str token/processFlow [, str activityName])
getbatch
(obj/str tokenOrBatch[, obj instanceObject, obj/str/num group])
Description
Gets the batch in a Batch activity by token or Group By value.
If a token is passed in as parameter 1, then the instanceObject and group parameters are not used.
Example
treenode batch = getbatch(token);
treenode batch = getbatch("Batch", current, 3);
treenode batch = getbatch("Batch", current, 3);
getchildtoken
(node parentToken [, int childIndex])
getchildtokenrank
(node childToken)
getlastacquiredresource
(node resource, node token)
Description
Gets the last object acquired by the token from the resource.
Example
treenode operator = getlastacquiredresource(operatorResource, token);
getparenttoken
(node token)
getprocessflowvar
(obj/str processFlow, str varname[, node token])
Description
Gets the value for the Process Flow Variable. The processflow parameter can either be a reference to the Process Flow object in the Tools or the name of the Process Flow object.
Example
double processTime = getprocessflowvar(processflow, "processTime");
treenode processor = getprocessflowvar(processflow, "processor", token);
gettoken
(obj instanceObject, obj/str activity, num index)
Description
Gets the token at the index of the activity for the given owner object (instance).
Example
treenode token = gettoken(fixedResource, activity, 3);
treenode token = gettoken(processor3, "Wait for Conveyor", 2);
treenode token = gettoken(processor3, "Wait for Conveyor", 2);
gettokenbyid
(num id [, obj/str processFlow])
gettokenid
(node token)
gettokens
(obj instanceObject, obj activityOrAsset[, num flags])
Description
Gets all the tokens "inside" an activity or shared asset. For activities,
this is the current set of tokens in the activity. For resources, it is the
set of tokens who have acquired the resource. For zones, it is the set of
tokens that have entered the zone. For a list, it is the set of tokens who
have been pushed to the list. Returns
an Array containing the result.
instanceObject - The object associated with the desired process flow instance. For general process flows this is the same as the process flow itself. For object process flows, it is the 3D object, i.e. task executer or fixed resource, associated with the process flow instance. If executed from within process flow activity logic, this will usually just be "current". If you pass NULL here, it will get tokens for all instances.
activityOrAsset - The target activity or shared asset. If NULL, the command will return all active tokens in the entire process flow instance.
flags - Defines optional flags. If GET_TOKENS_REQUESTS is passed for a shared asset, it will return the set of tokens requesting the shared asset (i.e. tokens waiting to enter a zone, tokens back ordering on a list, etc.).
instanceObject - The object associated with the desired process flow instance. For general process flows this is the same as the process flow itself. For object process flows, it is the 3D object, i.e. task executer or fixed resource, associated with the process flow instance. If executed from within process flow activity logic, this will usually just be "current". If you pass NULL here, it will get tokens for all instances.
activityOrAsset - The target activity or shared asset. If NULL, the command will return all active tokens in the entire process flow instance.
flags - Defines optional flags. If GET_TOKENS_REQUESTS is passed for a shared asset, it will return the set of tokens requesting the shared asset (i.e. tokens waiting to enter a zone, tokens back ordering on a list, etc.).
Example
Array tokensInActivity = gettokens(current, getactivity(processFlow, "Wait For Exit"));
Array resourceOwners = gettokens(current, getactivity(processFlow, "Resource1"));
releasebatch
(node batch, int failed [, int/str/obj connector])
Description
Releases batch from a Batch activity. If failed is 1, all tokens in the batch will be released and the release quantity and label values will be ignored.
Example
releasebatch(batch, false);
releasebatch(batch, true, "Failed");
releasebatch(batch, true, getactivity(processFlow, "Garbage"));
releasebatch(batch, true, "Failed");
releasebatch(batch, true, getactivity(processFlow, "Garbage"));
releasetoken
(node token [, int/str/obj connectorOrActivity])
releasewave
(node wave)
Description
Releases the wave from a Synchronize or Join activity. If the wave is in a Synchronize activity, tokens will exit the activity through the same connector rank that they entered through. If the wave is in a Join activity, the first token added to the wave will exit the activity.
Example
releasewave(wave);
settokencolor
(node token, num red{0-255}, num green{0-255}, num blue{0-255} [, num alpha{0-255}])
settokenshape
(node token, num index)
zonecheckrequests
(obj instanceObject, obj/str zone)
Description
Reevaluates all tokens in a zone's request list.
Example
zonecheckrequests(fixedResource, "Zone 1")
zonegetpartitionvaluefortoken
(obj zone, obj token)
Description
Gets the partition value for a token in the given zone.
Example
zonegetpartitionvaluefortoken(zone, token)
zoneistokeninsubset
(obj zone, obj token, str subsetName)
Description
Determines whether the given token is in the named subset of the given zone
Example
zoneistokeninsubset(zone, token, "MySubset")
Rack Object
Commands for accessing and assigning data on Rack objects.
rackdrawfilledcell
(obj rack, num bay, num level, num x, num y, num z, num sx, num sy, num sz, num red, num green, num blue)
Draws a box in the rack's given bay and level
Description
Draws a box in the rack's given bay and level. x,y, and z are numbers between 0 and 1 representing the percentage into the cell to start drawing the box. sx, sy, and sz are numbers between 0 and 1 representing the size percentage of the box. Red, green and blue specify the color of the box.
To ensure that the boxes are drawn correctly, you should disabled OpenGL textures with fglDisable(GL_TEXTURE_2D) before calling this command in a draw trigger.
To ensure that the boxes are drawn correctly, you should disabled OpenGL textures with fglDisable(GL_TEXTURE_2D) before calling this command in a draw trigger.
Example
fglDisable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
for (int bay = 1; bay <= 5; bay++) {
for (int level = 1; level <= 3; level++) {
rackdrawfilledcell(current, bay, level, 0,0,0, 0.5,1,1, 255,0,0);
}
}
fglEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
This example draws red boxes in bays 1-5, levels 1-3, that fill half of each cell's volume (sx = 0.5, sy =1, sz = 1).
for (int bay = 1; bay <= 5; bay++) {
for (int level = 1; level <= 3; level++) {
rackdrawfilledcell(current, bay, level, 0,0,0, 0.5,1,1, 255,0,0);
}
}
fglEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
This example draws red boxes in bays 1-5, levels 1-3, that fill half of each cell's volume (sx = 0.5, sy =1, sz = 1).
rackdrawvirtualcontent
(obj rack, num bayfillperc, num levelfillperc, num itemdepth, num red, num green, num blue, num virtualonly)
Draw the rack's virtual content
Description
Draws the rack's "virtual" content. This command will usually only be used if you are recycling flowitems using the rackrecycleitem command. When this command is executed, the rack goes through its content table, and draws a box for every flowitem in the rack, at its appropriate bay and level. If virtualonly is 1, then it will only draw a box in spots where a slot is filled, but no flowitem is present (the flowitem has been recycled). Bayfillperc and levelfillperc are values between 0 and 1, and specify the percent of the cell to fill with the drawn box. Item depth is the size each item takes up in the rack. For a floor storage rack, this the z size of the items. For a regular rack, it is the y size of the items.
Example
rackdrawvirtualcontent(current, 0.9,0.9,3, 256,0, 0, 1);
rackgetbaycontent
(obj rack, num bay)
Gets the number of flow items in the bay of the rack
Description
Returns the number of flow items in the specified bay of the rack
Example
int numitems = rackgetbaycontent(current, 5);
Sets numitems to the number of flowitems in bay 5 of the current rack.
Sets numitems to the number of flowitems in bay 5 of the current rack.
rackgetbayloc
(obj rack, num bay)
Gets the x location of bay relative to the rack's origin
Description
Returns the x location of the given bay of the rack, relative to the rack's origin.
Example
rackgetbayloc(current, 5);
Returns the rz of bay 5.
Returns the rz of bay 5.
rackgetbayofitem
(obj rack, obj item)
Gets the bay number of the rack that the item is placed in
Description
Returns the bay number of the rack that the item is placed in
Example
int baynum = rackgetbayofitem(current, item);
Sets baynum to the bay number containing item in the current rack.
Sets baynum to the bay number containing item in the current rack.
rackgetbaysize
(obj rack, num bay)
Gets the x size of bay of the rack
Description
Returns the x size of the given bay of the rack.
Example
rackgetbaysize(current, 5);
Returns the size of bay 5.
Returns the size of bay 5.
rackgetcellcontent
(obj rack, num bay, num level)
Gets the number of flow items in bay and level of the rack
Description
Returns the number of flow items in the specified bay and level of the rack
Example
int numitems = rackgetcellcontent(current, 5, 3);
Sets numitems to the number of flowitems in bay 5, level 3 of the current rack.
Sets numitems to the number of flowitems in bay 5, level 3 of the current rack.
rackgetcellvar
(obj rack, num bay, num level, num varnum, node storagenode)
Description
Returns the value stored in a three dimensional table with rows representing the rack's bays,
columns representing the rack's levels,
and sub-nodes of table cells representing different stored values for each cell of the Rack.
This allows you to store custom information for each cell of the rack.
Bay, level, and varnum reference bay (row), level (column), and variable number (sub-node rank) in the table.
storagenode references the node you have stored this table on. Usually this should be a label on the Rack.
columns representing the rack's levels,
and sub-nodes of table cells representing different stored values for each cell of the Rack.
This allows you to store custom information for each cell of the rack.
Bay, level, and varnum reference bay (row), level (column), and variable number (sub-node rank) in the table.
storagenode references the node you have stored this table on. Usually this should be a label on the Rack.
Example
int typeofcellitems = rackgetcellvar(current, 1,5,3, current.labels["storageData"]);
rackgetitembybaylevel
(obj rack, num bay, num level, num itemrank)
Gets a reference to an item in the bay and level of the rack
Description
Returns a reference to an item in the specified bay and level of the rack. Itemrank specifies the rank of the item in that cell.
Example
treenode theitem = rackgetitembybaylevel(current, 5, 4, 2);
Sets theitem pointer to the second flowitem in bay 5, level 4 of the current object.
Sets theitem pointer to the second flowitem in bay 5, level 4 of the current object.
rackgetitemcellrank
(obj rack, obj item)
Gets the item's rank within the rack's cell
Description
Returns the rank of the item within its given cell in a rack.
Example
int theRank = rackgetitemcellrank(current, item);
rackgetlevelloc
(obj rack, num bay, num level)
Gets the y or z location of the level relative to the rack's origin
Description
Returns the y or z location of the given level of the rack, relative to the rack's origin.
If the rack is a floor storage rack, this returns the y rz.
If the rack is a normal rack, this returns the z rz.
If the rack is a floor storage rack, this returns the y rz.
If the rack is a normal rack, this returns the z rz.
Example
rackgetlevelloc(current, 5, 4);
Returns the y or z location of bay 5, level 4.
Returns the y or z location of bay 5, level 4.
rackgetlevelofitem
(obj rack, obj item)
Gets the level number of the rack that the item is placed in
Description
Returns the level number of the rack that the item is placed in
Example
int levelnum = rackgetlevelofitem(current, item);
Set the levelnum variable to the level number containing item in the current rack.
Set the levelnum variable to the level number containing item in the current rack.
rackgetlevelsize
(obj rack, num bay, num level)
Gets the y or z size of the level of the rack
Description
Returns the y or z size of the given level of the rack.
If the rack is a floor storage rack, this returns the y size.
If the rack is a normal rack, this returns the z size.
If the rack is a floor storage rack, this returns the y size.
If the rack is a normal rack, this returns the z size.
Example
rackgetlevelsize(current, 5, 4);
Returns the y or z size of bay 5, level 4.
Returns the y or z size of bay 5, level 4.
rackgetnrofbays
(obj rack)
Gets the number of bays rack has
Description
Returns the number of bays that the rack has.
Example
return duniform(1,rackgetnrofbays(rack));
This returns a random number between one and the number of bays on the rack. This is the same as the "Random" option of the place in bay pick list.
This returns a random number between one and the number of bays on the rack. This is the same as the "Random" option of the place in bay pick list.
rackgetnroflevels
( obj rack [,num bay ] )
Gets the number of levels in the bay of the rack
Description
Returns the number of levels in the specified bay of the rack. If no bay parameter is passed into the function, then the nroflevels in the first bay will be returned.
Example
return duniform(1,rackgetnroflevels(rack, baynum));
This returns a random number between one and the number of levels on the chosen bay of the rack. This is the same as the "Random" option of the place in level pick list.
This returns a random number between one and the number of levels on the chosen bay of the rack. This is the same as the "Random" option of the place in level pick list.
rackrecycleitem
(obj rack, obj item, num binrank)
Recycles the flowitem into the flowitem bin
Description
Recycles the flowitem into the flowitem bin specified.
This command is for advanced users, and should not be used unless you are prepared to do some debugging.
Bin rank should be the rank of the flowitem in the flowitem bin (textured colored box = 5, etc.).
When this command is called, the flowitem is recycled, but the spot where it is located is designated as taken,
and further flowitems will be put into the rack as if this spot is already filled.
This can significantly increase the speed of a model.
Subsequent commands to rackgetbaycontent(), rackgetcellcontent(), etc. will return values as if the item were still there.
However, rackgetitembybaylevel() will return NULL for an item that has been recycled and has yet to be restored.
Make sure the item is not released or waiting for a transport before calling this command.
Note that max content of the rack will not work properly if this command is used. Also you will need to eventually restore the item using the
rackrestoreitem() command.
This command is for advanced users, and should not be used unless you are prepared to do some debugging.
Bin rank should be the rank of the flowitem in the flowitem bin (textured colored box = 5, etc.).
When this command is called, the flowitem is recycled, but the spot where it is located is designated as taken,
and further flowitems will be put into the rack as if this spot is already filled.
This can significantly increase the speed of a model.
Subsequent commands to rackgetbaycontent(), rackgetcellcontent(), etc. will return values as if the item were still there.
However, rackgetitembybaylevel() will return NULL for an item that has been recycled and has yet to be restored.
Make sure the item is not released or waiting for a transport before calling this command.
Note that max content of the rack will not work properly if this command is used. Also you will need to eventually restore the item using the
rackrestoreitem() command.
Example
rackrecycleitem(current, item, 5);
This recycles the flowitem into the 5th ranked flowitem of the flowitem bin (usually the textured colored box).
This recycles the flowitem into the 5th ranked flowitem of the flowitem bin (usually the textured colored box).
rackrestoreitem
(obj rack, num binrank, num bay, num level, num position)
Restores a flowitem from the flowitem bin into the bay and level
Description
Restores a flowitem from the flowitem bin into the given bay and level.
Example
rackrestoreitem(current, 5, 7, 3, 1);
This restores a flowitem from the 5th ranked flowitem of the flowitem bin (usually the textured colored box) into bay 7, level 3, position 1 of the rack.
This restores a flowitem from the 5th ranked flowitem of the flowitem bin (usually the textured colored box) into bay 7, level 3, position 1 of the rack.
racksetcellcontent
(obj rack, num bay, num level, num contentval)
Sets the virtual content of the rack's cell to contentval
Description
Sets the "virtual" content of the rack's cell to the specified value.
This should only be used if you are recycling and restoring items to the rack with rackrecycleitem() and rackrestoreitem().
You will usually use this command to set an initial "virtual" content on reset.
This should only be used if you are recycling and restoring items to the rack with rackrecycleitem() and rackrestoreitem().
You will usually use this command to set an initial "virtual" content on reset.
Example
racksetcellcontent(current, 5, 3, 2);
racksetcellvar
(obj rack,num bay, num level, num varnum, num setvalue, node storagenode)
Description
Sets the value in a three dimensional table with rows representing the rack's bays,
columns representing the rack's levels,
and sub-nodes of table cells representing different stored values for each cell of the Rack.
This allows you to store custom information for each cell of the rack.
Bay, level, and varnum reference bay (row), level (column), and variable number (sub-node rank) in the table.
Setvalue is the value to set it to.
storagenode references the node you have stored this table on. Usually this should be a label on the Rack.
columns representing the rack's levels,
and sub-nodes of table cells representing different stored values for each cell of the Rack.
This allows you to store custom information for each cell of the rack.
Bay, level, and varnum reference bay (row), level (column), and variable number (sub-node rank) in the table.
Setvalue is the value to set it to.
storagenode references the node you have stored this table on. Usually this should be a label on the Rack.
Example
racksetcellvar(current, 5, 3, 2, 4.6, current.labels["storageData"]);
This sets the 2nd value of bay 5, level 3 to 4.6
This sets the 2nd value of bay 5, level 3 to 4.6
Statistics
Commands for creating, manipulating, and accessing statistical data; including probability distributions.
addbundleentry
(node datanode[, field1val, field2val, ...])
Adds a new entry to the bundle (base 0)
Description
Adds a new entry to the bundle (base 0). All fields must be added before adding entries. The optional field values will be added to the fields in the given order. Up to 29 field values can be given. For bundles with more fields, use setbundlevalue.
Example
int lastentry = addbundleentry(x, time(), current.subnodes.length);
addbundlefield
(node datanode, str fieldname, num type[, num maxstrsize])
Adds a field to the bundle
Description
Adds a field to the bundle with the given field name. Returns the field rank (base 0) of the added field.
All fields for a bundle must be added before any entries are added.
The type is a bitwise flag that must be one of the following values:
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_DOUBLE : stores a 64-bit double
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_FLOAT : stores a 32-bit float
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_INT : stores a 32-bit integer
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_STR : stores a string. If used, you should also define the maximum string size, which will be the space allocated for each string entry. If maxstrsize is unspecified, the default will be 32 bytes. The field will be able to store strings at least as long as the specified length, and any longer strings will be truncated.
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_VARCHAR: stores a string. This field type does not impose a limit on string length. This field type is recommended if you need variable string lengths, or if strings are frequently repeated.
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_NODEREF : stores a reference to a node
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_BINARY : stores a 1 or 0 as a single bit. Bits are allocated in blocks of 32, so that one binary field requires 32 bits. However, 32 binary fields can share a single block.
You can optionally bitwise combine any of the above values (except BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_BINARY) with BUNDLE_FIELD_INDEX_MAP. All values in this type of field will be indexed for quick lookup (O(log n)) using getbundleindexentries().
You can optionally combine BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_INT, BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_STR, BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_VARCHAR, or BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_NODEREF with BUNDLE_FIELD_INDEX_HASH. All values in this type of field will be indexed for quick lookup (O(1)) using getbundleindexentries(). This type of field is only recommended for use with bundles that rarely, if ever, change size while the model is running.
You can optionally combine any of the above values (except BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_BINARY) with BUNDLE_FIELD_NULLABLE, to allow those fields to contain null values. If a field is nullable, you can pass a null Variant in to setbundlevalue(), and it is possible to get a null Variant from getbundlevalue().
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_DOUBLE : stores a 64-bit double
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_FLOAT : stores a 32-bit float
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_INT : stores a 32-bit integer
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_STR : stores a string. If used, you should also define the maximum string size, which will be the space allocated for each string entry. If maxstrsize is unspecified, the default will be 32 bytes. The field will be able to store strings at least as long as the specified length, and any longer strings will be truncated.
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_VARCHAR: stores a string. This field type does not impose a limit on string length. This field type is recommended if you need variable string lengths, or if strings are frequently repeated.
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_NODEREF : stores a reference to a node
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_BINARY : stores a 1 or 0 as a single bit. Bits are allocated in blocks of 32, so that one binary field requires 32 bits. However, 32 binary fields can share a single block.
You can optionally bitwise combine any of the above values (except BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_BINARY) with BUNDLE_FIELD_INDEX_MAP. All values in this type of field will be indexed for quick lookup (O(log n)) using getbundleindexentries().
You can optionally combine BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_INT, BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_STR, BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_VARCHAR, or BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_NODEREF with BUNDLE_FIELD_INDEX_HASH. All values in this type of field will be indexed for quick lookup (O(1)) using getbundleindexentries(). This type of field is only recommended for use with bundles that rarely, if ever, change size while the model is running.
You can optionally combine any of the above values (except BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_BINARY) with BUNDLE_FIELD_NULLABLE, to allow those fields to contain null values. If a field is nullable, you can pass a null Variant in to setbundlevalue(), and it is possible to get a null Variant from getbundlevalue().
Example
addbundlefield(x, "Object Name", BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_STR | BUNDLE_FIELD_NULLABLE, 64);
bernoulli
(num prob, num succeed-value, num fail-value[, num stream])
Returns one of two possible values, based on the given probability
Description
bernoulli( p, a, b, stream ) is a discrete probability distribution.
