The Route Panel
The Route panel has options for controlling the Route's properties.
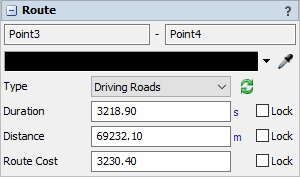
The following properties are on the Route panel:
Point Names
The names of the start point and end point of the route are shown at the top.
Color
The route lines will be drawn this color.
Type
The type affects how the route is drawn and how its duration, distance, and cost are calculated.
- Straight Rhumb Line The route is a straight line on a Mercator projection, crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle with a constant bearing.
- Flight Path - The route is a curved line which is the shortest distance between the two points on the surface of the globe.
- Driving Roads - The route is a series of lines following driving roads between the two points.
- Custom Types (Freight Railways, etc.) - Additional custom route types using other routing servers as configured in the GIS Navigator Properties.
 Update
Update
When the Update button is pressed, the route's path lines, duration, distance, and cost will be recalculated based on the route's type.
For driving roads, these values will be queried from a routing server using the URL specified on the GIS Navigator. For rhumb lines and flight paths, these values will be calculated mathematically based on the average air speed and cost settings on the GIS Navigator.
For rhumb lines and flight paths, their values will also be automatically recalculated when moving the start or end point of the route. To update driving roads, press the Update button after moving the start or end point.
Lock
Check a Lock box to prevent a value from being changed when the route is updated. You can use these checkboxes to specify particular values for your routes without concern that they will be overwritten when the route is updated.
Duration
This number defines the duration that will be used when traveling this route.
Distance
This number defines the distance that will be tracked when traveling this route.
Cost
This number defines the weighted cost of using this route when calculating a trip.
For example:
- To find the shortest trip, use distances for route cost.
- To find the fastest trip, use durations for route cost.