Tutorial Exercise 5.1
Analysis of Headway in Freight Rail Operations Using RailWorks
Objective
To analyze the headways that naturally arise from predefined schedules and train behaviors on a single-track railway line using FlexSim RailWorks. This study aims to identify patterns, potential bottlenecks, and efficiency metrics from the simulated operations of freight trains, especially those transporting ore.
Simulation Setup
Step 1 Track Layout
- Length: 200 Km of single-track railway suited for bidirectional travel.
- Stations: Four stations (Station A, B, C, and D), spaced unevenly along the route.
Step 2 Train Specifications
- Train Type: Freight trains designed for carrying ore.
- Maximum Speed: 22 m/s, a common speed for freight trains under loaded conditions.
- Acceleration: 1.2 m/s², facilitating efficient load movement.
- Deceleration: 1.5 m/s², ensuring safe and timely stops, crucial for heavy loads.
- Dwell Time at Stations: 30 minutes, optimized for loading and unloading ore without causing delays.
- Departure Frequency: Fixed departures from terminals (Stations A and D) every 120 minutes during operational hours.
Step 3 Control Systems
- Scheduling: Trains adhere to a strict timetable, with departures every two hours from their respective starting points.
Step 4 Building model
The model below is an example of how it can be built. It is a simplified version. Feel free to build the model as you wish respecting the specifications from steps 1-3.
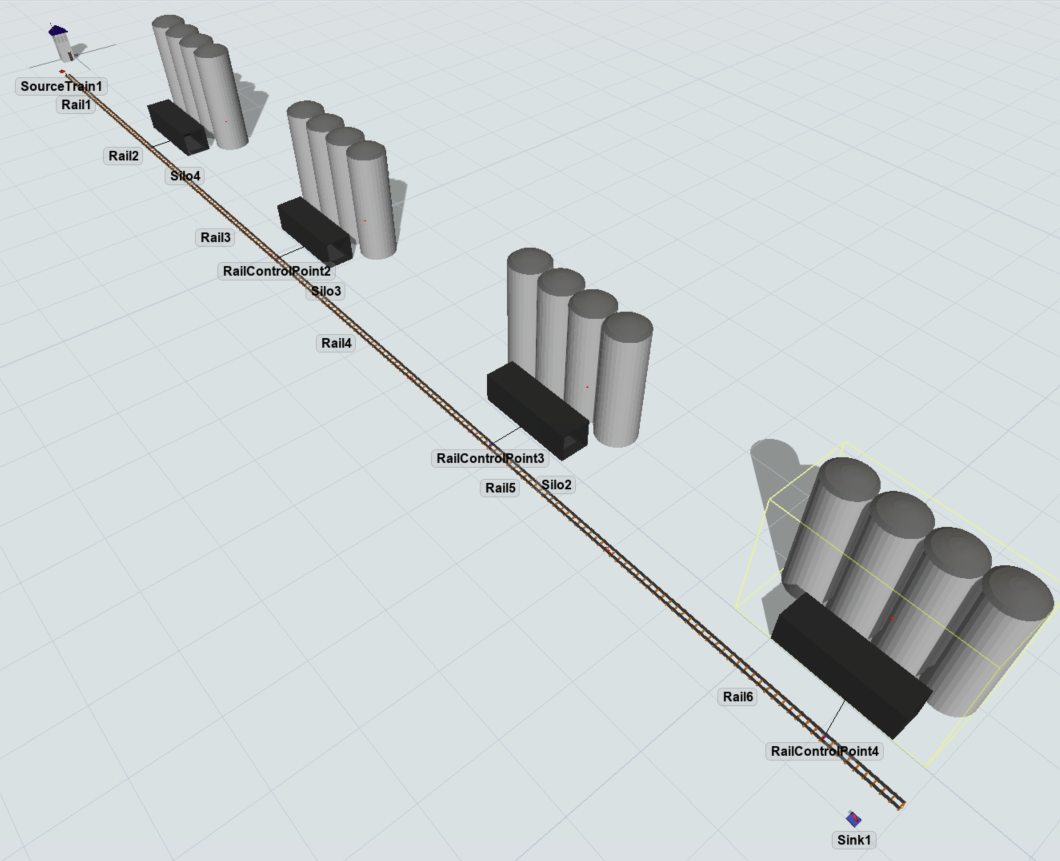
For this example, we will first create the single track. Considering its length, we will use the option "Virtual Distance" on the rails, removing the need to create too many objects. Therefore, create at least 6 rails. One rail to connect to the SourceTrain with size x as 10. For the rest, set the "Virtual Distance" as 40 Km (or 40000 m).