Inputs:
p is the probability that a will be returned; where p∈ ( 0, 100 )
100 −p is the probability that b will be returned.
a∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
b∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = { a , b }
mean = ( ap + b(100−p) ) ⁄ 100
variance = (p⁄100)(1 −p⁄100) when a=1 and b=0
Possible Applications:
Used to model a random occurrence that has two possible outcomes such as a pass/fail test. It is possible to generate more than two values by nesting bernoulli commands; however, it is better to use empirical distributions in these cases.
Comments:
The bernoulli(p, 1, 0) and binomial(1, p) distributions are the same.
Inputs:
p is the probability that a will be returned; where p∈ ( 0, 100 )
100 −p is the probability that b will be returned.
a∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
b∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = { a , b }
mean = ( ap + b(100−p) ) ⁄ 100
variance = (p⁄100)(1 −p⁄100) when a=1 and b=0
Possible Applications:
Used to model a random occurrence that has two possible outcomes such as a pass/fail test. It is possible to generate more than two values by nesting bernoulli commands; however, it is better to use empirical distributions in these cases.
Comments:
The bernoulli(p, 1, 0) and binomial(1, p) distributions are the same.
Example
treenode curoperator = current.centerObjects[bernoulli(90,1,2,1)];
The bernoulli command in this example has a 90 percent probability of returning 1 otherwise it will return 2, using random number stream 1. It is used within a centerObject reference such that 90 percent of the time curoperator references the object connected to center port 1 of the current object, otherwise curoperator references the object connected to center port 2.
The bernoulli command in this example has a 90 percent probability of returning 1 otherwise it will return 2, using random number stream 1. It is used within a centerObject reference such that 90 percent of the time curoperator references the object connected to center port 1 of the current object, otherwise curoperator references the object connected to center port 2.
beta
(num min, num max, num shape1, num shape2[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a beta distribution
Description
beta( a, b, α1, α2, stream ) is a bounded continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
a is the lower-endpoint parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
b is the upper-endpoint parameter( b > a )
α1 is the 1st shape parameter ( 0, ∞ )
α2 is the 2nd shape parameter ( 0, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( a , b )
mean = a + α1(b−a) ⁄ (α1 + α2)
variance = α1α2(b−a)²⁄ (α1 + α2)²(α1 + α2 + 1)
Probability Density Functions:
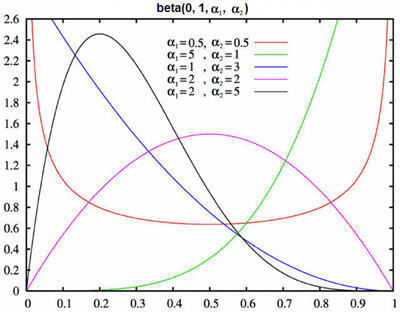
Possible Applications:
The beta distribution is often used to model task durations in the absence of real data because it can be definitively bounded between a minimum and maximum value, and it can take on a number of different probability density shapes depending on the two shape parameters used. For most real world task durations, the density shape will have a longer right tail than a left, so if you know the mean μ and the mode (most likely value) m, you can back calculate suitable shape parameters with the following equations:
α1 ≅ ( μ−a)(2m−a−b) ⁄ (m−μ)(b−a)
α2 ≅ α1(b−μ) ⁄ (μ−a)
Comments:
The beta( a, b, 1, 1) and uniform( a, b) distributions are the same.
The density is symmetric about (a + b) ⁄ 2 when α1 = α2.
The density will have a hump and longer right tail when α2 > α1 > 1.
The mean and mode are equal when α1 = α2 > 1.
Inputs:
a is the lower-endpoint parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
b is the upper-endpoint parameter( b > a )
α1 is the 1st shape parameter ( 0, ∞ )
α2 is the 2nd shape parameter ( 0, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( a , b )
mean = a + α1(b−a) ⁄ (α1 + α2)
variance = α1α2(b−a)²⁄ (α1 + α2)²(α1 + α2 + 1)
Probability Density Functions:

Possible Applications:
The beta distribution is often used to model task durations in the absence of real data because it can be definitively bounded between a minimum and maximum value, and it can take on a number of different probability density shapes depending on the two shape parameters used. For most real world task durations, the density shape will have a longer right tail than a left, so if you know the mean μ and the mode (most likely value) m, you can back calculate suitable shape parameters with the following equations:
α1 ≅ ( μ−a)(2m−a−b) ⁄ (m−μ)(b−a)
α2 ≅ α1(b−μ) ⁄ (μ−a)
Comments:
The beta( a, b, 1, 1) and uniform( a, b) distributions are the same.
The density is symmetric about (a + b) ⁄ 2 when α1 = α2.
The density will have a hump and longer right tail when α2 > α1 > 1.
The mean and mode are equal when α1 = α2 > 1.
Example
double ptime = beta(8, 12, 1.3, 3, 5);
The ptime variable is set equal to a beta distribution having a minimum value of 8, a maximum value of 12, and shape factors of 1.3 and 3 for α1 and α2 respectively. FlexSim's random stream number 5 will be used to generate variates from the distribution. The distribution density will have a nice humped curve with a long right tail.
The ptime variable is set equal to a beta distribution having a minimum value of 8, a maximum value of 12, and shape factors of 1.3 and 3 for α1 and α2 respectively. FlexSim's random stream number 5 will be used to generate variates from the distribution. The distribution density will have a nice humped curve with a long right tail.
binomial
(num trials, num prob[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a binomial distribution
Description
binomial( t, p, stream ) is a discrete probability distribution used to represent the number of successes in t independent Bernoulli trials with probability p of sucess on each trial.
Inputs:
t is the number of independent trials { 1, 2, ..., ∞ }.
p is the probability of success for any given trial (0, 100)
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = { 0, 1, 2, ..., t }
mean = tp⁄ 100
variance = t ( p⁄ 100 )( 1 −p⁄ 100 )
Possible Applications:
The binomial distribution is useful for modeling the number of defective parts in a batch of size t, or the actual number of people in random size groups, or maybe the number of items ordered from inventory.
Comments:
The binomial(1, p ) and bernoulli( p, 1, 0 ) distributions are the same.
The binomial( t, p ) distribution is symmetric when p = 50 percent.
Inputs:
t is the number of independent trials { 1, 2, ..., ∞ }.
p is the probability of success for any given trial (0, 100)
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = { 0, 1, 2, ..., t }
mean = tp⁄ 100
variance = t ( p⁄ 100 )( 1 −p⁄ 100 )
Possible Applications:
The binomial distribution is useful for modeling the number of defective parts in a batch of size t, or the actual number of people in random size groups, or maybe the number of items ordered from inventory.
Comments:
The binomial(1, p ) and bernoulli( p, 1, 0 ) distributions are the same.
The binomial( t, p ) distribution is symmetric when p = 50 percent.
Example
int fparts = binomial(item.batchsize, 10, 5);
The number of failed parts will be written to the fparts variable based on a 10% probability that any given part will fail within a batch quantity defined by a label on the flowitem named "batchsize". FlexSim's random stream number 5 will be used to generate variates from the distribution.
The number of failed parts will be written to the fparts variable based on a 10% probability that any given part will fail within a batch quantity defined by a label on the flowitem named "batchsize". FlexSim's random stream number 5 will be used to generate variates from the distribution.
calculateconfidence
(num stddev, num nrofdatapoints, num confidence)
Description
For developer use. Calculates the confidence interval for the given standard deviation and number of data points. The return value is the distance on one side of the interval from the sample mean. This uses the t distribution to calculate the confidence interval. Confidence values must be either 90, 95, or 99. This is used in the experimenter to calculate the confidence intervals for the mean of performance measures for each scenario.
Example
calculateconfidence(5.82, nrofsamples, 90)
cauchy
(num location, num scale[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a cauchy distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a cauchy distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
cempirical
(str/node/num table[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a continuous empirical distribution
Description
A continuous empirical distribution with percentages and values defined in the table specified.
Empirical distributions reference tables created by the user that contain a list of values and probability percentages associated with each value. Probability percentages must be entered in column 1 starting with row 1 of the table, and the associated values are entered in column 2. The table may have as many rows as needed to define as many values as desired. The percents are entered as numbers between 0 and 100, and should add up to a total of 100 percent; otherwise any values defined after a cumulative percentage of 100 is reached will never be returned.
There are three commands in FlexSim that can be used to generate random variates from the empirical distributions defined in tables. The three commands are dempirical(), empirical() and cempirical(). The first one is a discrete distribution and will return the explicit values listed in the table. The next two are bounded continuous distributions, meaning they return a continous number within a range. The values in column 2 for the continuous distributions must be in ascending order because they will interpolate values between two adjacent values in the table.
Let's assume we have a table with 4 rows and 2 columns. In column one are the percentages 10, 20, 30 and 40 adding up to 100 percent. In column two are the values 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 and 0.4. Now let's see the differences between the discrete empirical command and the two continuous empirical commands. The discrete command will only generate random variates that match exactly the values that were entered into column two of the table. The continuous commands will generate random variates that are real numbers uniformly distributed between two adjacent numbers in column two of the table. The difference between the two continuous commands is in how the bounds of the uniform ranges are defined.
The command dempirical("mytable") will return the number 0.1 for ten percent of the samples, the number 0.2 for twenty percent of the samples, the number 0.3 for thirty percent of the samples, and the number 0.4 for forty percent of the samples assuming a very large sample set.
The command empirical("mytable") will return a number uniformly distributed between 0.1 and 0.2 for ten percent of the samples, a number uniformly distributed between 0.2 and 0.3 for twenty percent of the samples, a number uniformly distributed between 0.3 and 0.4 for thirty percent of the samples and a number uniformly distributed between 0.4 and 0.4 for forty percent of the samples. If you want the last forty percent to be between 0.4 and 0.5 instead of 0.4, add a 5th row with column one being a value of 0 and column two being 0.5 or the desired upper bound.
The command cempirical("mytable") will return a number uniformly distributed between 0.0 and 0.1 for ten percent of the samples, a number uniformly distributed between 0.1 and 0.2 for twenty percent of the samples, a number uniformly distributed between 0.2 and 0.3 for thirty percent of the samples and a number uniformly distributed between 0.3 and 0.4 for forty percent of the samples. You can define a lower bound for the first ten percent to be a value different than 0.0 by adding a row to the beginning of the table (row 1) where column one is a value of 0 and column two is 0.05 or the desired lower bound.
Here is a summary in tabular form showing the possible return values ("x") for each of the three distribution functions:
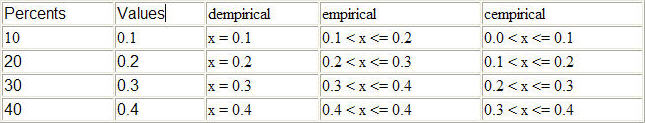
Here is an example of adding a "dummy" first row so that cempirical() starts at 0.05 instead of 0.0 (notice that row 1 has a probability of 0 percent):
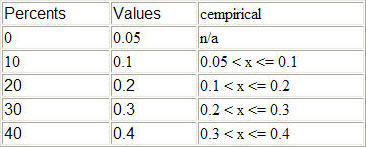
Here is an example of adding a "dummy" last row so that empirical() has a range between each value including the last (any number can be entered for the percent of the last row because the percents already add up to 100% with the previous row, so it doesn't matter what it is):
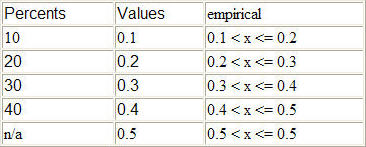
When using ExpertFit to determine an empirical distribution that matches your data, you need to be aware that if your data has been defined as integers, then ExpertFit will fit it for use with dempirical(), and if your data has been defined as real numbers, ExpertFit will fit it for use with empirical(). When your data set is composed of real numbers, ExpertFit will show the same percentage for the last value as for the previous to last value, but you'll notice that the percents add up to 100% with the second to last entry.
Empirical distributions reference tables created by the user that contain a list of values and probability percentages associated with each value. Probability percentages must be entered in column 1 starting with row 1 of the table, and the associated values are entered in column 2. The table may have as many rows as needed to define as many values as desired. The percents are entered as numbers between 0 and 100, and should add up to a total of 100 percent; otherwise any values defined after a cumulative percentage of 100 is reached will never be returned.
There are three commands in FlexSim that can be used to generate random variates from the empirical distributions defined in tables. The three commands are dempirical(), empirical() and cempirical(). The first one is a discrete distribution and will return the explicit values listed in the table. The next two are bounded continuous distributions, meaning they return a continous number within a range. The values in column 2 for the continuous distributions must be in ascending order because they will interpolate values between two adjacent values in the table.
Let's assume we have a table with 4 rows and 2 columns. In column one are the percentages 10, 20, 30 and 40 adding up to 100 percent. In column two are the values 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 and 0.4. Now let's see the differences between the discrete empirical command and the two continuous empirical commands. The discrete command will only generate random variates that match exactly the values that were entered into column two of the table. The continuous commands will generate random variates that are real numbers uniformly distributed between two adjacent numbers in column two of the table. The difference between the two continuous commands is in how the bounds of the uniform ranges are defined.
The command dempirical("mytable") will return the number 0.1 for ten percent of the samples, the number 0.2 for twenty percent of the samples, the number 0.3 for thirty percent of the samples, and the number 0.4 for forty percent of the samples assuming a very large sample set.
The command empirical("mytable") will return a number uniformly distributed between 0.1 and 0.2 for ten percent of the samples, a number uniformly distributed between 0.2 and 0.3 for twenty percent of the samples, a number uniformly distributed between 0.3 and 0.4 for thirty percent of the samples and a number uniformly distributed between 0.4 and 0.4 for forty percent of the samples. If you want the last forty percent to be between 0.4 and 0.5 instead of 0.4, add a 5th row with column one being a value of 0 and column two being 0.5 or the desired upper bound.
The command cempirical("mytable") will return a number uniformly distributed between 0.0 and 0.1 for ten percent of the samples, a number uniformly distributed between 0.1 and 0.2 for twenty percent of the samples, a number uniformly distributed between 0.2 and 0.3 for thirty percent of the samples and a number uniformly distributed between 0.3 and 0.4 for forty percent of the samples. You can define a lower bound for the first ten percent to be a value different than 0.0 by adding a row to the beginning of the table (row 1) where column one is a value of 0 and column two is 0.05 or the desired lower bound.
Here is a summary in tabular form showing the possible return values ("x") for each of the three distribution functions:

Here is an example of adding a "dummy" first row so that cempirical() starts at 0.05 instead of 0.0 (notice that row 1 has a probability of 0 percent):

Here is an example of adding a "dummy" last row so that empirical() has a range between each value including the last (any number can be entered for the percent of the last row because the percents already add up to 100% with the previous row, so it doesn't matter what it is):

When using ExpertFit to determine an empirical distribution that matches your data, you need to be aware that if your data has been defined as integers, then ExpertFit will fit it for use with dempirical(), and if your data has been defined as real numbers, ExpertFit will fit it for use with empirical(). When your data set is composed of real numbers, ExpertFit will show the same percentage for the last value as for the previous to last value, but you'll notice that the percents add up to 100% with the second to last entry.
Example
cempirical("mytable", 5);
Returns a random variate from a continuous empirical distribution defined in a global table named "mytable" using random number stream 5.
cempirical(current.labels["ptime"] 5);
Returns a random variate from a continuous empirical distribution defined in a node table defined on a label named "ptime" of the current object, and using random number stream 5.
Returns a random variate from a continuous empirical distribution defined in a global table named "mytable" using random number stream 5.
cempirical(current.labels["ptime"] 5);
Returns a random variate from a continuous empirical distribution defined in a node table defined on a label named "ptime" of the current object, and using random number stream 5.
clearbundle
(node datanode[, num resetflags = 0])
Clears all bundle data
Description
Clears the bundle data associated with datanode. This will clear all entries as well as all fields in the bundle.
resetflags is a bitwise mask for flags to initialize the bundle by. Valid values are:
BUNDLE_FLAG_UNPAGED = 0x1 - The bundle's entries will be stored in an unpaged, contiguous block of memory.
BUNDLE_FLAG_IR_OPT = 0x10 - The bundle will use additional memory (32 bits per row) to improve insert/remove performance for rows in the middle of the bundle.
BUNDLE_FLAG_UNPAGED = 0x1 - The bundle's entries will be stored in an unpaged, contiguous block of memory.
BUNDLE_FLAG_IR_OPT = 0x10 - The bundle will use additional memory (32 bits per row) to improve insert/remove performance for rows in the middle of the bundle.
Example
clearbundle(x);
dataplot
(obj tree, num type, num action, num x, num y, num z)
Description
For developer use. This command lets you create, reset or add data to a histogram, x/y chart, or a data series. The first three parameters define the associated node in the tree as well as the operation to do. The last three parameters, x,y and z, define the appropriate data for the operation. The first parameter should be the main node in the tree that holds the graph/histo data. The second parameter should be either 1, 2, or 3, and defines the type of data that the node holds. 1 means graphx data. For this data type the node contains a list of sub-nodes, and each sub-node contains a number that is a unique point in a data series. 2 means graphxy. For this data type, the node again contains a list of sub-nodes but this time the sub-nodes are paired together as x/y pairs. Nodes ranked 1 and 2 hold the x and y values for one data point, nodes 3 and 4 hold x and y values for the next data point, etc. A type parameter of 3 means histo data. Here the node holds data associated with a histogram. The action parameter should be either 1, 2, or 3, and defines the action that you want to do. 1 means a create operation. This is only needed for histogram type data, as it needs to set up the node's sub-tree structure. To create a histogram plot, pass the minimum value for the histogram as the x parameter, the maximum value of the histogram as the y value, and the number of divisions, or buckets, as the z parameter. An action parameter value of 2 means you want to reset the data. This will clear the content of the node for graphx or graphxy data, and will reset the histogram values for histogram data. An action parameter value of 3 means you want to add a data point. For graphx and histo data, pass the data point as the x parameter. For graphxy data, pass the as the x and y paramters. In summary: Type: 1-graphx/2-graphxy/3-histo.
Action: 1-create (only needed for histo data)/2-reset/3-add point.
Data: x,y are data points [histo create: x=start, y=end, z=nr of divisions].
Action: 1-create (only needed for histo data)/2-reset/3-add point.
Data: x,y are data points [histo create: x=start, y=end, z=nr of divisions].
Example
dataplot(stats_contentgraph(model.find("Processor2")),2,3,8.6,5,0); This adds a point to Processor2's content graph for time 8.6 and content 5. This example is only for demonstration purposes. You should never need to do this since the Processor automatically maintains its content graph.
dempirical
(str/node/num table[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a discrete empirical distribution
Description
A discrete empirical distribution.
The table referenced must contain a list of values and probability percentages associated with each of the values. Probability percentages must be entered in column 1 starting with row 1 of the table, and their associated values are entered in column 2. The table may have as many rows as needed to define as many values as desired. The percents are entered as numbers between 0 and 100, and should add up to a total of 100 percent; otherwise any values defined after a cumulative percentage of 100 is reached will never be returned.
A detailed description of the three empirical distributions used in FlexSim and their differences is included with the cempirical() command.
The table referenced must contain a list of values and probability percentages associated with each of the values. Probability percentages must be entered in column 1 starting with row 1 of the table, and their associated values are entered in column 2. The table may have as many rows as needed to define as many values as desired. The percents are entered as numbers between 0 and 100, and should add up to a total of 100 percent; otherwise any values defined after a cumulative percentage of 100 is reached will never be returned.
A detailed description of the three empirical distributions used in FlexSim and their differences is included with the cempirical() command.
Example
int ptype = dempirical("prodtypes", 5);
Assigns a value to the ptype variable using a discrete empirical distribution defined in a global table named "prodtypes" using random number stream 5.
dempirical(current.labels["route"], 5);
Returns a random variate from a discrete empirical distribution defined in a node table defined on the label named "route" of the current object, and using random number stream 5.
Assigns a value to the ptype variable using a discrete empirical distribution defined in a global table named "prodtypes" using random number stream 5.
dempirical(current.labels["route"], 5);
Returns a random variate from a discrete empirical distribution defined in a node table defined on the label named "route" of the current object, and using random number stream 5.
duniform
(num min, num max[, num stream])
Returns random integer between the min and max
Description
duniform( a, b, stream ) is a bounded discrete probability distribution.
Inputs:
a is the lower-endpoint parameter
b is the upper-endpoint parameter
a and b are integer numbers where a < b
b−a is the scale parameter
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = { a, a+1, ..., b }
mean = ( a + b ) ⁄ 2
variance = ( (b−a + 1)²− 1 ) ⁄ 12
Possible Applications:
Used to approximate a quantity that is felt to be randomly varying between a and b, but hardly anything else is known.
Comments:
There is an equal probability that an a, or b, or any discrete (integer) number inbetween will be returned.
Inputs:
a is the lower-endpoint parameter
b is the upper-endpoint parameter
a and b are integer numbers where a < b
b−a is the scale parameter
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = { a, a+1, ..., b }
mean = ( a + b ) ⁄ 2
variance = ( (b−a + 1)²− 1 ) ⁄ 12
Possible Applications:
Used to approximate a quantity that is felt to be randomly varying between a and b, but hardly anything else is known.
Comments:
There is an equal probability that an a, or b, or any discrete (integer) number inbetween will be returned.
Example
duniform(1, 6, 3);
Random number stream 3 will be used to generate a random variate from a discrete uniform distribution having a minimum value of 1 and a maximum value of 6. This simulates the roll of a dice.
Random number stream 3 will be used to generate a random variate from a discrete uniform distribution having a minimum value of 1 and a maximum value of 6. This simulates the roll of a dice.
empirical
(str/node/num table[, num stream])
Description
A continuous empirical distribution.
The table referenced must contain a list of values and probability percentages associated with each of the values. Probability percentages must be entered in column 1 starting with row 1 of the table, and their associated values are entered in column 2. The table may have as many rows as needed to define as many values as desired. The percents are entered as numbers between 0 and 100, and should add up to a total of 100 percent; otherwise any values defined after a cumulative percentage of 100 is reached will never be returned.
A detailed description of the three empirical distributions used in FlexSim and their differences is included with the cempirical() command.
The table referenced must contain a list of values and probability percentages associated with each of the values. Probability percentages must be entered in column 1 starting with row 1 of the table, and their associated values are entered in column 2. The table may have as many rows as needed to define as many values as desired. The percents are entered as numbers between 0 and 100, and should add up to a total of 100 percent; otherwise any values defined after a cumulative percentage of 100 is reached will never be returned.
A detailed description of the three empirical distributions used in FlexSim and their differences is included with the cempirical() command.
Example
empirical("mytable", 5);
Returns a random variate from a continuous empirical distribution defined in a global table named "mytable" using random number stream 5.
empirical(current.labels["ptime"], 5);
Returns a random variate from a continuous empirical distribution defined in a table defined on a label named "ptime" on the current object using random number stream 5.
Returns a random variate from a continuous empirical distribution defined in a global table named "mytable" using random number stream 5.
empirical(current.labels["ptime"], 5);
Returns a random variate from a continuous empirical distribution defined in a table defined on a label named "ptime" on the current object using random number stream 5.
erlang
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from an erlang distribution
Description
erlang( γ, β, m, stream ) is a non-negative continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
m is the shape parameter ∈ {1, 2, ... }
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + mβ
variance = mβ²
Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to complete some task such as assembly, customer service and machine repair.
Comments:
When γ = 0, this distribution is known as the m-Erlang(β) distribution.
The exponential( γ, β ) and erlang( γ, β, 1 ) distributions are the same.
For a positive integer m, the gamma( γ, β, m ) and erlang( γ, β, m ) distributions are the same.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
m is the shape parameter ∈ {1, 2, ... }
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + mβ
variance = mβ²
Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to complete some task such as assembly, customer service and machine repair.
Comments:
When γ = 0, this distribution is known as the m-Erlang(β) distribution.
The exponential( γ, β ) and erlang( γ, β, 1 ) distributions are the same.
For a positive integer m, the gamma( γ, β, m ) and erlang( γ, β, m ) distributions are the same.
Example
double servicetime = erlang(60, 2, 4, 5);
The servicetime variable is set equal to a erlang distribution with a location parameter of 60, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 4, using random stream number 5. The mean is 100 + (2*4) = 108.
The servicetime variable is set equal to a erlang distribution with a location parameter of 60, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 4, using random stream number 5. The mean is 100 + (2*4) = 108.
exponential
(num location, num scale [, num stream])
Returns a random sample from an exponential distribution
Description
exponential( γ, β, stream) is a non-negative continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( 0, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ, ∞ )
mean = γ + β
variance = β²
Possible Applications:
Often used to model the interarrival times of a continous stream of customers and/or customer orders into a system. It is also a popular distribution for modeling the time between failure of mechanical equipment.
Comments:
Variates less than the mean occur much more frequently than variates greater than the mean.
The exponential distribution is the only continuous distribution with the memoryless property of producing totally independent variates.
If the location parameter (γ) is set to zero, then β becomes the mean, and the distribution's variates will range between zero and infinity.
The exponential( γ, β ) and gamma( γ, β, 1 ) distributions are the same.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( 0, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ, ∞ )
mean = γ + β
variance = β²
Possible Applications:
Often used to model the interarrival times of a continous stream of customers and/or customer orders into a system. It is also a popular distribution for modeling the time between failure of mechanical equipment.
Comments:
Variates less than the mean occur much more frequently than variates greater than the mean.
The exponential distribution is the only continuous distribution with the memoryless property of producing totally independent variates.
If the location parameter (γ) is set to zero, then β becomes the mean, and the distribution's variates will range between zero and infinity.
The exponential( γ, β ) and gamma( γ, β, 1 ) distributions are the same.
Example
exponential(0, 10, 5);
An exponential distribution with a location of 0 and a scale of 10 (mean = 10). FlexSim's random stream number 5 will be used to generate variates from the distribution.
An exponential distribution with a location of 0 and a scale of 10 (mean = 10). FlexSim's random stream number 5 will be used to generate variates from the distribution.
exportdataset
(node datatree, str filename, num format[, str wrOption = "w"])
Description
Export tree dataset to .CSV (Comma Separated Value) format.
the format parameter can be:
1 = table
2 = graph
3 = graphxy
This implements the opposite functionality of importdataset(). Refer to importdataset() for more information.
the format parameter can be:
1 = table
2 = graph
3 = graphxy
This implements the opposite functionality of importdataset(). Refer to importdataset() for more information.
Example
exportdataset(so(),"mydataset.csv",1)
extremevalue1a
(num location, num scale[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a extremevalue1a distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a extremevalue1a distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
extremevalue1b
(num location, num scale[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a extremevalue1b distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a extremevalue1b distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
gamma
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a gamma distribution
Description
gamma( γ, β, α, stream ) is a non-negative continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
α is the shape parameter ( α > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + αβ
variance = αβ²
Probability Density Functions:
Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to complete some task such as assembly, customer service or machine repair.
Comments:
The exponential( γ, β ) and gamma( γ, β, 1 ) distributions are the same.
For a positive integer m, the gamma( γ, β, m ) and erlang( γ, β, m ) distributions are the same.
Shape values less than 1 are rarely used.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
α is the shape parameter ( α > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + αβ
variance = αβ²
Probability Density Functions:

Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to complete some task such as assembly, customer service or machine repair.
Comments:
The exponential( γ, β ) and gamma( γ, β, 1 ) distributions are the same.
For a positive integer m, the gamma( γ, β, m ) and erlang( γ, β, m ) distributions are the same.
Shape values less than 1 are rarely used.
Example
double repairtime = gamma(60, 2, 3.4, 5);
The repairtime variable is set equal to a gamma distribution with a location parameter of 60, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 4, and using random stream number 5. The mean is 100 + (2*3.4) = 106.8.
The repairtime variable is set equal to a gamma distribution with a location parameter of 60, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 4, and using random stream number 5. The mean is 100 + (2*3.4) = 106.8.
geometric
(num prob[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a geometric distribution
Description
Generates a discrete random number with a geometric distribution and parameters as specified.
Example
getbundlefieldname
(node datanode, num fieldnr)
Gets the name of the nth ranked field (base 0) in the bundle
Description
Returns the name of the nth ranked field (base 0) in the bundle.
Example
string fieldname = getbundlefieldname(x, 5);
getbundlefieldnr
(node datanode, str fieldname)
Gets the rank of the bundle field (base 0)
Description
Returns the rank of the bundle field (base 0). If the bundle field doesn't exist, returns -1.
Example
int index = getbundlefieldnr(x, "Field Name");
getbundlefieldtype
(node datanode, num fieldnr)
Gets the data type of the bundle field at rank fieldnr (base 0)
Description
Returns the data type of the bundle field at rank fieldnr (base 0). Available return values are:
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_DOUBLE
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_FLOAT
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_INT
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_STR
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_VARCHAR
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_NODEREF
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_DOUBLE
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_FLOAT
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_INT
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_STR
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_VARCHAR
BUNDLE_FIELD_TYPE_NODEREF
Example
int type = getbundlefieldtype(x, 5);
getbundleindexentries
(node datanode, str/num field, str/num value)
Gets all rows with a matching value in the given field
Description
If this command succeeds, it returns an int or an intarray containing
all entries (0-based) that contain the given value for the given field. If it fails,
it returns -1. It will fail if the datanode is not a bundle, or if the given field
is not an indexed field, or if none of values in the field match the given value.
See the addbundlefield command for information on how to make an indexed field.
Example
int entryNr = getbundleindexentries(data, "SKU", "FS2016-BLU");
getbundlenrentries
(node datanode)
Gets the total number of entries in the bundle
Description
Returns the total number of entries in the bundle.
Example
int nrentries = getbundlenrentries(x);
getbundlenrfields
(node datanode)
Gets the total number of fields in the bundle
Description
Returns the total number of fields in the bundle.
Example
int nrfields = getbundlenrfields(x);
getbundlevalue
(node datanode, num entrynr, str/num field)
Gets the value of the defined entry (base 0) and field (base 0) of the bundle
Description
Returns the value of the defined entry (base 0) and field (base 0) of the bundle.
Example
string name = getbundlevalue(x, 5, "Object Name");
getdatastat
(num stat, num/node nrSamples/parentNode, num sampler [, num p1, num p2, num p3])
Description
Calculates and returns a certain statistic of a data set.
stat - Can be one of the following values
stat - Can be one of the following values
nrSamples - defines the number of samples in the set.
Note: parameter 2 as a parentNode is deprecated and you should use the parameter 2 as nrSamples option because it
encompasses the other and is more flexible. The following deprecated functionality:
sampler - an expression that gets the nth value in the sample.
getdatastat(STAT_MEAN, myNode, 0, 0, 0, 0)
can be represented using the newer option with:
getdatastat(STAT_MEAN, myNode.subnodes.length, myNode.subnodes[count].value, 0, 0, 0)
Use count for determining which value is to be retrieved. Below are several examples:
For calculating the mean of all values in column 5 of global table GT1:
For calculating the sum of all values in field "Time" of a bundle:
For calculating the mean of all values in column 5 of global table GT1:
getdatastat(STAT_MEAN, Table("GT1").numRows, Table("GT1")[count][5])For calculating the sum of all values in field "Time" of a bundle:
getdatastat(STAT_SUM, Table("MyBundle").numRows, Table("MyBundle")[count]["Time"])Example
getstat
(node object, str name, int flag [, var p1, var p2, var p3])
Returns the statistic value for the given object
Description
It is preferred to use Object.stats instead. Gets the specified statistic from the given object.
name - The name of the statistic. Valid names can be enumerated using
flag - Can be one of the following values
p1, p2, and p3 are for providing "requirements" to resolve the correct statistic. For example, a list has several per-partition statistics. In order to get a partition's statistic, you need to pass the desired partition ID as p1. Requirements depend on the statistic that is being retrieved.
There are also several special stat names that you can use. They are: "State", "Output", "Input", "Content", "Staytime". If you use one of these names, the command will return the corresponding standard statistic of the object. Examples:
Note that some stats that do not make sense will not return valid data, such as average state, or average output.
STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE
If you want to get the STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE access, the statistic needs to track either historical or profile data. If it is an object's standard "State" statistic, FlexSim will automatically make it track its profile data, so you don't need to do any extra work for that. For other statistics, however, you will need to explicitly "subscribe" to the statistic to make it track its profile or history data. Historical data records each change of value and the corresponding simulation time of that value change. Profile data records the total time the variable was at each value. Only non-negative integer values are valid for profile data.
To subscribe to a tracked variable, first find where the tracked variable statistic is in the tree. For example if it's the "Content" statistic, you'll likely find it at object>stats/stats_content. Then call the following command on the node: function_s(statNode, "addSubscriber", needsHistory, needsProfile, persist). The needsHistory and needsProfile parameters are booleans telling which data you want to track. The persist is a boolean that tells if you want it to track these statistics indefinitely going forward. The tracked variable tries not to continue tracking extra data if it is not needed. If nobody subscribes to its data "persistently", then it will discontinue recording the data if it doesn't get subscribers for a while (I think after 5 or so model resets with no subscribers).
Recording historical data will allow you to get the STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE access. However, using historical data for getting STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE is slower than if you track profile data. With historical data, it must traverse the entire history to calculate STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE, whereas if you track profile data, it stores the total time at the value directly in the profile data.
name - The name of the statistic. Valid names can be enumerated using
function_s(object, "enumerateStatistics", targetNode). Documentation for the
meaning of the various statistics that an object provides should be found in each object's
documentation. The documentation may include spaces in the names of the statistics, for
readability. In passing these as the name parameter to getstat(), you should remove all spaces.flag - Can be one of the following values
p1, p2, and p3 are for providing "requirements" to resolve the correct statistic. For example, a list has several per-partition statistics. In order to get a partition's statistic, you need to pass the desired partition ID as p1. Requirements depend on the statistic that is being retrieved.
There are also several special stat names that you can use. They are: "State", "Output", "Input", "Content", "Staytime". If you use one of these names, the command will return the corresponding standard statistic of the object. Examples:
getstat(object, "Output", STAT_CURRENT) - returns the current (total) output of the object (same as object.stats.output)getstat(object, "Content", STAT_AVERAGE) - returns the average content of the objectgetstat(object, "State", STAT_CURRENT, 0) - returns the current state of the object (same as object.stats.state().value)getstat(object, "State", STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE, 0, STATE_IDLE) - returns the total idle time of the object (0 designates the
state profile, i.e. the default state profile)getstat(object, "Staytime", STAT_MAX) - returns the maximum recorded stay time of the objectNote that some stats that do not make sense will not return valid data, such as average state, or average output.
STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE
If you want to get the STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE access, the statistic needs to track either historical or profile data. If it is an object's standard "State" statistic, FlexSim will automatically make it track its profile data, so you don't need to do any extra work for that. For other statistics, however, you will need to explicitly "subscribe" to the statistic to make it track its profile or history data. Historical data records each change of value and the corresponding simulation time of that value change. Profile data records the total time the variable was at each value. Only non-negative integer values are valid for profile data.
To subscribe to a tracked variable, first find where the tracked variable statistic is in the tree. For example if it's the "Content" statistic, you'll likely find it at object>stats/stats_content. Then call the following command on the node: function_s(statNode, "addSubscriber", needsHistory, needsProfile, persist). The needsHistory and needsProfile parameters are booleans telling which data you want to track. The persist is a boolean that tells if you want it to track these statistics indefinitely going forward. The tracked variable tries not to continue tracking extra data if it is not needed. If nobody subscribes to its data "persistently", then it will discontinue recording the data if it doesn't get subscribers for a while (I think after 5 or so model resets with no subscribers).
Recording historical data will allow you to get the STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE access. However, using historical data for getting STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE is slower than if you track profile data. With historical data, it must traverse the entire history to calculate STAT_TIME_AT_VALUE, whereas if you track profile data, it stores the total time at the value directly in the profile data.
Example
getstatetableutilization
(Table stateTable, TrackedVariable stateProfile)
Description
Returns the utilization of a state profile given a state table. See State Table for more information on how to create and modify a state table.
Example
getstatetableutilization(Table("StateTable1"), Model.find("Processor1").as(Object).stats.state())
getstream
(node object)
Returns a unique random stream associated with the object
Description
Returns a unique random stream associated with the object.
Returns the number stored in the object's stream attribute. If the object does not yet own a stream attribute, or if its stream attribute is 0, FlexSim will assert the attribute and assign it a unique stream number. If the object passed into the function does not have object data, it will store the unique stream in a subnode. This subnode will be destroyed on model reset and reassigned during the model run as needed.
Assigned streams start at stream 101 and increase as they are assigned.
Returns the number stored in the object's stream attribute. If the object does not yet own a stream attribute, or if its stream attribute is 0, FlexSim will assert the attribute and assign it a unique stream number. If the object passed into the function does not have object data, it will store the unique stream in a subnode. This subnode will be destroyed on model reset and reassigned during the model run as needed.
Assigned streams start at stream 101 and increase as they are assigned.
Example
uniform(0, 1, getstream(current))
graphtohistogram
(obj graph, obj histogram, num start, num end, num res, num xyformat)
Description
For developer use. Generate histogram data from a list of values. This command will generate a histogram inside the node histogram based on the occurrence table given by graph. Mainly used internally by objects. The starting value of the histogram is specified as start. The ending value of the histogram is specified as end. The number of buckets in the histogram is specified as res. If xyformat is 0, it assumes that the graph is a y format occurrence table. If xyformat is 1, it assumed the graph is an xy format occurrence table. Similar to makehisto(). Refer to makehisto() for more information on these similarities.
Example
graphtohistogram(so(),so().next,1,10,5,0)
hypergeometric
(num trials, num successes, num size[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a hypergeometric distribution
Description
hypergeometric( t, m, n, stream ) is a discrete probability distribution
used to represent the number of successes in t draws without replacement from a population of size n
containing exactly m success states.
Example
importdataset
(node datatree, str filename, num format)
Description
Import tree dataset from a Comma Separated Value (CSV) file. datatree should be the node to import the data into. There are 3 possible formats to import. If format is 1, then the data is imported as a table, meaning each sub-node of datatree is a row in the table, and each sub-node of each row is a cell in the table. This is the same as using the importtable() command. If format is 2, then the data is imported as a simple data series. The csv file is assumed to have one column, and each row's value is imported into a sub-node of datatree. If format is 3, then the data is imported as a series of x,y pairs. The csv file is assumed to have 2 columns. Row 1 column 1 of the csv file is imported as sub-node 1 of datatree, row 1 column 2 is imported as sub-node 2 of datatree, row 2 column 1 is imported as sub-node 3 of datatree, and so forth.
Example
importdataset(so(),"C:\\mydataset.csv",1)
inversegaussian
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from an inversegaussian distribution
Description
inversegaussian( γ, β, α, stream ) is a non-negative continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
α is the shape parameter ( α > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + β
variance = β³⁄α
Probability Density Functions:
Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to complete some tasks.
Comments:
The inversegaussian( γ, 1, α ) and wald( γ, α ) distributions are the same.
As γ approaches infinity, the distribution becomes more like the normal (Gaussian) distribution.
The β parameter has elements of a shape parameter since it affects the skewness and kurtosis (width).
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
α is the shape parameter ( α > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + β
variance = β³⁄α
Probability Density Functions:

Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to complete some tasks.
Comments:
The inversegaussian( γ, 1, α ) and wald( γ, α ) distributions are the same.
As γ approaches infinity, the distribution becomes more like the normal (Gaussian) distribution.
The β parameter has elements of a shape parameter since it affects the skewness and kurtosis (width).
Example
double repairtime = inversegaussian(60, 2, 4, 5);
The repairtime variable is set equal to a inversegaussian distribution with a location parameter of 60, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 4, and using random stream number 5.
The repairtime variable is set equal to a inversegaussian distribution with a location parameter of 60, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 4, and using random stream number 5.
inverseweibull
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a inverseweibull distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a inverseweibull distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
invertedweibull
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from an inverted weibull distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from an inverted weibull distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
johnsonbounded
(num min, num max, num shape1, num shape2[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a johnson bounded distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a johnson bounded distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
johnsonunbounded
(num location, num scale, num shape1, num shape2[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a johnson unbounded distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a johnson unbounded distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
laplace
(num location, num scale[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a laplace distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a laplace distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
logarithmic
(num theta[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a logarithmic distribution
Description
Generates a discrete random variate from a logarithmic distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
logistic
(num location, num scale[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a logistic distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a logistic distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
loglaplace
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a log laplace distribution
Description
loglaplace( γ, β, α, stream ) is a non-negative continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
α is the shape parameter ( α > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + βα²⁄ ( α²− 1) for α > 1
variance = β²α² ( 2α² + 1 ) ⁄ ( α² - 1 )² ( α² - 4 ) for α > 2
Probability Density Functions:
Possible Applications:
Rarely used in defining processing times.