Now, we will distribute 4 RailControlPoints on the track. It can be done by creating the RailControlPoint in an empty space and then dragging on the rail in the desired position. For a better control on the distance the object will be on the rail, set the "Control Point Position" on the RailControlPoint after dragging it.
The last step is to create 4 Stations and connect them to each RailControlPoints using the S key. Considering the focus of this tutorial, it is not necessary to setup the Stations for any load or unload activities. Create a sink at the end of the track.
For the Processflow setup, the most basic flow of activities for this tutorial would be as below:
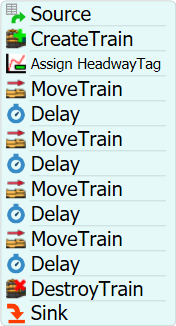
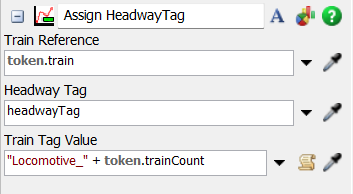
For this logic, it is important to setup the Assign HeadwayTag. First, in the Source activity, add a label naming it "trainCount" and for the value choose the "Arrival Row Number". In Assign HeadwayTag, add on the "Train Tag Value" the value ""Locomotive_" + token.trainCount". For each MoveTrain and Delay pair, set the destiny to the RailControlPoints and the time specified for load and unload process respectively.