Comments:
This distribution is also known as the double-exponential distribution because its density curve is essentially two exponential curves back-to-back.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
α is the shape parameter ( α > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + βα²⁄ ( α²− 1) for α > 1
variance = β²α² ( 2α² + 1 ) ⁄ ( α² - 1 )² ( α² - 4 ) for α > 2
Probability Density Functions:

Possible Applications:
Rarely used in defining processing times.
Comments:
This distribution is also known as the double-exponential distribution because its density curve is essentially two exponential curves back-to-back.
Example
loglaplace(0, 2, 8, 5);
A loglaplace distribution with a location parameter of 0, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 8, and random stream number 5.
A loglaplace distribution with a location parameter of 0, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 8, and random stream number 5.
loglogistic
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a log logistic distribution
Description
loglogistic(γ, β, α, stream) is a non-negative continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( 0, ∞ )
α is the shape parameter ( 0, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ, ∞ )
mean = γ + β(π⁄α)csc(π⁄α) for α > 1
variance = β²(π⁄α){2csc(2π⁄α) − (π⁄α)[csc(π⁄α)]²} for α > 2
Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to perform some task.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( 0, ∞ )
α is the shape parameter ( 0, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ, ∞ )
mean = γ + β(π⁄α)csc(π⁄α) for α > 1
variance = β²(π⁄α){2csc(2π⁄α) − (π⁄α)[csc(π⁄α)]²} for α > 2
Possible Applications:
Used to model the time to perform some task.
Example
loglogistic(0, 1, 2, 5);
A loglogistic distribution with a location (shift) of 0, a scale of 1, a shape factor of 2 and random stream number 5.
A loglogistic distribution with a location (shift) of 0, a scale of 1, a shape factor of 2 and random stream number 5.
lognormal2
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a lognormal distribution
Description
lognormal() and lognormal2() are similar functions, but with different parameter definitions. lognormal() uses parameter definitions as defined on wikipedia and other sites. lognormal2() uses parameters as defined in the latest versions of Expertfit. Essentially, the parameters can be converted as follows:
lognormal( location, normalmean, normalstdev ) = lognormal2( location, Math.exp( normalmean ), normalstdev )
lognormal2( location, scale, shape ) = lognormal( location, Math.log( scale ), shape ) (Math.exp(x) is e raised to the x power, and Math.log(x) is the natural logarithm of x.)
Please make sure you use the right distribution. Using the wrong distribution could result in bad simulation results.
lognormal( location, normalmean, normalstdev ) = lognormal2( location, Math.exp( normalmean ), normalstdev )
lognormal2( location, scale, shape ) = lognormal( location, Math.log( scale ), shape ) (Math.exp(x) is e raised to the x power, and Math.log(x) is the natural logarithm of x.)
Please make sure you use the right distribution. Using the wrong distribution could result in bad simulation results.
Example
double cycletime = lognormal2(0, 29.8, 0.31, 5);
Set the cycletime variable to a lognormal2 distribution with location parameter 0, scale parameter 29.8, shape parameter 0.31, and random stream number 5.
Set the cycletime variable to a lognormal2 distribution with location parameter 0, scale parameter 29.8, shape parameter 0.31, and random stream number 5.
makehisto
(obj datalist, obj histocontainer, num nrofbuckets)
Description
For developer use. Builds a histogram structure from the data list and puts it in the destination container node with the given number of buckets. This is similar to graphtohistogram() except that this command creates a more complete structure. To illustrate the operator instead., view a FlexSim object's attribute tree. The makehisto command will create the entire stucture of object>stats/staytime/staytimehisto, whereas graphtohistogram will only populate object>stats/staytime/staytimehisto/data. makehisto also assumes a standard, y data series structure, meaning each sub-node of datalist is its own data point (they are not paired as x/y values).
Example
makehisto(c.find("@>objectfocus+"), c.find(">histogram"), 20)
negbinomial
(num successes, num prob[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a negative binomial distribution
Description
Generates a discrete random variate from a negative binomial distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
normal
(num mean, num stddev[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a normal distribution
Description
normal(μ, σ, stream) is an unbounded continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
μ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
σ is the scale parameter ( 0, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( - ∞, ∞ )
mean = μ
variance = σ²
Probability Density Functions:
Possible Applications:
Used to model various types of error such as machined hole diameters for large quantities of parts. This distribution is not used much in simulation because variance found in real processes do not typically follow a symmetric distribution such as this.
Comments:
The normal distribution is completely symmetric meaning values below the mean have the same probability for occurance as values above the mean. The mode and mean are equal for the normal distribution. When using this distribution, be aware that negative values can be returned, and therefore truncating the distribution at 0 may be necessary as shown in the example below.
Inputs:
μ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
σ is the scale parameter ( 0, ∞ )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( - ∞, ∞ )
mean = μ
variance = σ²
Probability Density Functions:

Possible Applications:
Used to model various types of error such as machined hole diameters for large quantities of parts. This distribution is not used much in simulation because variance found in real processes do not typically follow a symmetric distribution such as this.
Comments:
The normal distribution is completely symmetric meaning values below the mean have the same probability for occurance as values above the mean. The mode and mean are equal for the normal distribution. When using this distribution, be aware that negative values can be returned, and therefore truncating the distribution at 0 may be necessary as shown in the example below.
Example
double thickness = Math.max(0.001, normal(5, 1.2));
The thickness is set a normal distribution having a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of 1.2 that is truncated for values less than 0.001. No random stream has been declared, so the default stream number 0 will be used to generate variates from the distribution.
The thickness is set a normal distribution having a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of 1.2 that is truncated for values less than 0.001. No random stream has been declared, so the default stream number 0 will be used to generate variates from the distribution.
pareto
(num min, num scale[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a pareto distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a pareto distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
pearsont5
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a pearson t 5 distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a Person-T5 distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
pearsont6
(num location, num scale, num shape1, num shape2[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a pearson t 6 distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a Person-T6 distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
poisson
(num mean[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a poisson distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a poisson distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
qstudentt
(num confidence [0.9/0.95/0.99], num degreesoffreedom)
Description
For developer use. Returns the quantity of the studentt distribution value for the given percent confidence and degrees of freedom.
Example
qstudentt(0.95, nrofsamples - 1)
randantithetic
(num on/off)
Description
Makes number streams antithetic. Using this command, users can switch random streams to generate numbers between 1 and 0; rather than the default of 0 to 1. This is helpful for determining if random numbers are having a big affect on the results of the model. It's also useful when experimenting with massive models and there isn't sufficient time to run the model for multiple iterations as required for good statistical sampling. The user can then choose to do just one regular run and one antithetic run of the model to obtain two diametrically apposed results. These two results can be averaged for an approximation that is somewhat better than if each run of the model used random stream generators without antithetic sampling.
Example
randantithetic(1);
randinit
(num stream, num seedvalue[, num seedvalue2, num seedvalue3, num seedvalue4, num seedvalue5, num seedvalue 6])
Initializes a random stream
Description
Initializes the random number stream by setting its first value to seedvalue. Although there are an unlimited number of random number streams available to the user, only the first one hundred streams numbered 0 through 99 have been initialized when the FlexSim application is opened. To create a new stream, simply execute the randinit() command for the new stream. For instance, executing randinit(105, 7628912) will create a new stream number 105 if it does not currently exist, and set its initial seed value to 7628912.
If "Repeat Random Streams" has been selected in the Statistics menu, then streams 0 through 99 will be automatically initialized with a default seed value for that stream whenever the model is reset. For streams 100 and above, you must use the randinit() command to set their initial seed values if you wish to repeat their random streams. Any positive integer may be passed in as the seedvalue for a random number stream. If you pass in a seedvalue of 0 for random streams 0 through 99, it is a special case that will initialize them to their default seed values.
seedvalues 2 through 6 are only used if you are using FlexSim's Combined MRG random number generator. To enable this generator, call maintenance(49,1) when your model opens.
If "Repeat Random Streams" has been selected in the Statistics menu, then streams 0 through 99 will be automatically initialized with a default seed value for that stream whenever the model is reset. For streams 100 and above, you must use the randinit() command to set their initial seed values if you wish to repeat their random streams. Any positive integer may be passed in as the seedvalue for a random number stream. If you pass in a seedvalue of 0 for random streams 0 through 99, it is a special case that will initialize them to their default seed values.
seedvalues 2 through 6 are only used if you are using FlexSim's Combined MRG random number generator. To enable this generator, call maintenance(49,1) when your model opens.
Example
Example 1:
randinit(5, 73241);
Initialize FlexSim's random stream number 5 with a sead value of 73241.
Example 2:
randinit(2,0);
for(int i = 100; i <= 199; i++)
{
randinit(i, realtime(1) * uniform(0, 1, 2));
}
First initialize standard stream number 2 to its default seed value, then execute a loop for 100 iterations to create (if necessary) streams 100 through 199 and set their initial seed value to the product of a random number pulled from stream 2 and the current number of real clock seconds.
randinit(5, 73241);
Initialize FlexSim's random stream number 5 with a sead value of 73241.
Example 2:
randinit(2,0);
for(int i = 100; i <= 199; i++)
{
randinit(i, realtime(1) * uniform(0, 1, 2));
}
First initialize standard stream number 2 to its default seed value, then execute a loop for 100 iterations to create (if necessary) streams 100 through 199 and set their initial seed value to the product of a random number pulled from stream 2 and the current number of real clock seconds.
randnext
(num stream)
Description
For development use. Returns the next random number from the stream. This command is used to pull random samples from probability distribution functions.
Example
randnext(1);
Gets the next random number in the stream of random numbers associated with stream generator number 1.
Gets the next random number in the stream of random numbers associated with stream generator number 1.
randomwalk
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a random walk distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
randstate
(num stream[, seednr])
Gets the current state value for the random number stream
Description
Returns the current state value for the specified random number stream. This state value may be useful as the seed value in the randinit() command for the purposes of restarting a saved state model from the same point in the random number stream of the initial run.
seednr is only needed if you are using FlexSim's Combined MRG random number generator, in which case the seednr should be a value 1-6 defining which seed value you want to get the state on. Refer to randinit() for using the Combined MRG.
seednr is only needed if you are using FlexSim's Combined MRG random number generator, in which case the seednr should be a value 1-6 defining which seed value you want to get the state on. Refer to randinit() for using the Combined MRG.
Example
int curstate = randstate(5);
Set the curstate variable to the current random integer value stream number 5.
Set the curstate variable to the current random integer value stream number 5.
removebundleentry
(node datanode, int entrynum)
Removes the entry entrynum (base 0) of the bundle
Description
Removes the entry entrynum (base 0) of the bundle.
Example
removebundleentry(x, 2);
removefirstbundleentry
(node datanode)
Removes the first entry in the bundle
Description
Removes the first entry in the bundle. For managing memory footprint of historical data.
Example
removefirstbundleentry(x);
removelastbundleentry
(node datanode)
Removes the last entry of the bundle
Description
Removes the last entry of the bundle.
Example
removefirstbundleentry(x);
setbundlevalue
(node datanode, num entrynr, str/num field, num/str val)
Sets the value of the entry (base 0) and field (base 0) of the bundle
Description
Sets the value of the defined entry (base 0) and field (base 0) of the bundle.
Example
setbundlevalue(x, 5, "Object Name", current.name);
triangular
(num min, num max, num mode[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a triangular distribution
Description
Generates a continuous random variate from a triangular distribution with parameters as defined.
Example
uniform
(num min, num max[, num stream])
Returns a random number between the min and max values
Description
uniform( a, b, stream ) is a bounded continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
a and b are real numbers with a < b
a is the location parameter defining the minimum variate
b defines the maximum variate
b−a is the scale parameter
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = [ a, b ]
mean = ( a + b ) ⁄ 2
variance = ( b−a )²⁄ 12
Possible Applications:
Used to approximate a value that is felt to be randomly varying between a and b but hardly anything else is known.
Comments:
There is an equal probability that an a, or b, or any real number inbetween will be returned.
The uniform(0, 1) distribution is essential in generating random variates from all the other distributions and will return a continuous set of random values between and inclusive of 0 and 1.
Inputs:
a and b are real numbers with a < b
a is the location parameter defining the minimum variate
b defines the maximum variate
b−a is the scale parameter
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = [ a, b ]
mean = ( a + b ) ⁄ 2
variance = ( b−a )²⁄ 12
Possible Applications:
Used to approximate a value that is felt to be randomly varying between a and b but hardly anything else is known.
Comments:
There is an equal probability that an a, or b, or any real number inbetween will be returned.
The uniform(0, 1) distribution is essential in generating random variates from all the other distributions and will return a continuous set of random values between and inclusive of 0 and 1.
Example
uniform(12.3, 27.5, 3);
Random number stream 3 will be used to generate a random variate from a uniform distribution having a minimum of 12.3 and a maximum of 27.5.
Random number stream 3 will be used to generate a random variate from a uniform distribution having a minimum of 12.3 and a maximum of 27.5.
weibull
(num location, num scale, num shape[, num stream])
Returns a random sample from a weibull distribution
Description
weibull( γ, β, α, stream ) is a non-negative continuous probability distribution.
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
α is the shape parameter ( α > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + ( β⁄α ) Γ(1 ⁄α) where Γ() is the Gamma function.
variance = ( β²⁄α ) { 2Γ(2 ⁄α) − 1 ⁄α [ Γ(1 ⁄α) ] ² }
Probability Density Functions:
Possible Applications:
The weibull distribution is commonly used when there is not sufficient data available because it can take on so many different shapes depending on the shape factor. It is a very common distribution used for representing the time between equipment failures, as well as the time to complete a manual task.
Comments:
The weibull( γ, β, 1 ) and exponential( γ, β ) distributions are the same.
The weibull( γ, β, 2 ) and rayleigh( γ, β ) distributions are the same.
The weibull distribution is skewed to the left if α > 3.6
Inputs:
γ is the location parameter ∈ ( - ∞, ∞ )
β is the scale parameter ( β > 0 )
α is the shape parameter ( α > 0 )
stream is a reference to one of FlexSim's random number streams {0,1,2,...}
Outputs:
range = ( γ , ∞ )
mean = γ + ( β⁄α ) Γ(1 ⁄α) where Γ() is the Gamma function.
variance = ( β²⁄α ) { 2Γ(2 ⁄α) − 1 ⁄α [ Γ(1 ⁄α) ] ² }
Probability Density Functions:

Possible Applications:
The weibull distribution is commonly used when there is not sufficient data available because it can take on so many different shapes depending on the shape factor. It is a very common distribution used for representing the time between equipment failures, as well as the time to complete a manual task.
Comments:
The weibull( γ, β, 1 ) and exponential( γ, β ) distributions are the same.
The weibull( γ, β, 2 ) and rayleigh( γ, β ) distributions are the same.
The weibull distribution is skewed to the left if α > 3.6
Example
weibull(0, 2, 3, 5);
A weibull distribution with a location parameter of 0, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 3, and random stream number 5.
A weibull distribution with a location parameter of 0, a scale parameter of 2, a shape parameter of 3, and random stream number 5.
Strings
Commands associated with strings, string manipulation and string comparisons.
asciistr
(str string [, num index])
Description
This command returns the ascii value of the character at the specified index (0-based) of the string. If index is not specified, the first character of the string is used.
Example
asciistr("fred",1) returns 114, the ascii value of 'r'
cdir
()
Description
Returns a string of the path to FlexSim's install directory.
Example
string userpath = cdir(); For a standard installation this will return C:\Program Files\Flexsim3\
currentfile
()
Gets the path to the currently open model
Description
Returns the path of the currently open model.
Example
currentfile();
documentsdir
()
Gets the full path to the currently active user's FlexSim Projects folder in My Documents
Description
Returns a full path to the currently active user's FlexSim Projects folder in My Documents
Example
documentsdir()
executestring
(str thestring[, node c, node i, obj eventdata])
Executes a string as flexscript
Description
Executes the given string as flexscript. Parameters 2-4 are the same as executefsnode.
Example
executestring("profileevents()");
getdirbrowse
(str initialdir, str message, node result)
Opens a browser window to pick a directory
Description
Opens a browser window to pick a directory. destnode should have string data, and the directory path will be written
to its text.
Example
getdirbrowse(documentsdir, "A folder", destnode)
getpath
(str truncatedpath)
Returns the full file path of the truncated path
Description
Takes a truncated, or relative file path, and returns the full file path.
Example
string fullpath = getpath("fs3d\\texturebox.wrl");
modeldir
()
Gets the path to the currently open model's directory
Description
Returns that path of the currently open model's directory.
Example
modeldir();
pdir
()
Description
This command returns a string containing the path on the hard drive to the FlexSim's program directory.
Example
string flexpath = pdir();
This sets flexpath FlexSim's program directory. A typical installation would return C:\Program Files\FlexSim7\program\ as the string.
This sets flexpath FlexSim's program directory. A typical installation would return C:\Program Files\FlexSim7\program\ as the string.
pfile
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the string attached to the end of the command line used to start the FlexSim application.
Example
If FlexSim was started with this command line:
"C:\Program Files\Flexsim7\program\flexsim.exe" "mymodel.fsm"
then a call to pfile() would return mymodel.fsm as a string.
"C:\Program Files\Flexsim7\program\flexsim.exe" "mymodel.fsm"
then a call to pfile() would return mymodel.fsm as a string.
programdatadir
()
Gets the full path to the directory where FlexSim stores program data
Description
Returns a full path to the directory where FlexSim stores program data, such as the help documents.
Example
programdatadir() returns a string like "C:\ProgramData\Flexsim\Flexsim7\"
replacedata_n
(obj startnode, num value, num replacement)
Description
For developer use. Search/Replace number data matched under startnode. Only number data nodes are searched. Returns the total number of matches found.
Example
replacedata_n(main(),25,42)
replacedata_s
(obj startnode, str string, str replacement[, num replication])
Description
For developer use. Search for a string data match under startnode and replace with the replacement string. Results appear in the output console. This function will recognize and replace substrings. The search is case-sensitive. Replication is currently not used. See searchdata_s(). Returns the total number of matches found.
Example
replacedata_s(main(),"jack","john")
replacename
(obj startnode, str searchname, str replacement)
Description
For developer use. Replace all node names found to be a match with searchname that fall under startnode. This function requires an exact match and will not recognize substrings. Returns the total number of matches found.
Example
replacename(main(),"jack","john")
searchdata_n
(obj startnode, num val)
Description
For developer use. Search for a number data match under startnode. Only number data nodes are searched. Results appear on the output console. Returns the total number of matches found.
Example
searchdata_n(main(),25)
searchdata_s
(obj startnode, str string [, num replication])
Description
For developer use. Search for a string data match under startnode. Results appear in the output console. This function will recognize substrings and report which nodes contain them, and how many. The search is case-sensitive. Replication is currently not used. Returns the total number of matches found.
Example
searchdata_s(main(),"glVertex()",1)
searchname
(obj startnode, str searchname)
Description
For developer use. Search for a name match under startnode. Results appear in the output console. The search is case-sensitive. Returns the total number of matches found.
Example
searchname(main(),"FixedResource")
strascii
(num asciivalue)
Description
This command returns a string that contains the character whose ascii value is character.
Example
strascii(91) + "alert(" + strascii(34) + "Hello There" + strascii(34) + ")" + strascii(93);
This returns a string that contains the following phrase: [alert("Hello There")]
This returns a string that contains the following phrase: [alert("Hello There")]
stringtoken
(str token, str delimit)
Finds the next token in a string
Description
Finds the next token in a string. The first parameter is a string containing delimited tokens. The second parameter is a string with a set of delimiter characters. Works similarly to strtok() in C++.
Example
string token = "Jacob,Emma,Michael,Isabella,Ethan";
string name = stringtoken(token,",");
while(stringlen(name)>0)
{
pt(name);pr();
name = stringtoken(NULL,",");
}
This prints each name in the list to a different line of the output console.
string name = stringtoken(token,",");
while(stringlen(name)>0)
{
pt(name);pr();
name = stringtoken(NULL,",");
}
This prints each name in the list to a different line of the output console.
tostring
(thing)
Description
For developer use. Assert as pchar string. Assert that the number val is of type char*. Only serves a real purpose in C++, but is safe to use in Flexscript.
Example
tostring(eventdata)
truncatemediapath
(str path)
Description
Returns a truncated media path based on the full path of the file passed. If this file exists relative to the model
directory, then the path will be truncated to be relative to the model directory. It will also be truncated if it is relative to
the FlexSim install directory.
Example
truncatemediapath("C:\\Program Files\\Flexsim4\\fs3d\\texturebox.wrl");
This example will return the string "fs3d\\texturebox.wrl"
This example will return the string "fs3d\\texturebox.wrl"
userdatadir
()
Gets the full path to the directory where FlexSim stores user data
Description
Returns a full path to the directory where FlexSim stores user data, such as global preferences and compiler settings.
Example
userdatadir() returns a string like "C:\Users\USERNAME\AppData\Roaming\Flexsim\Flexsim7\"
Tables
Commands for accessing, assigning and managing data in tables.
exporttable
(node exportnode, str filename[, num exportcolumnnames = 0, num exportrownames = 0, str listseparator = 0, str decimalseparator = 0])
Export a table in .CSV format
Description
Export a table in .CSV (Comma Separated Value) format.
Example
exporttable(so(),"mytable.csv",1, 1)
This exports the table designated as so(), including row and column headers.
This exports the table designated as so(), including row and column headers.
importtable
(node importnode, str filename[, num importcolheaders = 0, num importrowheaders = 0, str listseparator = 0, str decimalseparator = 0, str thousandseparator = 0])
Imports table data into importnode from a csv file. When importing both row and column headers, the first value in the file will be skipped. When importing into a bundle table, each field will use the data type of its first imported cell (row 1).
Description
Imports table data into the node from a csv (comma-separated values) file.
Example
importtable(current.labels["data"], "C:/modeldata.csv", 1, 1)
TaskExecuter Object
Commands associated with TaskExecuter objects and a tasksequence.
addsphere
(obj object, num x, num y, num z, num radius)
Description
For developer use. Adds a collision sphere with the specified radius to the specified object at location x, y, z relative to the object. TaskExecuters allow users to add collision spheres and draw collision spheres through the object's Parameters window, but commands are needed to add and draw collision spheres to other objects when needed.
Example
addsphere(Processor1, 2, -1.25, .75, 1);
changetask
(obj tasksequence, num taskrank, num type [, obj involved1, obj involved2 , num var1, num var2, num var3, num var4] )
Dynamically change a task in tasksequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TaskSequence and TaskSequence.Task class methods and properties instead. This command lets you change a task dynamically. For example, if you want an operator to travel to object B instead of traveling to object A, but a task has already been created for him to travel to object A, you can use this command to change the task.
The first parameter (tasksequence) specifies the tasksequence containing the task. The second parameter (taskrank) specifies the rank of the task in the tasksequence. All other parameters are the same as for the inserttask command.
This command should only be executed if the task is not the currently active task in the task sequence!
The first parameter (tasksequence) specifies the tasksequence containing the task. The second parameter (taskrank) specifies the rank of the task in the tasksequence. All other parameters are the same as for the inserttask command.
This command should only be executed if the task is not the currently active task in the task sequence!
Example
changetask(gettasksequence(current, 0), 4, TASKTYPE_TRAVEL, current.centerObjects[5]);
This example changes the fourth task in the current object's active task sequence to a travel task to travel to the object connected to the 5th center port of the current object.
This example changes the fourth task in the current object's active task sequence to a travel task to travel to the object connected to the 5th center port of the current object.
createcoordinatedtasksequence
(obj dispatcher)
Create a new, empty coordinated task sequence
Description
Create a new, empty coordinated task sequence on the specified Dispatcher. Must be followed at some point by dispatchcoordinatedtasksequence.
Example
createcoordinatedtasksequence(current.centerObjects[1]);
createemptytasksequence
(obj dispatcher, num priority, num preempting)
Creates a new task sequence in the dispatcher's queue and returns a reference to it
Description
This command is deprecated. Use TaskSequence.create() instead. Creates an empty task sequence in the dispatcher's tasksequence queue. Tasks should be added to this task sequence once it is created, using the inserttask command. The task sequence is dispatched with the dispatchtasksequence command. This command returns a pointer to the newly created tasksequence node. The possible values for preempting are:
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
0 - PREEMPT_NOT
1 - PREEMPT_ONLY
2 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 - PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
createemptytasksequence(current.centerObjects[1], 1, PREEMPT_NOT);
dispatchcoordinatedtasksequence
(obj tasksequence)
Dispatches the coordinated task sequence
Description
Dispatches the specified coordinated task sequence. Must be called after calling createcoordinatedtasksequence().
Example
dispatchcoordinatedtasksequence(newts);
dispatchtasksequence
(obj tasksequence)
Dispatches the task sequence, initiating handling/execution of the task sequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use TaskSequence.dispatch()
instead. Tells the dispatcher/taskexecuter in which the specified task sequence resides to handle that task sequence. Users should create the task sequence using the createemptytasksequence command, then add tasks using the inserttask command, then cause the task sequence to be handled using the dispatchtasksequence command.
Example
dispatchtasksequence(newtasksequence);
distancetotravel
(obj traveler, obj destination)
Gets the distance a traveler would need to travel to reach destination
Description
Returns the distance that a traveler (Operator, Transporter, etc) would need to travel in order to reach the given destination. If the object is connected to a network, then it will return the travel distance along the network.
Example
distancetotravel(current.centerObjects[1], current);
drawspheres
(obj object, obj view)
Description
For developer use. Draws the collision spheres assigned to the specified object. TaskExecuters allow users to add collision spheres and draw collision spheres through the object's Parameters window, but commands are needed to add and draw collision spheres to other objects when needed
Example
drawspheres(current,view);
freeoperators
(obj taskexecuter, obj involved)
Release all operators connected to taskexecuter that are working on involved
Description
Release all operators connected to the specified dispatcher that are currently working on the involved object. This command should be executed from a trigger when you want to release operator(s) that you have called to a process using the requestoperators command or using a utilize task. The first parameter can be either a dispatcher connected to operator(s) that you want to free, or it can be the operator itself. The second parameter is a key for releasing the appropriate operator(s). If you have called the operator(s) using the requestoperators command, then the second parameter of the freeoperators command should match the third parameter of the requestoperators command. If you have given an operator a utilize task, then the second parameter of the freeoperators command should match the involved1 parameter of the utilize task. You would probably execute this command from a trigger like OnProcessFinish or OnSetupFinish. For more information, refer to the task sequence section of the user manual.
Example
freeoperators(current.centerObjects[1], item);
getallocatedfromkey
(obj coordtasksequence, num key)
Gets a reference to the object allocated for the allocate task for the given key
Description
Returns a reference to the object that has been allocated for the allocate task specified by the given key.
Example
treenode allocatedobj = getallocatedfromkey(getcoordinatedtasksequence(current.centerObjects[1], 0), mykey);
getcoordinatedtasksequence
(obj dispatcher, num tasksequencerank)
Gets a reference to a coordinated task sequence
Description
Returns a reference to the coordinated task sequence that is associated with allocation request with the specified rank in the specified dispatcher's
task sequence queue. If the specified rank is zero, then the command assumes that the dispatcher is actually a TaskExecuter, and it returns
a reference to the coordinated task sequence that it is currently allocated for.
task sequence queue. If the specified rank is zero, then the command assumes that the dispatcher is actually a TaskExecuter, and it returns
a reference to the coordinated task sequence that it is currently allocated for.
Example
treenode coordtasksequence = getcoordinatedtasksequence(current.centerObjects[1], 5);
getcurtask
(node tasksequence)
Gets the current task number of tasksequence
Description
Returns the current task number of the task sequence
Example
if(getcurtask(ts) > 5)
pt("The operator has finished the first five tasks");
pt("The operator has finished the first five tasks");
getnroftasks
(obj tasksequence)
Gets the number of uncompleted tasks in the tasksequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TaskSequence and TaskSequence.Task class methods and properties instead. Returns the number of tasks that still need to be completed in the tasksequence (including the current task).
Example
if(getnroftasks(mytasksequence) > 5)
pt("There are more than 5 tasks in the tasksequence queue.");
pt("There are more than 5 tasks in the tasksequence queue.");
getpreempt
(node tasksequence)
Gets the preempt value of the tasksequence
Description
Returns the preempt value of the tasksequence.
Possible values are:
PREEMPT_NOT,
PREEMPT_ONLY,
PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE,
PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Possible values are:
PREEMPT_NOT,
PREEMPT_ONLY,
PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE,
PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
if(getpreempt(mytasksequence) == PREEMPT_ONLY)
pt("This tasksequence is a preempting task");
pt("This tasksequence is a preempting task");
getpriority
(node tasksequence)
Gets the priority value of the tasksequence
Description
Returns the priority value of the tasksequence.
Example
if(getpriority(mytasksequence) > 5)
pt("This tasksequence has a priority greater than 5.");
pt("This tasksequence has a priority greater than 5.");
gettaskinvolved
(obj tasksequence, num taskrank, num involvednum)
Gets a reference to the first or second involved object of the task of the tasksequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TaskSequence and TaskSequence.Task classes instead. Returns a reference to either the first or second involved object for the nth ranked task of the specified task sequence.
The ranking is based on the initial ranking of the task, when the task sequence was initially created and tasks were
added. It is not based on the ranking at a given time in the simulation, as tasks may have already been completed
and subsequently destroyed. The third parameter defines which involved object it is (1 or 2)
You can also pass a reference to the TaskExecuter as the first parameter, and the value 0 as the second parameter
to get the involved of the object's currently active task.
The ranking is based on the initial ranking of the task, when the task sequence was initially created and tasks were
added. It is not based on the ranking at a given time in the simulation, as tasks may have already been completed
and subsequently destroyed. The third parameter defines which involved object it is (1 or 2)
You can also pass a reference to the TaskExecuter as the first parameter, and the value 0 as the second parameter
to get the involved of the object's currently active task.
Example
treenode loaditem = getinvolved(gettasksequence(current.centerObjects[1], 0), 2, 1);
gettasksequence
(obj dispatcher, num tasksequencerank)
Gets a reference to a task sequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Dispatcher and TaskExecuter class methods and properties instead. Returns a reference to the task sequence that has the specified rank in the specified dispatcher's task sequence queue.
If the specified rank is zero, then the command assumes that the dispatcher is actually a TaskExecuter, and it returns
a reference to its currently active task sequence.
If the specified rank is zero, then the command assumes that the dispatcher is actually a TaskExecuter, and it returns
a reference to its currently active task sequence.
Example
treenode mytasksequence = gettasksequence(current.centerObjects[1], 5);
gettasksequencequeue
(obj dispatcher)
Gets a reference to the dispatcher's tasksequence queue
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the Dispatcher class properties instead. Returns a reference to the specified dispatcher's task sequence queue.
Example
treenode tsqueue = gettasksequencequeue(current.centerObjects[1]);
gettaskstate
(obj tasksequence, num taskrank)
Gets the state of the task at rank taskrank of tasksequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TaskSequence and TaskSequence.Task class methods and properties instead. Gets the state of the task at rank taskrank of tasksequence. The following are task states:
TASKSTATE_UNFINISHED
TASKSTATE_ACTIVE
TASKSTATE_FINISHED
TASKSTATE_COORDINATED
TASKSTATE_UNFINISHED
TASKSTATE_ACTIVE
TASKSTATE_FINISHED
TASKSTATE_COORDINATED
Example
if(gettaskstate(gettasksequence(current.centerObjects[1], 0), 2) == TASKSTATE_ACTIVE)...
gettasktype
(obj tasksequence, num taskrank)
Gets the task type of the task at rank taskrank of tasksequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TaskSequence and TaskSequence.Task class methods and properties instead. Returns the task type for the nth ranked task of the specified task sequence.
The ranking is based on the initial ranking of the task, when the task sequence was initially created
and tasks were added. It is not based on the ranking at a given time in the simulation, as tasks
may have already been completed and subsequently destroyed.
You can also pass a reference to the TaskExecuter as the first parameter, and the value 0 as the second parameter
to get the task type of the object's currently active task.
The ranking is based on the initial ranking of the task, when the task sequence was initially created
and tasks were added. It is not based on the ranking at a given time in the simulation, as tasks
may have already been completed and subsequently destroyed.
You can also pass a reference to the TaskExecuter as the first parameter, and the value 0 as the second parameter
to get the task type of the object's currently active task.
Example
if(gettasktype(gettasksequence(current.centerObjects[1], 0), 2) == TASKTYPE_LOAD)...
gettaskvariable
(obj tasksequence, num taskrank, num variablenum)
Gets the tasksequence variable for the task at rank taskrank of tasksequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TaskSequence and TaskSequence.Task class methods and properties instead. Returns a reference to one of the four task variables for the nth ranked task of the specified task sequence.
The ranking is based on the initial ranking of the task, when the task sequence was initially created and tasks were
added. It is not based on the ranking at a given time in the simulation, as tasks may have already been completed
and subsequently destroyed. The third parameter defines which task variable it is (1 - 4)
You can also pass a reference to the TaskExecuter as the first parameter, and the value 0 as the second parameter
to get the task variable of the object's currently active task.
The ranking is based on the initial ranking of the task, when the task sequence was initially created and tasks were
added. It is not based on the ranking at a given time in the simulation, as tasks may have already been completed
and subsequently destroyed. The third parameter defines which task variable it is (1 - 4)
You can also pass a reference to the TaskExecuter as the first parameter, and the value 0 as the second parameter
to get the task variable of the object's currently active task.
Example
double myvar = gettaskvariable(gettasksequence(current.centerObjects[1], 0), 2, 1);
gettotalnroftasks
(obj tasksequence)
Gets the total number of tasks that were ever added to the tasksequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use the TaskSequence and TaskSequence.Task class methods and properties instead. Returns the total number of tasks that were ever added to the tasksequence.
Example
gettotalnroftasks(mytasksequence)
getutilizedobject
(obj dispatcher, obj involved, obj station, num utilizednr)
Gets a reference to an operator that is currently executing a utilize task
Description
Finds and returns a reference to an operator that is currently executing a utilize task
with the given involved and station variables. If multiple operators are being used, then utilizednr allows
you to distinguish which one you want to reference.
Example
treenode op = getutilizedobject(current.centerObjects[1], item, current, 1);
insertallocatetask
(obj tasksequence, obj dispatcher, num priority, num preempt [, num noblock] )
Inserts an allocate task into the coordinated task sequence
Description
Inserts an Allocate Task into the specified coordinated task sequence. By default the allocation task is a blocking task, but if noblock is 1, then the allocation does not block further execution of the task sequence.
Example
insertallocatetask(newts, current.centerObjects[2], 0, 0);
insertdeallocatetask
(obj tasksequence, num allocationkey [, num noblock] )
Inserts a deallocate task into the coordinated task sequence
Description
Inserts a Deallocate Task into the specified coordinated task sequence to deallocate the resource specified by allocationkey. By default this task will block, but if noblock is 1, it will not block.
Example
insertdeallocatetask(newts,forkkey);
insertproxytask
(obj tasksequence, num executerkey, num type [, num/obj involved1, num/obj involved2 , num var1, num var2, num var3, num var4])
Inserts a proxy task into the coordinated task sequence
Description
Inserts a proxy task into the specified coordinated task sequence.
Example
insertproxytask(newts, dispatchkey, TASKTYPE_TRAVEL, current.centerObjects[1], NULL,0,0,0,0);
insertsynctask
(obj tasksequence, num taskkey)
Inserts a sync task into the coordinated task sequence
Description
Insert a Sync Task for the specified task in a coordinated task sequence.
Example
insertsynctask(newts, travelkey);
inserttask
(obj tasksequence, num type [, obj involved1, obj involved2 , num var1, num var2, num var3, num var4] )
Inserts a new task to the task sequence
Description
This command is deprecated. Use TaskSequence.addTask() instead. Inserts a task into the specified tasksequence of the specified type. Depending on the task type, the remaining parameters will have a different meaning. Refer to the Task Type Quick Reference guide in the Users Manual for an explanation of the parameters associated with each task type.
Example
inserttask(ts, TASKTYPE_TRAVEL, current, NULL);
movetasksequence
(obj tasksequence, obj dispatcher)
Moves tasksequence into the dispatcher's tasksequence queue
Description
This command is deprecated. Use TaskSequence.move() instead. Moves the specified tasksequence into the specified dispatcher's tasksequence queue.
WARNING!! This command should never be called on a tasksequence that is already being executed by a TaskExecuter.
WARNING!! This command should never be called on a tasksequence that is already being executed by a TaskExecuter.
Example
movetasksequence(tasksequence, current.centerObjects[1]);
pickoffsetx
(obj station, obj item, obj loadingobject)
Description
This command queries the station for an x offset for the loadingobject to travel from its x center in order to load the item.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
Example
int xoffset = pickoffsetx(item.up,item,current);
pickoffsety
(obj station, obj item, obj loadingobject)
Description
This command queries the station for a y offset for the loadingobject to travel from its y center in order to load the item.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
Example
int yoffset = pickoffsety(item.up,item,current);
pickoffsetz
(obj station, obj item, obj loadingobject)
Description
This command queries the station for a z offset for the loadingobject to travel from its z base in order to load the item.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
Example
int zoffset = pickoffsetz(item.up,item,current);
placeoffsetx
(obj station, obj item, obj unloadingobject)
Description
This command queries the station for an x offset for the unloadingobject to travel from its x center in order to unload the item.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
Example
int xoffset = placeoffsetx(current.centerObjects[1],item,current);
placeoffsety
(obj station, obj item, obj unloadingobject)
Description
This command queries the station for a y offset for the unloadingobject to travel from its y center in order to unload the item.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
Example
int yoffset = placeoffsety(current.centerObjects[1],item,current);
placeoffsetz
(obj station, obj item, obj unloadingobject)
Description
This command queries the station for a z offset for the unloadingobject to travel from its z base in order to unload the item.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
For more information on offset travel, refer to the TaskExecuter documentation.
Example
int zoffset = placeoffsetz(current.centerObjects[1],item,current);
profiletasksequence
(node tasksequence)
Prints information on a task sequence to the output console
Description
Prints information on a task sequence to the output console.
The output console must be open to write to it.
To open the output console, use menus View | Output Console.
You can also pass a reference to the TaskExecuter object instead of a specific task sequence.
This will profile the object's currently active task sequence.
The output console must be open to write to it.
To open the output console, use menus View | Output Console.
You can also pass a reference to the TaskExecuter object instead of a specific task sequence.
This will profile the object's currently active task sequence.
Example
profiletasksequence(gettasksequence(so(), 0));
Writes all the tasksequence information to the output console for the active (0) tasksequence of the selected object (so()).
Writes all the tasksequence information to the output console for the active (0) tasksequence of the selected object (so()).
reordertasks
(obj dispatcher)
Causes the dispatcher to reorder all its task sequences according to its queue strategy
Description
Causes the involved Dispatcher/TaskExecuter to reorder all its task sequences according to its queue strategy.
Example
reordertasks(c)
requestoperators
(obj dispatcher, obj station, obj involved, num nrofops, num priority, num preempting)
Description
Request a specified number of operators to come to the station object and work on the involved object until released. The involved object will later need to be passed into the freeoperators() command when releasing the operators. The operator(s) being called must either be the object referenced by dispatcher, or be connected to its output ports.
The tasksequence which is sent to the operator(s) will be given a priority and preempting value. The possible values for preempting are as follows:
0 = PREEMPT_NOT
1 = PREEMPT_ONLY
2 = PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 = PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
For each operater that needs to be called, stopobject() will be called on the station, and a tasksequence that looks like the following will be sent to the dispatcher (or operator) object.
1. put a preempt "bookmark" in the task sequence (TASKTYPE_MILESTONE)
2. travel to the station (TASKTYPE_TRAVEL)
3. resume the station (TASKTYPE_STOPREQUESTFINISH)
4. be utilized at the station (TASKTYPE_UTILIZE)
The tasksequence which is sent to the operator(s) will be given a priority and preempting value. The possible values for preempting are as follows:
0 = PREEMPT_NOT
1 = PREEMPT_ONLY
2 = PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE
3 = PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
For each operater that needs to be called, stopobject() will be called on the station, and a tasksequence that looks like the following will be sent to the dispatcher (or operator) object.
1. put a preempt "bookmark" in the task sequence (TASKTYPE_MILESTONE)
2. travel to the station (TASKTYPE_TRAVEL)
3. resume the station (TASKTYPE_STOPREQUESTFINISH)
4. be utilized at the station (TASKTYPE_UTILIZE)
Example
requestoperators(current.centerObjects[1], current, item, 2, 0, PREEMPT_NOT);
This calls 2 operators connected to the object that is connected to the first center port of the current object to come to the current object, and work on the item.