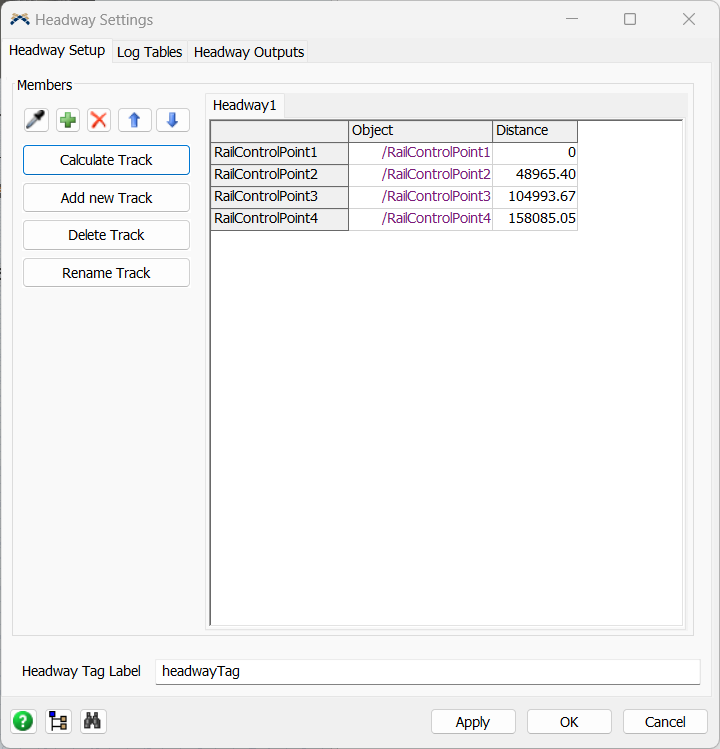
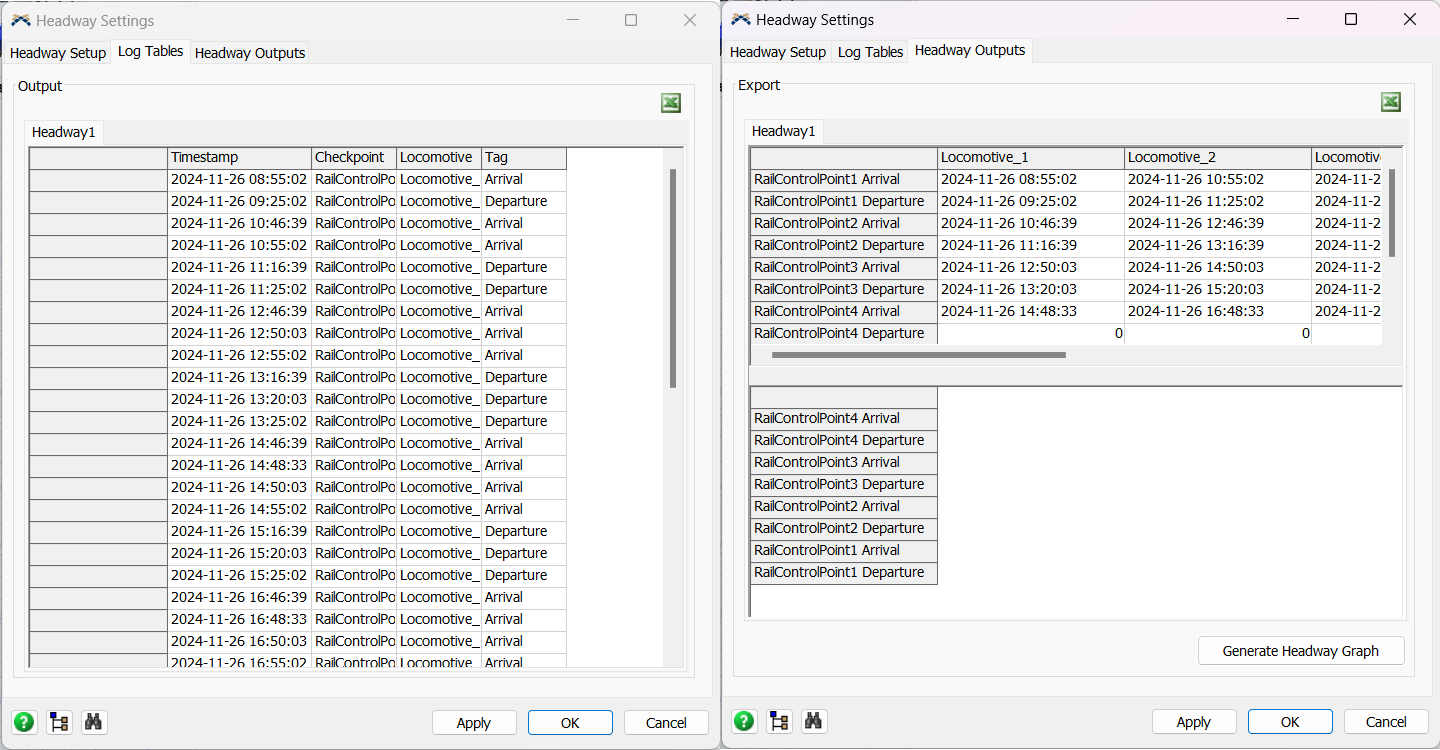
Lastly, it is necessary to configure the Headway. For this, click on the Headway Settings in the RailSystem. On the first
tab, add the RailControlPoints by clicking on the sample or + button and click on the Calculate Track. Make sure to reset the
model before calculating the distance. The other 2 tabs will contain the Headway data collected during the simulation.
See more about the
Headway feature.
After the simulation is done, the other two tabs on the Headway Settings should be similar to the image below:
Methodology for Simulation
- Fixed Headway Evaluation: Evaluate the natural headways resulting from set departure frequencies and train specifications.
- Data Collection: Record the arrival times of each train at each station to calculate the actual headways achieved throughout the day.
-
Critical Analysis Points:
- Train Interactions at Loops: Pay special attention to interactions at passing loops to identify any potential inefficiencies or unnecessary waiting.