This calls 2 operators connected to the object that is connected to the first center port of the current object to come to the current object, and work on the item.
rerankbesttask
(obj object)
Description
This command forces the object specified as dispatcher to search through its task sequence queue and put the task sequence with the highest priority in the front of its queue. This will not reorder the other task sequences in the queue.
Example
rerankbesttask(current);
setcollisioncheck
(obj taskexecuter, num checkstate [, num checkinterval])
Sets the state and interval for collision checking on the taskexecuter
Description
Sets the state and interval for collision checking on the taskexecuter. If checkstate is 1, then check for collisions, else don't. If interval is >0, then reset the "Time between Collision Checks" for the taskexecuter specified.
Example
setcollisioncheck(traveler,1,5);
Starts the traveler checking for collisions every 5 time units.
Starts the traveler checking for collisions every 5 time units.
setpreempt
(obj tasksequence, num newpreempt)
Sets the preempt value of the tasksequence
Description
Sets the preempt value of the tasksequence to the value of newpreempt. Possible values are:
PREEMPT_NOT,
PREEMPT_ONLY,
PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE,
PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
PREEMPT_NOT,
PREEMPT_ONLY,
PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ACTIVE,
PREEMPT_AND_ABORT_ALL
Example
setpreempt(tasksequence, PREEMPT_NOT);
This example changes the task sequence's preempt value to not preempt.
This example changes the task sequence's preempt value to not preempt.
setpriority
(obj tasksequence, num newpriority)
Sets the priority of the tasksequence
Description
Sets the priority value of the tasksequence to the value newpriority.
Example
setpriority(myts, 1);
This example sets the priority value of the task sequence myts to the value of 1.
This example sets the priority value of the task sequence myts to the value of 1.
Tree Access
Commands for referencing nodes or objects through FlexSim's tree structure.
library
()
Reference to the library node in the main tree
Description
This command returns a reference to the library node in the main tree. It is used as a fast way of referencing the library.
Example
treenode SourceObj = library().find("?Source");
This sets the variable SourceObj so that it references the node called Source in the library.
This sets the variable SourceObj so that it references the node called Source in the library.
maintree
()
Reference to the main tree
Description
Returns a reference to the main tree. When defining string paths to nodes in the main tree, MAIN can be used as in the following example node("MAIN:/project/exec/globals/cppfunctions");
Example
maintree().find("project/exec/globals/cppfunctions");
model
()
Reference the model's root node
Description
This command returns a reference to the model node in the main tree. It is used as a fast way of referencing the model.
Example
treenode SourceObj = Model.find("Source1");
This sets the variable SourceObj so that it references the node called Source1 in the model.
This sets the variable SourceObj so that it references the node called Source1 in the model.
views
()
Reference to the views tree
Description
This command returns a reference to the views tree. The views tree contains all of the information about the windows that are currently open as well as all of the available GUIs. When defining string paths to nodes in the view tree, VIEW can be used as in the following example: node("VIEW:/standardviews/ortho");
Example
activateview(views().find("standardviews/runcontrol"));
This activates the GUI called "runcontrol" which is stored in the node called "standardviews" of the view tree.
This activates the GUI called "runcontrol" which is stored in the node called "standardviews" of the view tree.
Tree Node Data
Commands for accessing and assigning data to nodes in the tree. Many of these commands can be used on objects as well, because objects are also nodes in the tree.
$iter
(num index)
See User Manual > Miscellaneous Concepts > SQL Queries
Description
See Miscellaneous Concepts > SQL Queries for more information.
Example
checkdllconnection
(node dllnode, num force)
Returns 1 if the node is properly connected with a dll function
Description
Returns 1 if the node is properly connected with a dll function. Otherwise returns 0. If force is 1, then if the node is not connected, it will attempt to bind it to a dll function, and will return 1 if successful, 0 if not. The node must be toggled as DLL and have proper data specifying the path to the dll and the function name.
Example
if(!checkdllconnection(getvarnode(current, "exittrigger"), 1)) msg("DLL Error","Error connecting to dll.")
This will attempt to connect and object's exit trigger node with a dll function, and will print a message if it is unsuccessful.
This will attempt to connect and object's exit trigger node with a dll function, and will print a message if it is unsuccessful.
comparetrees
(obj tree1, obj tree2)
Description
For developer use. Test trees for equality.
Example
comparetrees(node("MAIN:/project/model/1"),node("MAIN:/project/model/2"))
createcoupling
(node container1, node container2)
Creates a pointer coupling inside the two container nodes
Description
Creates a pointer coupling inside the two container nodes
Example
createcoupling(current.labels["items"], item.labels["owner"]);
enablecode
(node codenode [, num mode])
Makes the node a code node
Description
If mode is 0, then the node is set to FlexScript unless the node is already a code node and then it leaves the node as is. If mode is non-zero, then it forces a given toggle: 1-FlexScript, 2-C++, 3-DLL.
This command is used in the code edit window to toggle the node as FlexScript or DLL.
This command is used in the code edit window to toggle the node as FlexScript or DLL.
Example
enablecode(getvarnode(current, "exittrigger"));
findownerobject
(node thenode)
Description
Like ownerobject(), this command returns the object node containing thenode. Unlike ownerobject(), this command does not
cache the result, but searches in the tree for the "owner" node. For example when a TaskExecuter transfers from one NetworkNode to another on a network path, a coupling node is transferred to the new node to keep track of the TaskExecuter's current node, and findownerobject() is used to get access to the correct "owner" node.
Example
findownerobject(c)
getsdtvalue
(node sdtNode, str valName)
For developer use
Description
Primarily for developer use only. Returns the value of the named class member of a node that has "SimpleDataType" data. We
discourage using this command in model code because you risk breaking forward-compatibility. Future versions may redefine class members
and their names, so model code that accesses these values by name may not work in future versions.
Example
nodebreak
(node a)
Description
For developer use. Breaks a coupling pointer on a node that has coupling data that is pointing to another node. If the node is part of a bi-directional coupling, the other coupling is not affected.
Example
nodebreak(so())
nodeinsertafter
(node targetnode)
Creates a new node immediately after targetnode
Description
This command creates a new node in the tree immediately after the targetnode. The new node has no data attached to it. Data is attached using the nodeadddata() command. Any node in the tree can be passed as targetnode.
Example
nodeinsertafter(item.find(">labels").last).dataType = DATATYPE_NUMBER;
This creates a new label on the object referenced by item that holds number data.
This creates a new label on the object referenced by item that holds number data.
nodeinsertinto
(node containernode)
nodejoin
(node a, node b)
Description
For developer use. Join two pointer nodes to form a bi-directional coupling. A bi-directional coupling in FlexSim is a pair of nodes who's data points to each other. FlexSim automatically manages the coupling. If either one of the endpoints is deleted or nullified, FlexSim cleans up to prevent dangling pointers. The two nodes a and b must have coupling data.
Example
nodejoin(so(),so().next)
objectexists
(obj object)
Check if an object exists
Description
If you're trying to test if an object exists when using dot syntax you can omit the objectexists. For example, if (current.labels["MyLabel"]) or if (current.next).
This command returns true (1) if the object specified as object exists in the tree. If the object does not exist, this command returns false (0).
This command returns true (1) if the object specified as object exists in the tree. If the object does not exist, this command returns false (0).
Example
if (objectexists(next(current)))
{
moveobject(item, next(current), 1);
}
This checks to see if there is an object in the tree after current. If there is, the object referenced by item is moved into it through port number 1.
{
moveobject(item, next(current), 1);
}
This checks to see if there is an object in the tree after current. If there is, the object referenced by item is moved into it through port number 1.
ownerobject
(node thenode)
Gets the object that "owns" the executing node, usually the current object
Description
This command returns the node with object data attached to it that is the start of the sub-tree that thenode is in.
In other words, it returns the object node that contains thenode. The result of this command is cached on thenode, so that subsequent calls
to ownerobject(thenode) do not search in the tree, but return the cached result. If thenode subsequently changes parent, ownerobject(thenode) will
return the cached result.
This command is used in most code fields and trigger fields to set the access variable current. In these fields, c references the node that contains the code, and ownerobject(c) references the object that "owns" that node.
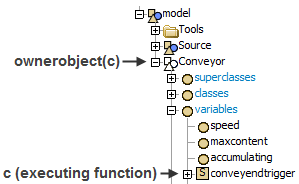
This command is used in most code fields and trigger fields to set the access variable current. In these fields, c references the node that contains the code, and ownerobject(c) references the object that "owns" that node.

Example
string objname = ownerobject(c).name;
This sets objname to the name of the object that contains the node referenced by c. The c usually refers to the node where the code is being written.
treenode current = ownerobject(c);
This example is present in most code fields in FlexSim, and retrieves access to the "current" object.
This sets objname to the name of the object that contains the node referenced by c. The c usually refers to the node where the code is being written.
treenode current = ownerobject(c);
This example is present in most code fields in FlexSim, and retrieves access to the "current" object.
removeallcouplingreferences
(node thenode)
Recursively breaks couplings from a node and its subnodes in the tree
Description
Recursively breaks couplings from a node and its subnodes in the tree.
Example
removeallcouplingreferences(current);
setsdtvalue
(node sdtNode, str valName, num/str/node toVal)
For developer use
Description
Primarily for developer use only. Sets the value of the named class member of a node that has "SimpleDataType" data. We
discourage using this command in model code because you risk breaking forward-compatibility. Future versions may redefine class members
and their names, so model code that accesses these values by name may not work in future versions.
Example
swapnoderanks
(obj/node parentnode, num index1, num index2)
Swap the ranks for two nodes in a parent node's sub-tree
Description
This command swaps the ranks of two nodes in the parent node's sub-tree. Swapping ranks can be faster than using setrank() especially for very large lists of nodes.
Example
swapnoderanks(parentNode,4,parentNode.subnodes.length);
This swaps the 4th ranked node in parentNode's sub-tree with the last node in parentNode's sub-tree. This can make removing that node from parentNode's sub-tree faster if the list is very long. Note that this will put the last node into the 4th position, so ordering in the tree should not matter to be able to do this. In other words, this would break fifo ordering.
This swaps the 4th ranked node in parentNode's sub-tree with the last node in parentNode's sub-tree. This can make removing that node from parentNode's sub-tree faster if the list is very long. Note that this will put the last node into the 4th position, so ordering in the tree should not matter to be able to do this. In other words, this would break fifo ordering.
switch_cppfunc
(node thenode[, num off/on])
Get or set the "C++" flag of thenode
Description
Get or set the "C++" flag of thenode. A value of 1 is C++, a value of 0 is not C++, a value of -1 gets the current value. If a node is toggled as C++ it will be compiled as a C++ function at time of compile.
Example
switch_cppfunc(so(),1)
switch_destroyonreset
(obj thenode[, num off/on])
Get or set the "destroy on reset" flag of the object
Description
Get or set a node's "destroy on reset" flag. If the flag is 1, the node will be deleted when the model is reset. An off/on value of 0 or 1 sets the flag, and -1 gets the current value.
Example
switch_destroyonreset(so(),1)
switch_dllfunc
(node dllnode[, num on/off/get])
Description
Switches the node's dll toggle on or off. 1 switches it on, 0 off, and -1 gets the current state.
Example
switch_dllfunc(getvarnode(current, "exittrigger"), 1);
switch_expanded
(node thenode[, num off/on])
Expand/collaps sub-level nodes of thenode
Description
Expand or collapse sub-level nodes of thenode in the tree view. This is analogous to clicking the + and - sign of thenode in the tree view. A value of 1 is expand, a value of 0 is collapse, a value of -1 gets the current value.
Example
switch_expanded(so(),1)
switch_flexscript
(obj object[, num on/off/query])
Description
For developer use. This command switches the flexscript toggle of a node.
0 = toggle node non-flexscript
1 = toggle node as flexscript
-1 = query whether node is toggled (1) or not (0)
0 = toggle node non-flexscript
1 = toggle node as flexscript
-1 = query whether node is toggled (1) or not (0)
Example
switch_flexscript(var_s(current, "code"), 1);
switch_hashedlist
(obj thenode[, num off/on])
Get or set the "Hashed List" flag of thenode
Description
Get or set the "Hashed List" flag of the thenode. A value of 1 sets the node to store a hashed list of its subnodes for fast lookup by name, a value of 0 sets the node to not store a hashed list of subnodes, a value of -1 gets the current value.
Example
switch_hashedlist(so(),1)
switch_noselect
(obj object[, num off/on])
Get or set the "No Select" flag of the object
Description
Get or set the "No Select" flag of the node object (the object node will have a gray highlight in the treeview to indicate protected). A value of 1 is unselectable, a value of 0 is selectable, and a value of -1 gets the current value. Setting no select on an object keeps it from being clicked on with the mouse in the 3D view.
Example
switch_noselect(so(),1)
switch_orphancoupling
(obj thenode[, num off/on])
Get or set the "orphan coupling" flag of the object
Description
Get or set a node's "orphan coupling" flag. If the flag is 1, when the coupling node is copied, the copy won't be destroyed if it no longer points to a valid node. An off/on value of 0 or 1 sets the flag, and -1 gets the current value.
Example
switch_orphancoupling(so(),1)
switch_preservecoupling
(obj thenode[, num off/on])
Get or set the "preserve coupling" flag of the object
Description
Get or set a node's "preserve coupling" flag. If the flag is 1, when the coupling node is copied, the copy will also point to its partner. For one-way couplings, the original and the copy will both point at the same partner node. For two-way couplings, a new partner node will be created. An off/on value of 0 or 1 sets the flag, and -1 gets the current value.
Example
switch_preservecoupling(so(),1)
switch_protected
(obj object[, num off/on])
Get or set the "Protected" flag of the object
Description
Get or set the "Protected" flag of the node object (the object node will have a gray highlight in the treeview to indicate protected). A value of 1 is protected, a value of 0 is unprotected, and a value of -1 gets the current value. Protecting an object keeps it from being moved, rotated, or resized with the mouse, but not from being double-clicked to access the Parameters window for the object. View windows have an attribute named viewignoreobjects which can be used to ignore ALL the objects in their view which means the objects can not be manipulated in any way with the mouse including double-clicking.
Example
switch_protected(so(),1)
switch_selected
(obj thenode[, num off/on])
Get or set the "Selected" flag of thenode
Description
Get or set the "Selected" flag of thenode (red highlight). A value of 1 is selected, a value of 0 is unselected, a value of -1 gets the current value.
Example
switch_selected(so(),1)
switch_statelocked
(obj object[, num off/on])
Description
Get or set the "is code state locked" flag of the node object. A value of 1 is enable, a value of 0 is disable, a value of -1 gets the current value. If enabled, the node will be locked as either C++ or flexscript depending on what it currently is (the model will not change it when "Make All Code C++/Flexscript" is chosen through the main menu.
Example
switch_statelocked(so(),1)
switch_stateused
(obj thenode[, num off/on])
Description
For developer use. Get or set where a node inside a state profile is used by the object. This flag is automatically set in the setstate() command,
so developers can know which states are used by an object, for UI development.
Example
switch_stateused(so(),1)
User Interface
Commands associated with implementing and managing user interfaces such as menus, toolbars, views and edit windows.
activateview
(obj viewnode)
Description
For developer use. This command makes a GUI window active and visible. It should be used to open a window that is stored in the view tree without creating a copy of the view in the active tree, in order to make direct changes that will be saved in the view tree instead of being deleted when the window is closed. Generally, the command createview() should be used to open GUI windows. Use makeactive() if you want to make an already open view the active, or top, window.
Example
activateview(views.find("standardviews/other/FindReplace"));
This opens the node called FindReplace in the folder called standardviews/other in the view tree.
This opens the node called FindReplace in the folder called standardviews/other in the view tree.
activedocumentnode
()
Gets the currently active document window
Description
Returns the currently active document window. If the active document window is a tabbed window, it will return the active tab page node.
Example
treenode activedoc = activedocumentnode();
activedocumentview
()
Gets the currently active document window as an HWND
Description
Returns the currently active document window as an HWND. To get the node associated with the window, use activedocumentnode().
Example
treenode activedoc = nodefromwindow(activedocumentview());
activeview
()
Gets the currently active window as an HWND
Description
Returns the currently active window as an HWND. To get the node associated with the window, use nodefromwindow()
Example
treenode viewnode = nodefromwindow(activeview());
addviewtext
(node view, string text)
Description
For developer use. Add text to the specified window.
Example
addviewtext(sv(),"Hello")
applicationcommand
(str name[, p1, p2, p3, ...])
Description
For developer use. Execute a command based on its name. This command will search for the named node in VIEW:/nodefunctions, then in MAIN:/project/exec/globals/nodefunctions, then in VIEW:/commands, and lastly in the FlexSim Engine. If it finds a toggled node, it will call nodefunction on that node passing in up to 10 number parameters. If it finds an untoggled node, it will call executefsnode() on that node passing in n1 as c, n2 as i, and n3 as eventcode.
Example
applicationcommand("outputconsole");
applyalleditstonodes
([obj view])
Description
For developer use. Applies all view edits. This is done before a compile or save.
Example
applyalleditstonodes
applyeditstonode
(obj view, obj editednode)
Description
For developer use. Applies view changes to a node. This is usually only needed for a table view, and is essentially the same as mouse-clicking off of the table's currently active cell. This is the opposite of applytoedits.
Example
applyeditstonode(ownerview(c), current)
applylinks
(node view [, num refresh])
Description
For developer use. This command applies all of the hotlinks and coldlinks in the view window specified as view. If refresh is 1, then the links will be refreshed, meaning the values from the model will be retrieved and set on the window controls themselves. If refresh is 0, then the values in the model will be set according to what the user specified in the view. This command is used in Flexscript GUI programming.
Example
applylinks(ownerview(c));
This applies all of the links in the window that is currently designated as the selected view.
This applies all of the links in the window that is currently designated as the selected view.
applytoedits
(obj view, obj editednode)
Description
For developer use. Applies programmatic changes to a node if that node has been selected in a view. This is usually only needed for a table view. This is the opposite of applyeditstonode().
Example
applytoedits(ownerview(c), current)
attlink
(node viewdatanode, str path)
Description
For developer use. Find a node by text path, relative to the view's objectfocus. This command will return the node on the path relative to the object focus of the ownerview of viewdatanode. For example, let viewdatanode be a node inside the structure of a view, such as an OnPress event node. Then, let the objectfocus of the parent view point to an object in the model called "Processor". Now, whatever is passed to the path argument of attlink() will be relative to the Processor object. So, if ">variables" was passed to path in the attlink call, then attlink would return the pointer to "variables" of the Processor. If the node does not exist, attlink will return a null "safenode" which signals a failure to find the requested node. The return value can be tested for validity with the objectexists() command.
Example
attlink(so(),">variables") // where so() is data node inside view
beginaggregatedundo
(obj view, str description)
Description
Begins an aggregated undo record for the specified view. Any undoable commands that are executed between this command and the next endaggregatedundo() command will be encapsulated into a single undoable operation. Returns the id for the created record.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
int id = beginaggregatedundo(c.find("@/TheTable"),"Name Change");
beginignoreundo
()
Description
Used in conjunction with beginaggregatedundo() and endaggregatedundo(). Any commands called between beginignoreundo() and endignoreundo() will not be added as undoable commands within the aggregated undo record.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
beginignoreundo();
callwebscriptmethod
(obj view, str domid, str methodname, int type [, num/str data ...])
Description
Call a method on a DOM element in the HTML document of an HTML view. You must define the type of data of any parameters that are to be passed
into the method. The following types are available:
CWSM_DOUBLE
CWSM_STRING
CWSM_NODE
CWSM_BUNDLE
CWSM_BUNDLE_HEADER
CWSM_BUNDLE_DATA
CWSM_JSON
The last parameter passed into the method must be CWSM_END.
When using the CWSM_JSON type, the json string must start with json:. For example, json:{"title":"My Title"}
CWSM_DOUBLE
CWSM_STRING
CWSM_NODE
CWSM_BUNDLE
CWSM_BUNDLE_HEADER
CWSM_BUNDLE_DATA
CWSM_JSON
The last parameter passed into the method must be CWSM_END.
When using the CWSM_JSON type, the json string must start with json:. For example, json:{"title":"My Title"}
Example
callwebscriptmethod(view, "chart", "updateData", CWSM_DOUBLE, time(), CWSM_NODE, getvarnode(current, "data"), CWSM_STRING, "My Title", CWSM_END);
This examples calls the method named updateData on the element with id "chart".
This examples calls the method named updateData on the element with id "chart".
checkforexistingview
(obj view [, num mode])
Description
For developer use. Checks to see if there are any currently active windows that match this window.
Compares the beginning of each name of each window in the active view node with the beginning of the name of the specified view.
Along with comparing the beginning of the names, this compares each objectfocus as well.
If mode is specified and is not 0, it will compare the viewfocus instead of the objectfocus.
Compares the beginning of each name of each window in the active view node with the beginning of the name of the specified view.
Along with comparing the beginning of the names, this compares each objectfocus as well.
If mode is specified and is not 0, it will compare the viewfocus instead of the objectfocus.
Example
checkforexistingview(c)
clearundohistory
([obj view])
Description
Deletes all undo records in the undohistory of the specified view. If no view is specified, it will clear the global undo history used by the 3D and tree windows.
Example
clearundohistory(view);
clickcode
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the type of click in a view. Used in the OnClick event.
DOUBLE_CLICK returns 1
LEFT_PRESS returns 2
LEFT_RELEASE returns 3
RIGHT_PRESS returns 4
RIGHT_RELEASE returns 5
DOUBLE_CLICK returns 1
LEFT_PRESS returns 2
LEFT_RELEASE returns 3
RIGHT_PRESS returns 4
RIGHT_RELEASE returns 5
Example
if(clickcode()==2)
{
pt("Clicked!!");pr();
}
This prints the statement "Clicked!!" to the output console when the left mouse button is pressed.
{
pt("Clicked!!");pr();
}
This prints the statement "Clicked!!" to the output console when the left mouse button is pressed.
closeview
(node viewnode)
Description
For developer use. This command closes the view specified as viewnode. If viewnode is not a viewwindow or GUI, this command does nothing. The view is not removed from the active views folder, however. Use destroyobject() to remove it.
Example
treenode activewindows = views().find("active");
while (activewindows.subnodes.length != 0)
{
closeview(activewindows.first);
}
This closes all of the windows that are in the active node of the views tree. This will generally close all of the windows that are currently open.
while (activewindows.subnodes.length != 0)
{
closeview(activewindows.first);
}
This closes all of the windows that are in the active node of the views tree. This will generally close all of the windows that are currently open.
codetotemplate
(obj code, obj edit)
Description
For developer use.
Converts C++/Flexscript code into template code and sets the view text of edit to the template code. The code parameter should reference a node that contains text with C++/Flexscript code on it. This is used in a picklist's template code drop-down to create template code from the actual C++/Flexscript code.
Converts C++/Flexscript code into template code and sets the view text of edit to the template code. The code parameter should reference a node that contains text with C++/Flexscript code on it. This is used in a picklist's template code drop-down to create template code from the actual C++/Flexscript code.
Example
codetotemplate(so(),sv())
codetotemplatetext
(node codeobject, node toobjecttext [, num firstcommentonly])
Description
For developer use. Converts C++/Flexscript code into template code. Sets the text in toobjecttext to the template code of the code found in codeobject's text
Example
combocurrentnode
(obj combonode)
Description
For developer use. Returns the current node of the specified picklist combobox.
Example
createview(
"VIEW:/standardviews/picklisttemplate","",
combocurrentnode(c.find("../pickoptions").getPath(0, 1)
);
"VIEW:/standardviews/picklisttemplate","",
combocurrentnode(c.find("../pickoptions").getPath(0, 1)
);
comborefresh
(obj combonode)
Description
For developer use. Refreshes a picklist combobox contents.
Example
comborefresh(current);
controlpressed
()
Description
For devloper use. Test if CTRL key is pressed
Example
controlpressed()
createpopup
(str viewpath, str objectfocus, str viewfocus, obj relativeto, num x, num y, num sx, num sy)
Creates a new popup window
Description
Similar to the createview command in that it creates a new window. However, FlexSim manages this window so that whenever the user clicks outside of the window, the window will be closed. Code template pop-ups use this command to create a drop-down in which you can edit the template code. The pop-up view must contain a style attribute with the WS_POPUP style. You also specify a view node "relative to" which the popup's location will be set (usually whatever view you're writing code on). Also specify an offset location in pixels from relativeto's top-left corner, and a size of the pop-up.
Example
treenode combobox = c.find("../pickoptions");
createpopup(
"VIEW:/standardviews/picklisttemplate",
combobox.find(">pickprimary+").getPath(0,1),
combocurrentnode(combobox).getPath(0,1),
combobox,
0,20,combobox.location.x, 150
);
This code is similar to what is used to create the template code pop-up for many of FlexSim's edit fields.
createpopup(
"VIEW:/standardviews/picklisttemplate",
combobox.find(">pickprimary+").getPath(0,1),
combocurrentnode(combobox).getPath(0,1),
combobox,
0,20,combobox.location.x, 150
);
This code is similar to what is used to create the template code pop-up for many of FlexSim's edit fields.
createundorecord
(obj view, obj object, num undocode[, num p1, num p2, num p3])
Description
Creates an undo record for the specified view. Returns the uniqueid for the created record.
Undo codes:
UNDO_AGGREGATED 1
UNDO_MOVE_SIZE_ROTATE 2
UNDO_MOVE_SIZE_ROTATE_GROUP 3
UNDO_SELECTION_CHANGE 4
UNDO_CREATE_OBJECT 5
UNDO_DELETE_OBJECT 6
UNDO_CHANGE_DATA 7
UNDO_CHANGE_RANK 8
UNDO_CHANGE_NAME 9
UNDO_MOVE_OBJECT 10
UNDO_DELETE_COUPLING 11
UNDO_AGGREGATED_FIRST_RECORD 12
UNDO_DESTROY_BRANCH 13
UNDO_CHANGE_FLAGS 14
UNDO_REPLACE_OBJECT 15
UNDO_CUSTOM 16
UNDO_CALLBACK 17
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Undo codes:
UNDO_AGGREGATED 1
UNDO_MOVE_SIZE_ROTATE 2
UNDO_MOVE_SIZE_ROTATE_GROUP 3
UNDO_SELECTION_CHANGE 4
UNDO_CREATE_OBJECT 5
UNDO_DELETE_OBJECT 6
UNDO_CHANGE_DATA 7
UNDO_CHANGE_RANK 8
UNDO_CHANGE_NAME 9
UNDO_MOVE_OBJECT 10
UNDO_DELETE_COUPLING 11
UNDO_AGGREGATED_FIRST_RECORD 12
UNDO_DESTROY_BRANCH 13
UNDO_CHANGE_FLAGS 14
UNDO_REPLACE_OBJECT 15
UNDO_CUSTOM 16
UNDO_CALLBACK 17
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
int id = createundorecord(ownerobject(c), selectedobject(ownerobject(c)), UNDO_CUSTOM);
createview
(str viewpath[, str objectfocus, str viewfocus])
Description
For developer use. This command creates a new GUI window in the active node of the views tree. This window is a copy of the window whose path is given in viewpath. The window will have an object focus of objectfocus and a view focus of viewfocus. Objectfocus and viewfocus are generally the same for most GUI windows. They should be the path of the node that this GUI window is representing.
Example
createview("VIEW:/standardviews/other/FindReplace","MAIN:/project/model/Tools/precision","MAIN:/project/model/Tools/precision");
This creates the Find Replace GUI.
This creates the Find Replace GUI.
cursorinfo
(obj/num view, num operation, num x/y/z, num pos/move)
Description
For developer use. This command represents a lot of functionality wrapped up into one command.
It is a way of getting information regarding the position/state of the mouse for a window control.
view: the associated view, such as an ortho or planar view. This can also be an HWND (stored in a double).
operation: the type of operation you want to do:
1 - gets x or y positions of the cursor in a planar view
2 - get orthographic or perspective view coordinates
3 - get current mouse button state.
return value:
0 : no buttons down
1 : left down
2 : right down
3 : right and left down
4 : double left click
4 - update the cursor position
5 - gets x or y positions of the cursor relative to the view
6 - gets x or y positions of the cursor in screen coordinates
7 - sets the x or y position of the cursor
xyz: 1(x), 2(y), or 3(z); not used for operation 3. For operation 4, if xyz=1, the cursor position will be updated with objects being drawing, if xyz=2 it will be updated with only the floor drawn.
pos/move: 1(pos) or 2(move); 1 gets absolute mouse position, and 2 gets the change since last update. only used for operations 1-2.
The best way to test this functionality out is just by trial and error. Add an OnMouseMove attribute to the ortho view (make sure you rebind the view's attributes after you've added it: Build|Rebind Object Attributes), then print information to the output console.
view: the associated view, such as an ortho or planar view. This can also be an HWND (stored in a double).
operation: the type of operation you want to do:
1 - gets x or y positions of the cursor in a planar view
2 - get orthographic or perspective view coordinates
3 - get current mouse button state.
return value:
0 : no buttons down
1 : left down
2 : right down
3 : right and left down
4 : double left click
4 - update the cursor position
5 - gets x or y positions of the cursor relative to the view
6 - gets x or y positions of the cursor in screen coordinates
7 - sets the x or y position of the cursor
xyz: 1(x), 2(y), or 3(z); not used for operation 3. For operation 4, if xyz=1, the cursor position will be updated with objects being drawing, if xyz=2 it will be updated with only the floor drawn.
pos/move: 1(pos) or 2(move); 1 gets absolute mouse position, and 2 gets the change since last update. only used for operations 1-2.
The best way to test this functionality out is just by trial and error. Add an OnMouseMove attribute to the ortho view (make sure you rebind the view's attributes after you've added it: Build|Rebind Object Attributes), then print information to the output console.
Example
cursorinfo(c,2,1,1)
deselectall
()
Description
For developer use. Deselects all objects in the model.
Example
deselectall()
distcutoff
(num radius)
Sets a globally applied cutoff radius for object drawing
Description
Sets a globally applied cutoff radius (from the viewpoint) for object drawing.
Example
discutoff(10)
distfromviewpoint
(obj object, obj view)
How far from the viewpoint object is in the window view
Description
Returns how far from the viewpoint the object specified as object is in the view window specified as view. This value is only meaningful if view is a reference to a Perspective window.
Example
double dist = distfromviewpoint(model().subnodes[2],sv());
This sets dist to the distance from the first object in the model to the viewer's eye.
This sets dist to the distance from the first object in the model to the viewer's eye.
draginfo
(num operation[, num val])
Gets or set values related to draggin the mouse
Description
Get or set values related to dragging the mouse.
Operations:
DRAG_INFO_DX 1 - gets dx
DRAG_INFO_DY 2 - gets dy
DRAG_INFO_DZ 3 - gets dz
DRAG_INFO_MDX 4 - gets mdx
DRAG_INFO_MDY 5 - gets mdy
DRAG_INFO_BUTTON_STATE 6 - gets the button state
DRAG_INFO_SET_DX 7 - sets dx to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_DY 8 - sets dy to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_DZ 9 - sets dz to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_MDX 10 - sets mdx to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_MDY 11 - sets mdy to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_BUTTON_STATE 12 - sets the button state to val
Operations:
DRAG_INFO_DX 1 - gets dx
DRAG_INFO_DY 2 - gets dy
DRAG_INFO_DZ 3 - gets dz
DRAG_INFO_MDX 4 - gets mdx
DRAG_INFO_MDY 5 - gets mdy
DRAG_INFO_BUTTON_STATE 6 - gets the button state
DRAG_INFO_SET_DX 7 - sets dx to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_DY 8 - sets dy to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_DZ 9 - sets dz to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_MDX 10 - sets mdx to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_MDY 11 - sets mdy to val
DRAG_INFO_SET_BUTTON_STATE 12 - sets the button state to val
Example
double dx = draginfo(DRAG_INFO_DX);
dropnodefrom
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the view from which a node was dropped.
Example
dropnodefrom()
dropnodeto
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the view into which a node was dropped.
Example
dropnodeto()
dropx
()
Gets the x position of a drop action
Description
Get the x position of a drop action
Example
dropx()
dropy
()
Gets the y position of a drop action
Description
Get the y position of a drop action
Example
dropy()
dropz
()
Gets the z position of a drop action
Description
Get the z position of a drop action
Example
dropz()
endaggregatedundo
(obj view, num id)
Description
Ends an aggregated undo record for the specified view. Any undoable commands that are executed between this command and the previous beginaggregatedundo() command will be encapsulated into a single undoable operation. Pass the id returned by the beginaggregatedundo() function.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
endaggregatedundo(c.find("@/TheTable"),id);
endignoreundo
()
Description
Used in conjunction with beginaggregatedundo() and endaggregatedundo(). Any commands called between beginignoreundo() and endignoreundo() will not be added as undoable commands within the aggregated undo record.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
endignoreundo();
findundorecordbyid
(obj view, num id)
Description
Returns the undo record with the specified id for the specified view.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
int id = createundorecord(ownerobject(c), selectedobject(ownerobject(c)), UNDO_CUSTOM);
treenode record = findundorecordbyid(ownerobject(c),id);
treenode record = findundorecordbyid(ownerobject(c),id);
finishundorecord
(obj view, num uniqueid)
Description
Finishes an undo record for the specified view.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
finishundorecord(view, getundorecordid(record));
getchecked
(obj window)
Description
For developer use. Returns the checked state of a button.
Example
getchecked(c)
getcurrentundorecord
(obj view)
Description
Returns a pointer to the treenode associated with the current undo record in the undohistory of the specified view.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
treenode record = getcurrentundorecord(view);
getdashboardcontrol
(str id [, node startnode])
Returns a reference to the dashboard control associated with id
Description
Returns a reference to the dashboard control that has the ID value of id. This command will search through all open dashboards until it finds a control with matching ID. Passing in a value for startnode will cause the command to only search through the dashboard containing startnode. Dashboard controls include edit fields, buttons, comboboxes, etc.
Example
treenode accelEdit = getdashboardcontrol("accelEdit", c); //Searches through the current dashboard only
getfilebrowse
(str extension, str extensiondescription[, str defaultreturn, str location, num savemode, node filelist])
Opens a standard windows file browser dialog window
Description
This command opens a standard Windows file browser dialog window. The files shown in the window will have the extensions defined in extension. Different extensions should be separated by semicolons (;) in extension. The text passed as description will be used in the file browser to describe the type of file to open. This command returns a string that is the path of the selected file. If no file is selected, or Cancel is pressed, the command returns an empty string. See filebrowse() command.
Example
string shapefile = getfilebrowse("*.3ds; *.wrl","3D shape files");
This sets the variable shapefile to the path of a file chosen from a file browser that displays files with the .3ds and .wrl extensions.
This sets the variable shapefile to the path of a file chosen from a file browser that displays files with the .3ds and .wrl extensions.
getfilesindirectory
(str directory, str extension, node destnode)
Description
Retrieves all files in the specified directory that match the specified extension, and populates the content of destnode with nodes
holding the path to each matching file. The command returns the number of matching files that were found. The extension parameter
should be the specific three (or sometimes four) letter extension that you want to get. For example, if you want all .fsm model files, specify the string "fsm".
Also, if you pass "directories" as the extension parameter, then the command will retrieve the list of directories inside the directory. To get all
files, no matter the extension, pass "*" as the extension parameter. File paths will be set on the string data (as opposed to the name) of nodes
inserted into destnode.
Example
treenode destnode = Model.find("Tools").subnodes.assert("Files");
int nrfiles = getfilesindirectory(documentsdir(), "*", destnode);
for(int i = 1; i <= nrfiles; i++)
{
mpt("file: ");
mpt(destnode.subnodes[i].value);
mpr();
}
getparentwindow
(HWND window)
Description
For developer use. Returns the parent window of the specified window. Use windowfromnode as a parameter to pass into this function.
Example
getpickingdrawfocus
(obj theview, num whattoget, num pickedid)
Gets the picking draw focus
Description
Gets the picking draw focus. Used in OnClick to know what was clicked.
The whattoget parameter can be PICK_TYPE, PICK_OBJECT, or PICK_SECONDARY_OBJECT.
pickedid should be PICK_PRESSED for the "pressed" pick, PICK_HOVERED for the "hovered" pick, PICK_RELEASED for the "released" pick, or PICK_MOVED for "mouse moved" pick.
Example
int picktype = getpickingdrawfocus(view, PICK_TYPE, 0);
getpickingmode
(obj view)
Gets the picking mode for view
Description
Gets the picking mode for the specified view.
Example
int isselectionmode = getpickingmode(view);
getsystemmetric
(num metric[, HWND win])
Description
For developer use. Returns system screen metrics. These values for metric return the following values (if not specified, values are in logical units):
1: desktop width
2: desktop height
3: the left position of the work area of the monitor under the cursor
4: the right position of the work area of the monitor under the cursor
5: the top position of the work area of the monitor under the cursor
6: the bottom position of the work area of the monitor under the cursor
7: the width of window win in pixels
8: the height of window win in pixels
9: the left position of the monitor under the cursor
10: the right position of the monitor under the cursor
11: the top position of the monitor under the cursor
12: the bottom position of the monitor under the cursor
13: the width of window win
14: the height of window win
1: desktop width
2: desktop height
3: the left position of the work area of the monitor under the cursor
4: the right position of the work area of the monitor under the cursor
5: the top position of the work area of the monitor under the cursor
6: the bottom position of the work area of the monitor under the cursor
7: the width of window win in pixels
8: the height of window win in pixels
9: the left position of the monitor under the cursor
10: the right position of the monitor under the cursor
11: the top position of the monitor under the cursor
12: the bottom position of the monitor under the cursor
13: the width of window win
14: the height of window win
Example
getsystemmetric(1)
gettableviewselection
(obj tableview, num val)
Description
For developer use. Returns values based on the blue selection range in a table view: val 1 returns the start row, val 2 returns the start col, val 3 returns the end row, val 4 returns the end col.
Example
int startrow = gettableviewselection(c,1);
getundorecordid
(obj record)
Description
Returns the id of the specified undo record.
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
int id = getundorecordid(getcurrentundorecord(view));
getviewhwnd
(obj view, int windowtype)
Gets the HWND handle for a certain window of a view
Description
Returns a windows HWND handle for a certain window of a view. Each view may use several windows to display data properly. For example, a tree view contains the main window that displays the tree as well as a window that displays the string or number data on a node for editing, as well as a window that displays/edits the name of a node. The windowtype parameter specifies which window handle you want returned, as follows:
1 - the main control (same as using windowfromnode())
2 - datacontrol - The scintilla code control that displays data of a node in a tree, and in a script view
3 - control - the control that displays/edits a highlighted node's name in the tree
4 - statusbar - the statusbar of the view if it has one
5 - tooltip - the tooltip control of the view
6 - pointercontrol - I think this is only used in a tree that displays list heads
1 - the main control (same as using windowfromnode())
2 - datacontrol - The scintilla code control that displays data of a node in a tree, and in a script view
3 - control - the control that displays/edits a highlighted node's name in the tree
4 - statusbar - the statusbar of the view if it has one
5 - tooltip - the tooltip control of the view
6 - pointercontrol - I think this is only used in a tree that displays list heads
Example
sendwindowmessage(getviewhwnd(treeview,2), SCI_SETSEL, 4, 8);
getviewscale
(obj view)
Description
For developer use. Returns the view scale factor.
Example
getviewscale(sv())
getviewtext
(obj/num window)
Description
For developer use. Returns the text of a window.
Example
getviewtext(sv())
highlightviewtext
(node view, num pos, num span, num mode span/lines)
Highlights text in a code edit window
Description
Highlights text in a scintilla code edit window. This is used by the flexscript syntax checker to go to highlight a syntax error in the code edit window. You can either highlight whole lines or individual characters. To highlight individual characters, specify mode as 2. For lines specify mode as 1. For lines, specify pos as the start line to highlight(the first line is line 1) and span the number of lines to highlight. For individual characters, specify pos as the start position and span as the number of characters to highlight (position 0 is the position to the left to the first character)
Example
highlightviewtext(c, 0, 5, 2)
This will highlight the first 5 characters of the scintilla text edit.
highlightviewtext(c, 1, 1, 1)
This will highlight the first line of the scintilla text edit.
This will highlight the first 5 characters of the scintilla text edit.
highlightviewtext(c, 1, 1, 1)
This will highlight the first line of the scintilla text edit.
iskeydown
([num key])
Description
For developer use. Returns 1 if the specified keyboard key is being held down. If the first parameter is not passed, then the function will return 1 if any key is being held down. Otherwise, the function returns 0.
Example
iskeydown(74)
keyboardfocus
([HWND/node focus])
Gets/Sets keyboard focus
Description
Used in GUI development. Gets/Sets the keyboard focus. If the focus parameter is left out, then this command will
return a reference to the current keyboard focus as an HWND handle.
Otherwise, it will set the focus to the keyboard focus to the passed parameter. Use windowfromnode() or getviewhwnd() to get access
to the HWND handle of a view node.