- Station Efficiency: Assess the effectiveness of scheduled dwell times and their impact on overall headway.
Expected Analysis
- Headway Consistency: Measure the consistency of headways at different points along the track and during different times of the day.
- Operational Efficiency: Evaluate how effectively the railway operates under the constraints of fixed headways, including throughput and potential delays.
- Bottleneck Identification: Identify any route segments where delays are frequent, suggesting possible modifications or upgrades.
Projected Outcomes
- Headway Insights: Gain detailed understanding of how fixed headways affect freight rail operations, particularly in identifying optimal and problematic aspects.
- Operational Recommendations: Provide actionable recommendations to improve station management and potentially adjust train frequencies to better suit actual conditions.
-
Infrastructure Suggestions: Recommend improvements at critical points
like stations and loops to enhance overall service efficiency.
- Signaling: develop a signaling system to ensure safe train
movements, especially critical in single-track sections with freight traffic. See more about how to
build a Signaling System.
- Signaling: develop a signaling system to ensure safe train
movements, especially critical in single-track sections with freight traffic. See more about how to
build a Signaling System.
This setup leverages FlexSim RailWorks to provide a comprehensive analysis of the operational dynamics under natural headway conditions, aiming to enhance both the reliability and efficiency of freight rail services transporting ore.
Additional Benefits of Analyzing Headway with FlexSim RailWorks
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Understanding headway patterns helps managers make informed decisions regarding train schedules, fleet management, and capacity planning.
- Risk Reduction: Identifying and addressing bottlenecks reduces operational risks and enhances safety.
- Cost Efficiency: Optimizing train schedules and headways can lead to significant cost savings by minimizing delays and improving fuel efficiency.
Follow up questions:
- How can consistent headway measurements enhance operational efficiency and what might be the consequences of ignoring headway variability in freight rail systems?
- What strategies could be implemented to adjust train frequencies based on observed headway patterns, and what operational changes might be necessary if analysis reveals frequent delays?
- How could infrastructure improvements at stations and loops enhance service efficiency and which upgrades would you prioritize based on headway analysis?
- How can optimizing headways lead to cost savings and what risk management benefits can be derived from a detailed headway analysis?
- How can headway analysis information aid in planning for increased traffic or route expansions, and what challenges might arise from scaling operations based on this analysis?
Understanding Headway Insights:
Consistent headway measurements enhance operational efficiency by ensuring trains are spaced optimally, reducing delays and improving timetable adherence. Ignoring headway variability can lead to bottlenecks and increased waiting times, which disrupt service and reduce the overall efficiency of the rail network.
Operational Recommendations:
Strategies to adjust train frequencies based on observed headway patterns could include altering departure times, adjusting the number of trains on certain routes during peak and off-peak hours, and improving coordination at stations and junctions. If the analysis reveals frequent delays, operational changes might involve increasing passing loops, enhancing signaling systems, or even adjusting train speeds or the loading process at stations.
Infrastructure Suggestions:
Infrastructure improvements at stations could include expanding track capacities, enhancing signaling and communication systems, and improving station facilities to speed up loading and unloading processes. Priority upgrades might focus on the most congested areas where delays are frequent, such as installing additional tracks at stations or expanding the size and number of passing loops.
Cost and Risk Management:
Optimizing headways can lead to significant cost savings by improving fuel efficiency, reducing the need for additional rolling stock, and minimizing the operational costs associated with delays and disruptions. Risk management benefits include increased safety due to better-spaced trains and reduced likelihood of accidents, as well as improved service reliability that can enhance customer satisfaction and trust in the rail service.
Future Planning and Scalability:
Headway analysis provides critical data that aids in planning for increased traffic or route expansions by highlighting current capacity limits and operational inefficiencies. Challenges that might arise from scaling operations based on this analysis include the need for significant capital investment in infrastructure and the potential disruption during construction phases. However, these challenges can be addressed by phased implementation and careful planning to minimize impact on current operations.