Example
keyboardfocus(windowfromnode(edit));
keyedclick
(obj object, num key[, obj view])
Description
For developer use. Executes the object's keyed click functionality (X, C, V)
Example
keyedclick(model().last, 88)
lastclickednode
()
Description
For developer use. Returns a pointer to the last clicked node.
Example
lastclickednode()
lastkey
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the keycode of a keypress in OnKeyPress event.
Example
lastkey()
lastkeydown
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the keycode of a keypress in OnKeyPress event.
Example
lastkeydown()
lastkeyup
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the keycode of a keypress in OnKeyPress event.
Example
lastkeyup()
listboxrefresh
(obj listbox)
Refreshes the contents of a listbox
Description
Refreshes the contents of a listbox.
Example
listboxrefresh(c.find("../Collision Members"))
makeactive
(obj viewwindow)
Description
For developer use. Makes the specified window active.
Example
makeactive(ownerview(c));
msg
(str caption, str text [, num buttontype])
Display a message dialog
Description
This command creates a message box with a title bar displaying the caption and the text written inside the box.
The buttons displayed on the message box are based on the value for buttontype.
If OK or Yes are pressed, msg() returns 1. If No is pressed, msg() returns 0. The value returned when Cancel is pressed depends on the buttontype.
If buttontype is 3, Cancel returns -1; otherwise it returns 0.
If buttontype is not specified, it is assumed to be 0.
Values for buttontype:
0 - OK, Cancel
1 - OK
2 - OK, Cancel
3 - Yes, No, Cancel
4 - Yes, No
Values for buttontype:
0 - OK, Cancel
1 - OK
2 - OK, Cancel
3 - Yes, No, Cancel
4 - Yes, No
Example
if (msg("Finished", "Close the database?") == 1)
dbclose();
dbclose();
nodefromwindow
(num window)
Description
For developer use. Get the node of a window handle
Example
nodefromwindow(windowfromnode(sv()))
ownerview
(obj viewobj)
Description
For developer use. Get the topmost node of a view structure.
Example
ownerview(sv())
pickcolor
()
Description
For developer use. Opens a color picker window to allow the user to pick a color. Use pickedcolorred(), pickedcolorgreen(), pickedcolorblue() commands to retrieve the rgb color component values.
Example
pickcolor();
int bluecomponent = pickedcolorblue();
The bluecomponent variable will be set to the rgb value for the blue component of the color chosen with pickcolor().
int bluecomponent = pickedcolorblue();
The bluecomponent variable will be set to the rgb value for the blue component of the color chosen with pickcolor().
pickcolornode
(obj colornode)
Description
For developer use. Open a color picker window to set the rgb color values of the color attribute node of an object.
Example
pickcolornode(color(current));
Opens a color picker window and then sets the color of the current object to the chosen color.
Opens a color picker window and then sets the color of the current object to the chosen color.
pickedcolorblue
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the blue component of a color picked with the pickcolor() command.
Example
pickcolor();
int bluecomponent = pickedcolorblue();
The bluecomponent variable will be set to the rgb value for the blue component of the color chosen with pickcolor().
int bluecomponent = pickedcolorblue();
The bluecomponent variable will be set to the rgb value for the blue component of the color chosen with pickcolor().
pickedcolorgreen
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the green component of a color picked with the pickcolor() command.
Example
pickcolor();
int greencomponent = pickedcolorgreen();
The greencomponent variable will be set to the rgb value for the green component of the color chosen with pickcolor().
int greencomponent = pickedcolorgreen();
The greencomponent variable will be set to the rgb value for the green component of the color chosen with pickcolor().
pickedcolorred
()
Description
For developer use. Returns the red component of a color picked with the pickcolor() command.
Example
pickcolor();
int redcomponent = pickedcolorred();
The redcomponent variable will be set to the rgb value for the red component of the color chosen with pickcolor().
int redcomponent = pickedcolorred();
The redcomponent variable will be set to the rgb value for the red component of the color chosen with pickcolor().
pickfile
(str extension, str extensiondescription[, str defaultreturn])
Description
For developer use. Opens a file browser for the user to choose a file. The browser will be looking for files with the specified extension. The extensiondescription is any text which describes the type of files allowed. This command will return the full path to the chosen file. Convert the return value with tostr(). See filebrowse() command.
Example
pickfile("*.xls","Excel Workbooks")
picklistapply
(obj combobox)
Description
For developer use. Applies the selected picked option from a picklist combobox. This is done when applylinks is called, or when and OK or Apply button is pressed.
Example
picklistapply(c)
redirectconsole
(num console:output/system/compiler/trace, obj view)
Redirects any prints to a given console
Description
This redirects any prints to a given console so that they will instead be printed to the view text of the specified view.
CONSOLE_OUTPUT redirects the output console, CONSOLE_SYSTEM redirects the system console, CONSOLE_COMPILER redirects the compiler console, CONSOLE_TRANCE redirects the trace console. To redirect it back to its original console, call the command again and specify NULL as the view parameter.
Example
redirectconsole(2, c);
buildnodeflexscript(getvarnode(Model.find("Processor1"), "exittrigger"));
redirectconsole(2, NULL);
This redirects the compiler console to the view c and then builds flexscript on a node in the model. Thus, any errors in building flexscript will be directed to the view c instead of to the compiler console.
buildnodeflexscript(getvarnode(Model.find("Processor1"), "exittrigger"));
redirectconsole(2, NULL);
This redirects the compiler console to the view c and then builds flexscript on a node in the model. Thus, any errors in building flexscript will be directed to the view c instead of to the compiler console.
redirectpicklists
(obj view)
Description
For developer use. Adjusts all picklists of a parameters or properties window that has been redirected.
Example
redo
(obj view)
Description
Redoes the previously undone action for the specified view. The specified view must have an undohistory attribute to record undoable actions.
Example
redo(view);
refreshview
(obj view)
Description
For developer use. Regenerate the window from it's view definition.
Example
refreshview(c)
repaintall
()
Description
For developer use. Repaint all windows.
Example
repaintall()
repaintallactive
()
Description
For developer use. Repaint all windows in the active list.
Example
repaintallactive()
repaintview
(obj view)
Description
For developer use. Repaint the window without regenerating.
Example
repaintview(c)
repositionhighlightededits
(obj view)
Description
For developer use. Repositions the edit controls for a tree view's highlighted object.
Example
scrollinfo
(obj/HWND view, num get_set {0-1}, num horz_vert_ctl {0-2}, num scrollinfo {1-4}[, num value])
Description
For developer use. Gets or sets scrollinfo for a scrollbar on a view. The value parameter is only used if get_set is 1. The position of the scrollbar (nPos) is changed with scrollinfo 4. You can also get and set the nMin, nMax, and nPage values of the scrollbar with scrollinfo 1, 2, and 3 respectively.
Example
scrollinfo(TheTable,1,1,4,scrollinfo(c,0,1,4)-amount);
select
(obj window)
Description
For developer use. Select the specified view object. Convert the return value with tonode().
Example
select(ownerview(c))
selectedobject
(obj window [, num reset])
Description
For developer use. Get the highlighted node in a view.
Example
selectedobject(ownerview(c))
selectedx
(obj window)
Description
For developer use. Get the x position of the highlighted object in a view.
Example
selectedx(ownerview(c))
selectedy
(obj window)
Description
For developer use. Get the y position of the highlighted object in a view.
Example
selectedy(ownerview(c))
selectedz
(obj window)
Description
For developer use. Get the z position of the highlighted object in a view.
Example
selectedz(ownerview(c))
sendonactivatenotify
()
Description
For developer use. Causes each palette windows' OnActivateNotify event to fire.
Example
sendonactivatenotify();
setcameradirection
(obj view, num x, num y, num z, num rx, num ry, num rz)
Sets the viewpoint direction of the 3D view
Description
Set the viewpoint direction of an orthographic or perspective view. (x,y,z) is the location of the focus point of the camera. (rx, ry, rz) is the rotation of the camera. The associated view attribute names are: viewpointx, viewpointy, viewpointradius, viewpointrx, viewpointry, viewpointrz respectively.
Example
setcameradirection(sv(), 0, 0, 0, -40, 0, 25);
setcameravolume
(obj view, num w, num h, num nearclip, num farclip, num magnification, num fov, num projtype, num firstperson)
Description
For developer use. Set the OpenGL camera volume. Sets additional view parameters not set with setcameradirection.
Example
No example.
setchecked
(obj view, num value)
Description
For developer use. Set the checked state of a button.
Example
setchecked(c,0) ;
setcursor
(num cursorid[, num forgetCount = 0])
Sets the visual look of the mouse pointer
Description
Sets the visual look of the mouse pointer. Valid ids are as follows
1: Arrow
2: IBeam
3: Wait
4: Cross
5: UpArrow
6: Size
7: Icon
8: SizeNWSE
9: SizeNESW
10: SizeWE
11: SizeNS
12: SizeAll
13: No
14: Hand
15: AppStarting
16: Help
The forgetCount defines if/when FlexSim should go back to the default cursor. If 0 (default), then FlexSim will keep that cursor until the user calls setcursor() again. If you pass a positive number then FlexSim will reset the cursor back to the default after forgetCount number of mouse move messages are received from the system, if you have not called setcursor() again in that interval.
1: Arrow
2: IBeam
3: Wait
4: Cross
5: UpArrow
6: Size
7: Icon
8: SizeNWSE
9: SizeNESW
10: SizeWE
11: SizeNS
12: SizeAll
13: No
14: Hand
15: AppStarting
16: Help
The forgetCount defines if/when FlexSim should go back to the default cursor. If 0 (default), then FlexSim will keep that cursor until the user calls setcursor() again. If you pass a positive number then FlexSim will reset the cursor back to the default after forgetCount number of mouse move messages are received from the system, if you have not called setcursor() again in that interval.
Example
setcursor(3)
setdropcoords
(obj view[, obj dropnodefrom, obj dropnodeto])
Description
For developer use. Sets the dropx() and dropy() coordinate commands for the view based on current mouse location.
You can optionally also set the dropnodefrom and dropnodeto parameters, which will define the nodes returned by dropnodefrom() and dropnodeto().
Example
setdropcoords()
setpickingdrawfocus
(obj theview, obj focus, num what[, obj secondaryfocus, num flags])
Description
For developer use. Sets the draw code following this call to be picked as the focus when clicking or dragging. Usually you would use this
to draw custom sizers and grippers on your object, and then implement an OnDrag or an OnClick event on the object that would call getpickingdrawfocus()
to figure out what part was clicked.
flags is a bitwise combination of one "DETECT_DRAG" setting, as well as optional "override" bits. The override bits aren't used to define picking focus, but will cause FlexSim to override its normal drawing of sizers and bounding boxes.
DETECT_DRAG_X, DETECT_DRAG_Y, DETECT_DRAG_Z - will only detect dragging along the given axis, relative to the object being drawn. Use this with the draginfo() command in your OnDrag event to determine where the object is being dragged.
DETECT_DRAG_XY, DETECT_DRAG_YZ, DETECT_DRAG_XZ - will only detect dragging along the given plane. Again you would use this with the draginfo() command in the OnDrag event.
OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_X, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_Y, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_Z, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_X_NEG, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_Y_NEG, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_Z_NEG, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_ALL - these flags will cause the engine to not draw the flagged sizers
OVERRIDE_DRAW_YELLOW_BOX - causes FlexSim to not draw the yellow box around the object when selected
OVERRIDE_DRAW_GREEN_BOX - causes FlexSim to not draw the green "statistics-active" box around the object
OVERRIDE_DRAW_REDBOX - causes FlexSim to not draw the red selection box around the object when selected
OVERRIDE_DRAW_HOVERBOX - causes FlexSim to not draw the yellow hover box around the object when hovering over it
OVERRIDE_DRAW_ALL - causes FlexSim to not draw any sizers or boxes around the object
OVERRIDE_SET_MOUSE_DOWN_PICK - explicitly sets the view's "mouse down" pick to the defined values. This is called outside of the drawing sequence, and updates the pick information "as-if" the mouse had been pressed on the given object.
OVERRIDE_SET_MOUSE_DOWN_PICK - explicitly sets the view's "mouse up" pick to the defined values. This is called outside of the drawing sequence, and updates the pick information "as-if" the mouse had been released on the given object.
OVERRIDE_SET_MOUSE_MOVE_PICK - explicitly sets the view's "mouse move" pick to the defined values. This is called outside of the drawing sequence, and updates the pick information "as-if" the mouse had been moved on the given object.
OVERRIDE_SET_MOUSE_HOVER_PICK - explicitly sets the view's "mouse hover" pick to the defined values. This is called outside of the drawing sequence, and updates the pick information "as-if" the mouse had been hovered over the given object.
flags is a bitwise combination of one "DETECT_DRAG" setting, as well as optional "override" bits. The override bits aren't used to define picking focus, but will cause FlexSim to override its normal drawing of sizers and bounding boxes.
DETECT_DRAG_X, DETECT_DRAG_Y, DETECT_DRAG_Z - will only detect dragging along the given axis, relative to the object being drawn. Use this with the draginfo() command in your OnDrag event to determine where the object is being dragged.
DETECT_DRAG_XY, DETECT_DRAG_YZ, DETECT_DRAG_XZ - will only detect dragging along the given plane. Again you would use this with the draginfo() command in the OnDrag event.
OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_X, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_Y, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_Z, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_X_NEG, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_Y_NEG, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_Z_NEG, OVERRIDE_DRAW_SIZER_ALL - these flags will cause the engine to not draw the flagged sizers
OVERRIDE_DRAW_YELLOW_BOX - causes FlexSim to not draw the yellow box around the object when selected
OVERRIDE_DRAW_GREEN_BOX - causes FlexSim to not draw the green "statistics-active" box around the object
OVERRIDE_DRAW_REDBOX - causes FlexSim to not draw the red selection box around the object when selected
OVERRIDE_DRAW_HOVERBOX - causes FlexSim to not draw the yellow hover box around the object when hovering over it
OVERRIDE_DRAW_ALL - causes FlexSim to not draw any sizers or boxes around the object
OVERRIDE_SET_MOUSE_DOWN_PICK - explicitly sets the view's "mouse down" pick to the defined values. This is called outside of the drawing sequence, and updates the pick information "as-if" the mouse had been pressed on the given object.
OVERRIDE_SET_MOUSE_DOWN_PICK - explicitly sets the view's "mouse up" pick to the defined values. This is called outside of the drawing sequence, and updates the pick information "as-if" the mouse had been released on the given object.
OVERRIDE_SET_MOUSE_MOVE_PICK - explicitly sets the view's "mouse move" pick to the defined values. This is called outside of the drawing sequence, and updates the pick information "as-if" the mouse had been moved on the given object.
OVERRIDE_SET_MOUSE_HOVER_PICK - explicitly sets the view's "mouse hover" pick to the defined values. This is called outside of the drawing sequence, and updates the pick information "as-if" the mouse had been hovered over the given object.
Example
setpickingdrawfocus(view, current, 20, drawsurrogate(current).first.subnodes[3], DETECT_DRAG_Y);
setselectedobject
(obj view, obj selected)
Description
For developer use. Sets the selectedobject (yellow highlighted object) of the view. Note that this is different than so(). The highlighted object is accessed by the selectedobject() command.
Example
setselectedobject(ownerview(c), model().first)
settableviewselection
(obj tableview, num startrow, num startcol, num endrow, num endcol[, num rangeselected])
Description
For developer use. Sets the blue selection range in a table view. If any of the number parameters are less than 0, it deselects everything. Use 0 to select header cells.
Example
settableviewselection(c,0,1,2,2);
setviewtext
(obj/HWND window, str text)
Description
For developer use. Set the text of a gui edit field.
Example
setviewtext(c,"hello")
shiftpressed
()
Description
For developer use. Test if SHIFT key is pressed.
Example
shiftpressed()
showcompilerconsole
()
Description
For developer use. Show the compiler console.
Example
showcompilerconsole()
showhelp
(str topicname)
Description
For developer use. Opens a help topic specified by the topic name.
Example
showhelp("getting_started");
showhtmlhelp
(str topic)
Description
For developer use. Open FlexSim's User Manual with the given topic to open.
Example
showhtmlhelp("Welcome_to_Flexsim.html")
standardpreopen
(obj object[, int nobuild])
Description
For developer use. Queries if there are any open windows that are the same as the current window being opened. If so, then the current window is closed.
Example
standardpreopen(c)
sv
()
Gets a reference to the last view desginated as sv()
Description
This command returns a reference to the last view window that was designated the selected view. To designate a view window, right-click on the window, not on any objects drawn in that window, and select "Set as (sv)". Any open view window (e.g. Ortho or VR) can be designated the selected view.
Example
flypath(sv(),1);
This begins flypath number 1 in the view that is currently designated the selected view.
This begins flypath number 1 in the view that is currently designated the selected view.
systemwindow
(num windowtype)
Description
For developer use. Get HWND handle to a system window: 1-Output 2-System 3-Compiler 4-Trace 5-Commands 6-Attributes 7-Completions 8-app 9-appsb 10-Output Edit 11-Compiler Edit 12-Trace Edit 13-System Edit
Example
systemwindow(1)
tabcontrolrefresh
(obj tabcontrolnode)
Description
For developer use. Refreshes a tab control.
Example
tabcontrolrefresh(c.find("@/tabcontrol"));
templatetocode
(obj code, obj edit)
Description
For developer use. Apply template code to c++. This is used in a picklist's template code drop-down to apply edited template code back to the C++/Flexscript code that created it.
Example
templatetocode(so(),sv())
undo
(obj view)
Description
Undoes the previously recorded action for the specified view. The specified view must have an undohistory attribute to record undoable actions.
Example
undo(view);
updateundorecord
(obj view, num uniqueid[, num updatetype, num p1, num p2])
Description
Updates an undo record for the specified view.
The following undo record types should be updated:
UNDO_MOVE_SIZE_ROTATE
UNDO_MOVE_SIZE_ROTATE_GROUP
UNDO_SELECTION_CHANGE
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
The following undo record types should be updated:
UNDO_MOVE_SIZE_ROTATE
UNDO_MOVE_SIZE_ROTATE_GROUP
UNDO_SELECTION_CHANGE
See Miscellaneous Concepts > Advanced Undo for more information.
Example
updateundorecord(view, getundorecordid(record));
viewdist
(obj view, obj object)
Gets the distance from the focus point of view to object
Description
Returns the distance from the focus point of the view to object.
Example
if(viewdist(view, current) > 100) ;
This command queries whether the distance between the point that the view is looking at and the location of the current object is greater than 100.
This command queries whether the distance between the point that the view is looking at and the location of the current object is greater than 100.
webcommand
(str name[, p1, p2, p3, ...])
Used to manipulate FlexSim's HTML engine/widgets
Description
A command used for manipulating FlexSim's HTML engine, html widgets, etc.
Example
string innerhtml = webcommand("getelementinnerhtml", view, "title");
windowflash
(HWND window, num count, num timeout)
Description
For developer use. Causes the specified window to flash. Count is the number of times to flash the window. Timeout controls the time between flashes. If timeout is 0, the default cursor blink rate is used.
Example
windowflash(windowfromnode(ownerview(c)),2,125);
windowfromnode
(obj viewnode)
Description
For developer use. Get the window handle (HWND) of a view node.
Example
windowfromnode(c)
windowgray
(HWND window, num graystate)
Description
For developer use. Enables or disables the window based on the graystate parameter (1 or 0).
Example
graywindow(windowfromnode(c),1);
windowmove
(HWND window, num x, num y, num sx, num sy[, num refresh])
Description
For developer use. Move a window to the specified x,y pixel location and give it the sx,sy size in pixels. If refresh is 1, then the window will repaint itself.
Example
windowmove(windowfromnode(c),10,10,200,200,1)
windowshow
(HWND/node thewindow , num show)
Description
For developer use. Show or hide a window. If the second parameter is 1, then the window will be shown. Otherwise the window will be hidden.
Example
windowshow(windowfromnode(c))
windowstyle
(HWND/obj window [, num style, num useexstyle])
Gets the windowstyle of window
Description
Used in GUI development. Dynamically gets/sets the window style of the given window.
If style is 0, this will simply return the current style of the window. Otherwise, it will set it.
If useexstyle is 1, it will apply/get the extended style of the window. Refer to Windows SDK documentation for more information on
window styles.
Example
As an example, this command is used in the perspective view's "Full Screen" context menu option to change
the style of the perspective window so that it no longer has a title bar when it is in full screen mode.